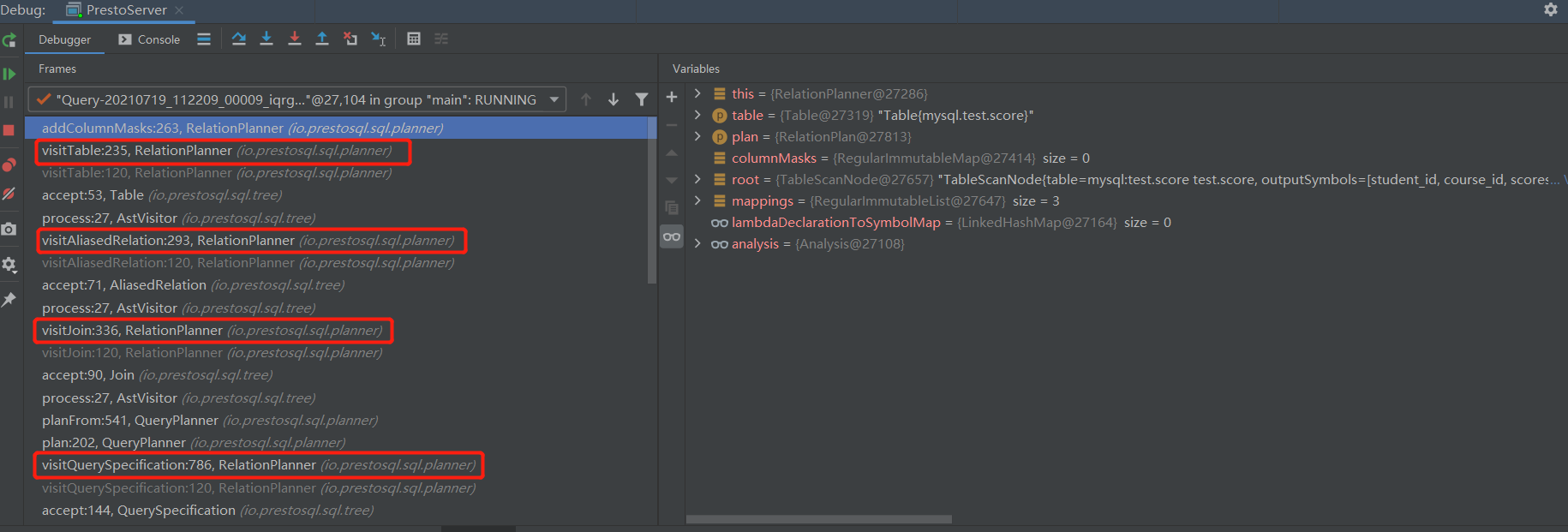
planFrom
private PlanBuilder planFrom(QuerySpecification node){RelationPlan relationPlan;// 如果From语句存在if (node.getFrom().isPresent()) {relationPlan = new RelationPlanner(analysis, planSymbolAllocator, idAllocator, lambdaDeclarationToSymbolMap, metadata, session, namedSubPlan, uniqueIdAllocator).process(node.getFrom().get(), null); // 继续获取From子句进行}else {relationPlan = planImplicitTable();}return planBuilderFor(relationPlan);}
process继续处理到Join类
from 子句为Join类型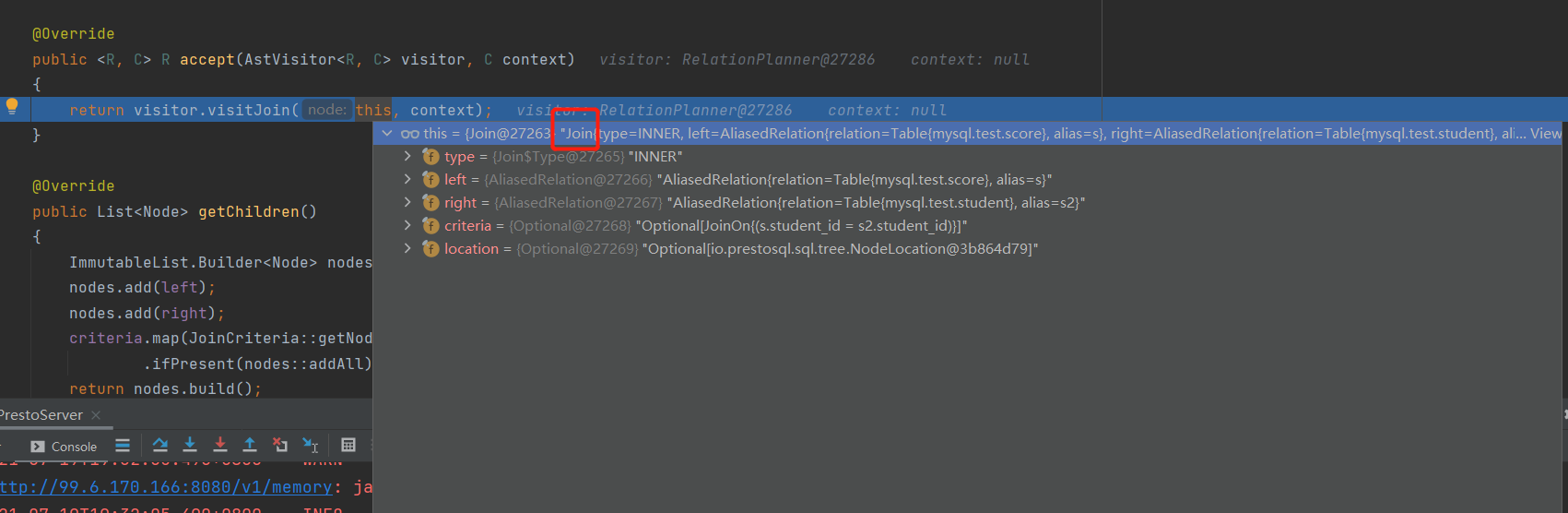
visitJoin 子句先对join左边子句进行处理,然后对右边子句进行处理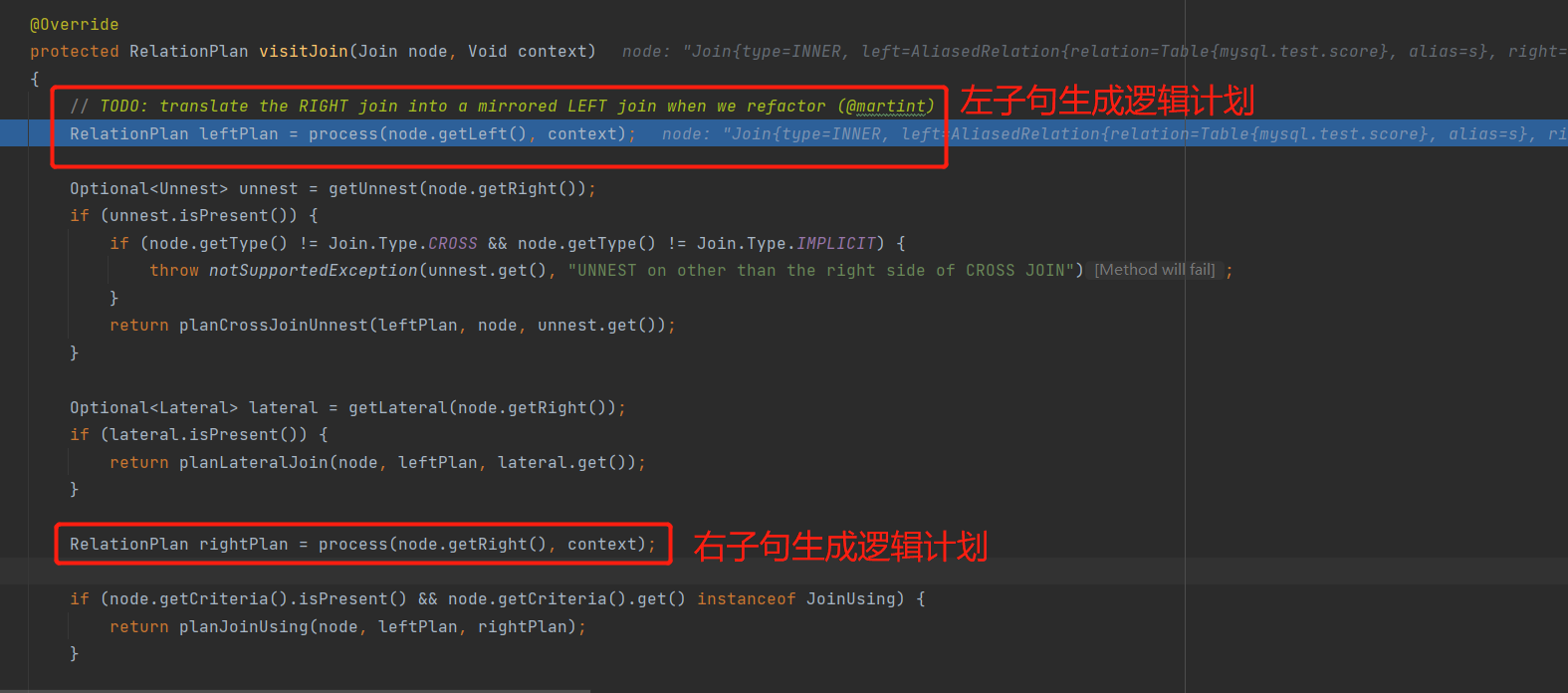
左边子句处理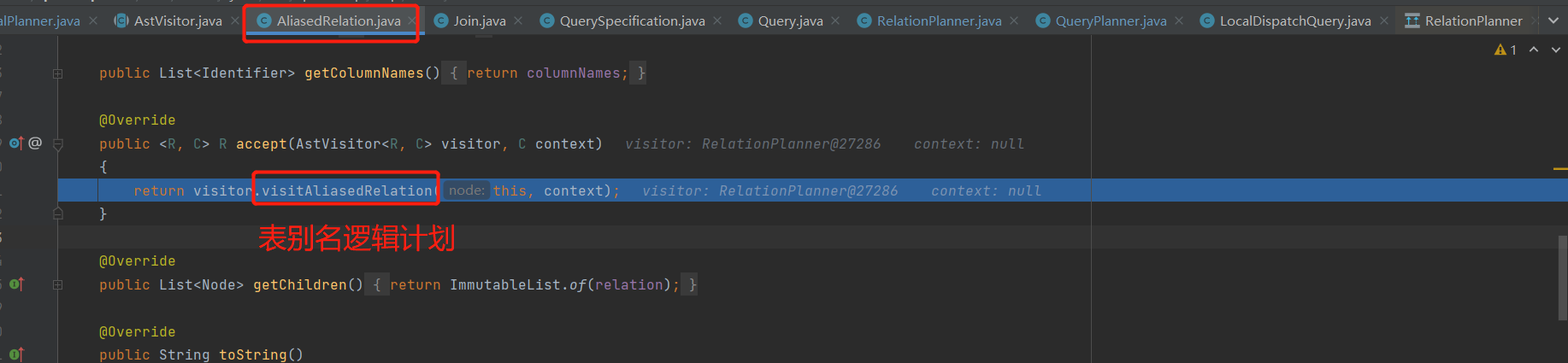
visitAliasedRelation子句对表继续处理
RelationPlanner::visitTable
@Overrideprotected RelationPlan visitTable(Table node, Void context){// 获取表// 根据节点Table获取对应的字段信息Scope scope = analysis.getScope(node);// 查询from子句是否是with子句Query namedQuery = analysis.getNamedQuery(node);// 如果包含with子句需要进一步处理if (namedQuery != null) {RelationPlan subPlan = process(namedQuery, null);// Add implicit coercions if view query produces types that don't match the declared output types// of the view (e.g., if the underlying tables referenced by the view changed)// 如果视图查询生成的类型与视图的声明输出类型不匹配(例如,如果视图引用的基础表发生了变化),则添加隐式强制转换Type[] types = scope.getRelationType().getAllFields().stream().map(Field::getType).toArray(Type[]::new);RelationPlan withCoercions = addCoercions(subPlan, types);if ((!isCTEReuseEnabled(session) || getExecutionPolicy(session).equals("phased"))|| (getCteMaxQueueSize(session) < getTaskConcurrency(session) * 2) || !