特殊的概率分布,固定的模式,方便计算概率,期望,方差
几何分布
#card=math&code=P%28X%3Dx%29&height=20&width=72)表示x能取概率分布的任何值
#card=math&code=P%28X%3Dr%29&height=20&width=70)表示x等于特定值r
- 即x可以取任何值,包括固定值r
公式
%3Dq%5E%7Br-1%7Dp#card=math&code=P%28X%3Dr%29%3Dq%5E%7Br-1%7Dp&height=23&width=131)
- p代表成功的概率
- q代表失败的概率,q=1-p
表示取得第r次首次成功所需要进行的试验次数的概率
条件
- 一系列相互独立试验
- 均有成功,失败的可能,且单次概率相同
- 求得为取得第一次成功所需要进行多少次试验(用变量X表示)
图像特点
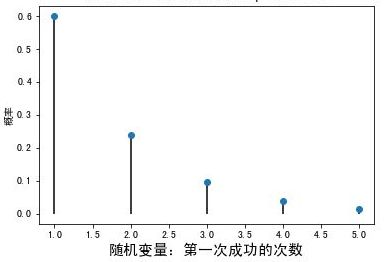
- 当r=1时,P(X=r)达到最大值,随着r的增加,P(X=r)逐渐减少
- 任何几何分布的众数都是1,因为1时,具有的概率最大
- 第一次尝试,可能性最大
不等式几何分布
%3Dq%5Er%0A#card=math&code=P%28X%3Er%29%3Dq%5Er%0A&height=20&width=107)
- X表示为取得第一次成功所需要进行多少次试验
- r表示试验进行的次数
%3D1-q%5Er%0A#card=math&code=P%28X%E2%89%A4r%29%3D1-q%5Er%0A&height=20&width=136)
- 表示为了取得一次成功需要尝试r次或r次的以下概率
%2BP(X%3Er)%3D1#card=math&code=P%28X%E2%89%A4r%29%2BP%28X%3Er%29%3D1&height=20&width=191)
如果一个变量X的概率符合几何分布,单次成功的概率为p,写作
~
#card=math&code=Geo%28p%29&height=20&width=50)
期望
X~#card=math&code=Geo%280.2%29&height=20&width=63)时,E(X)可以通过
#card=math&code=%5Csum%20xP%28X%3Dx%29&height=28&width=108)进行计算:

#card=math&code=%5Csum%20xP%28X%3Dx%29&height=28&width=108)图
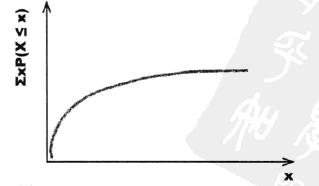
%3D%5Cfrac%7B1%7D%7Bp%7D#card=math&code=E%28X%29%3D%5Cfrac%7B1%7D%7Bp%7D&height=41&width=77)
期望等于1除以成功概率
方差
X~#card=math&code=Geo%280.2%29&height=20&width=63)时,E(X)可以通过
#card=math&code=x%5E2%20P%28X%3Dx%29&height=23&width=89)进行计算:
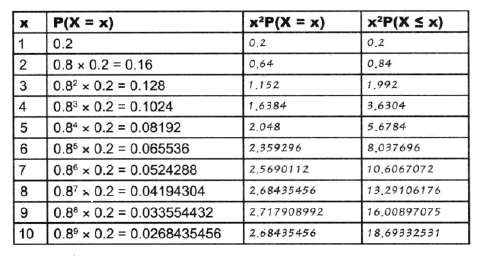
#card=math&code=x%5E2%20P%28X%3Dx%29&height=23&width=89)图
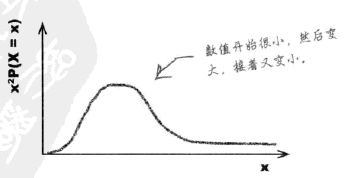
%3DE(X%5E2)-E%5E2(X)%3Dx%5E2%20P(X%3Dx)-E%5E2(X)#card=math&code=Var%28X%29%3DE%28X%5E2%29-E%5E2%28X%29%3Dx%5E2%20P%28X%3Dx%29-E%5E2%28X%29&height=23&width=376),得到方差分布图

如果X~#card=math&code=Gep%28p%29&height=20&width=51),则
%3D%5Cfrac%7Bq%7D%7Bp%5E2%7D#card=math&code=Var%28X%29%3D%5Cfrac%7Bq%7D%7Bp%5E2%7D&height=40&width=101)
二项式分布
公式
%3D%5EnC_rp%5Erq%5E%7Bn-r%7D#card=math&code=P%28X%3Dr%29%3D%5EnC_r%2Ap%5Er%2Aq%5E%7Bn-r%7D&height=21&width=198)
其中!%7D#card=math&code=%5EnC_r%3D%5Cfrac%7Bn%21%7D%7Br%21%28n-r%29%21%7D&height=45&width=124)
每道题答对的概率是p 答错的概率是q=1-p
条件
- 独立试验
- 均有成功,失败的可能,且单次概率相同
- 试验次数有限
p是没一次试验的成功概率,n是试验次数。写作:X~#card=math&code=B%28n%2Cp%29&height=20&width=52)
图像

期望
%3Dnp#card=math&code=E%28X%29%3Dnp&height=20&width=81)
方差
%3Dnpq#card=math&code=Var%28X%29%3Dnpq&height=20&width=105)
泊松分布
条件
- 单独时间在给定区间(时间或者空间)内随机、独立地发生
- 已知改区间的时间平均发生次数(发生率)通常用
(lambda)表示
每个区间内平均发生次,或者说发生率为
,写作X~
#card=math&code=Po%28%5Clambda%29&height=20&width=43)
公式
%3D%5Cfrac%7Be%5E%7B-%5Clambda%7D%5Clambda%20%5Er%7D%7Br!%7D#card=math&code=P%28X%3Dr%29%3D%5Cfrac%7Be%5E%7B-%5Clambda%7D%5Clambda%20%5Er%7D%7Br%21%7D&height=42&width=140)
是数学的常数,一般为2.718
期望
%3D%5Clambda#card=math&code=E%28X%29%3D%5Clambda&height=20&width=72)
方差
%3D%5Clambda#card=math&code=Var%28X%29%3D%5Clambda&height=20&width=89)
图形
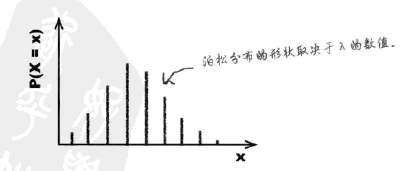
- $\lambda $值小,分布向右
- $\lambda $值大,分布逐渐变得对称
- $\lambda
\lambda
\lambda -1$
x+y泊松分布
如果X和Y是独立随机变量,则:
%3DP(X)%2BP(Y)#card=math&code=P%28X%2BY%29%3DP%28X%29%2BP%28Y%29&height=20&width=195)
%3DE(X)%2BE(Y)#card=math&code=E%28X%2BY%29%3DE%28X%29%2BE%28Y%29&height=20&width=195)
即如果X~ #card=math&code=Po%28%5Clambda_x%29&height=20&width=52)且Y~
#card=math&code=Po%28%5Clambda_y%29&height=21&width=51),则:
X+Y~ #card=math&code=Po%28%5Clambda_x%2B%5Clambda_y%29&height=21&width=90)
如果X和Y都复合泊松分布,则X+Y也符合泊松分布
使用二项式分布替代
当n很大且p很小时,可以用X~
#card=math&code=Po%28np%29&height=20&width=52) 近似代替X~
#card=math&code=B%28n%2Cp%29&height=20&width=52).


