JDK1.7
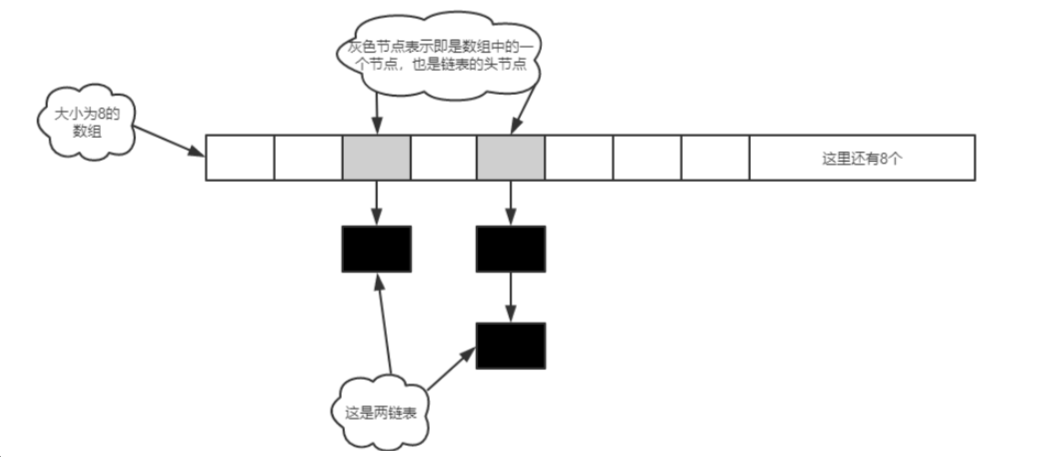
HashMap的实现 数组+ 链表
图示:
用法:
Map<String, String> hashMap = new HashMap<>();hashMap.put("key ","value");
构造过程:
- 初始化一个数组 大小为0;
- put 时会初始化,默认大小为16
可以指定数组的长度
Map<String, String> hashMap = new HashMap<>(7);可以指定大小,但实际的大小是2的次幂
put的过程 采用头插法
- 先根据key 的 hashCode 确定数组的下标
- 替换原来的链表的头节点
- 把新的头的节点的引用指向数组
如果key = null ,会放在第一个节点位置
获取下标的方法
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {// assert Integer.bitCount(length) == 1 : "length must be a non-zero power of 2";return h & (length-1);}
获取一个数的最近的一个2次幂的值的算法
/*** Returns a power of two size for the given target capacity.*/static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) {int n = cap - 1;n |= n >>> 1;n |= n >>> 2;n |= n >>> 4;n |= n >>> 8;n |= n >>> 16;return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;}
思路:
想把 0001 ** 后面变成1
再把 1右 移一位
在减去 后面的1 就全减为0 了
结果就是事 0001 0000了
put 的主要逻辑
- put(key ,value)
- int hashCode = key.hashCode();
- int index = hashCode & (数组长度-1)
- 遍历index位置的链表,如果存在相同就进行value的覆盖 ,并发挥旧的value
- 讲key value 封装成Entry
- 将节点插在index位置上的链表头部
- 把链表头节点移动到数组上
可能会带来 循环链表的问题
在扩容时,多个线程操作链表
就造成数据不一样,从而有可能会形成循环列表
扩容过程
1:声明一个新的大小的数据
2:遍历旧数组,就链表
3:根据新数据的大小,扩展因子重新hash值
4:将就元素引用指向新的数组
initHashSeedAsNeeded 初始一个hash种子,
为了让元素更加的分散
并发修改异常
modCount++
在put,remove 时会修改这个modCount
判断是否有过修改,实现快速失败
HashTable:
put 的时候加锁
对这个table加锁
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {// Make sure the value is not nullif (value == null) {throw new NullPointerException();}// Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;int hash = key.hashCode();int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")Entry<K,V> entry = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];for(; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) {if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) {V old = entry.value;entry.value = value;return old;}}addEntry(hash, key, value, index);return null;}
ConcurrentHashMap
结构:
Segment [] table;
Entry [] tab;
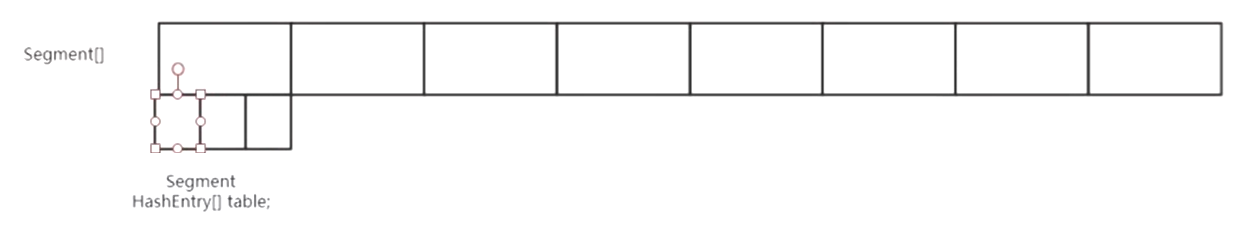
ssize : segment数组的带下,与并发级别有关
最小是2
先扩容 HashEntry [] 的这个数组