(analysis.getStatement() instanceof Query) || !((Query) analysis.getStatement()).getWith().isPresent()) {if (getCteMaxQueueSize(session) < getTaskConcurrency(session) * 2) {LOG.info("Main queue size " + getCteMaxQueueSize(session) + "should be more than 2 times of concurrent task " + getTaskConcurrency(session));}return new RelationPlan(withCoercions.getRoot(), scope, withCoercions.getFieldMappings());}Integer commonCTERefNum;if (namedSubPlan.containsKey(node.getName())) {commonCTERefNum = namedSubPlan.get(node.getName());}else {commonCTERefNum = uniqueIdAllocator.getNextId();namedSubPlan.put(node.getName(), commonCTERefNum);}PlanNode cteNode = new CTEScanNode(idAllocator.getNextId(),withCoercions.getRoot(),withCoercions.getFieldMappings(),Optional.empty(),node.getName().toString(),new HashSet<>(),commonCTERefNum);subPlan = new RelationPlan(cteNode, scope, withCoercions.getFieldMappings());return subPlan;}// 获取表句柄TableHandle handle = analysis.getTableHandle(node);ImmutableList.Builder<Symbol> outputSymbolsBuilder = ImmutableList.builder();ImmutableMap.Builder<Symbol, ColumnHandle> columns = ImmutableMap.builder();// 遍历字段类型for (Field field : scope.getRelationType().getAllFields()) {// 字段的名称 字段的类型Symbol symbol = planSymbolAllocator.newSymbol(field.getName().get(), field.getType());// 缓存到输出列中outputSymbolsBuilder.add(symbol);columns.put(symbol, analysis.getColumn(field));}// 输出字段信息List<Symbol> outputSymbols = outputSymbolsBuilder.build();/// 判断是否是删除语句(DELETE)boolean isDeleteTarget = analysis.isDeleteTarget(createQualifiedObjectName(session, node, node.getName()));// 创建TableScanNodePlanNode root = TableScanNode.newInstance(idAllocator.getNextId(), handle, outputSymbols, columns.build(), ReuseExchangeOperator.STRATEGY.REUSE_STRATEGY_DEFAULT, new UUID(0, 0), 0, isDeleteTarget);// 从from递归到表名后,生成对应的RelationPlan tableScan = new RelationPlan(root, scope, outputSymbols);tableScan = addRowFilters(node, tableScan);tableScan = addColumnMasks(node, tableScan);return tableScan;}
addRowFilters的方法
private RelationPlan addRowFilters(Table node, RelationPlan plan){// 添加行过滤器 初始化计划构造器PlanBuilder planBuilder = initializePlanBuilder(plan);for (Expression filter : analysis.getRowFilters(node)) {planBuilder = subqueryPlanner.handleSubqueries(planBuilder, filter, filter);planBuilder = planBuilder.withNewRoot(new FilterNode(idAllocator.getNextId(),planBuilder.getRoot(),castToRowExpression(planBuilder.rewrite(filter))));}// 跟节点 表与根节点return new RelationPlan(planBuilder.getRoot(), plan.getScope(), plan.getFieldMappings());}
addColumnMasks
// 添加字段掩码private RelationPlan addColumnMasks(Table table, RelationPlan plan){Map<String, List<Expression>> columnMasks = analysis.getColumnMasks(table);PlanNode root = plan.getRoot();List<Symbol> mappings = plan.getFieldMappings();// 保存字段映射关系TranslationMap translations = new TranslationMap(plan, analysis, lambdaDeclarationToSymbolMap);translations.setFieldMappings(mappings);PlanBuilder planBuilder = new PlanBuilder(translations, root, analysis.getParameters());for (int i = 0; i < plan.getDescriptor().getAllFieldCount(); i++) {Field field = plan.getDescriptor().getFieldByIndex(i);for (Expression mask : columnMasks.getOrDefault(field.getName().get(), ImmutableList.of())) {planBuilder = subqueryPlanner.handleSubqueries(planBuilder, mask, mask);Map<Symbol, RowExpression> assignments = new LinkedHashMap<>();for (Symbol symbol : root.getOutputSymbols()) {assignments.put(symbol, castToRowExpression(toSymbolReference(symbol)));}assignments.put(mappings.get(i), castToRowExpression(translations.rewrite(mask)));planBuilder = planBuilder.withNewRoot(new ProjectNode(idAllocator.getNextId(),planBuilder.getRoot(),Assignments.copyOf(assignments)));}}return new RelationPlan(planBuilder.getRoot(), plan.getScope(), mappings);}
Group分组语句
1.预处理所有标量输入
1).过滤器表达式需要先投影 (group by
- 分组
- 重写聚合参数
- 重写分组列
- 这会在考虑复杂表达式之前跟踪分组集(请参阅下面的评论)
- 它还用于计算实现 grouping() 所需的描述符
- 为了“distinct”的目的,我们需要规范化可能具有不同的列引用,句法形式(例如,“t.a”与“a”)。因此我们需要枚举基于底层的分组集,fieldId 与每个列引用表达式相关联。
- 问题在于简单的 group-by 表达式可以是任意表达式(这与 SQL 规范背道而驰)。但是,它们不会影响分组集的数量或“distinct”的行为。我们可以根据 fieldId 计算所有候选分组集,适当地进行重复数据删除,然后将它们与复杂的表达式交叉连接。
- 添加复杂的表达式,然后根据计划列具体化分组集
- 生成 GroupIdNode(多个分组集)或 ProjectNode(单个分组集)
- 重写聚合
- 处理之后
- 重新添加我们在 2.a 中删除的隐式转换
- 处理并重写所有分组函数

