SynchronousQueue
没有数据缓冲的BlockingQueue
生产者线程对其的插入操作put必须等待消费者的移除操作take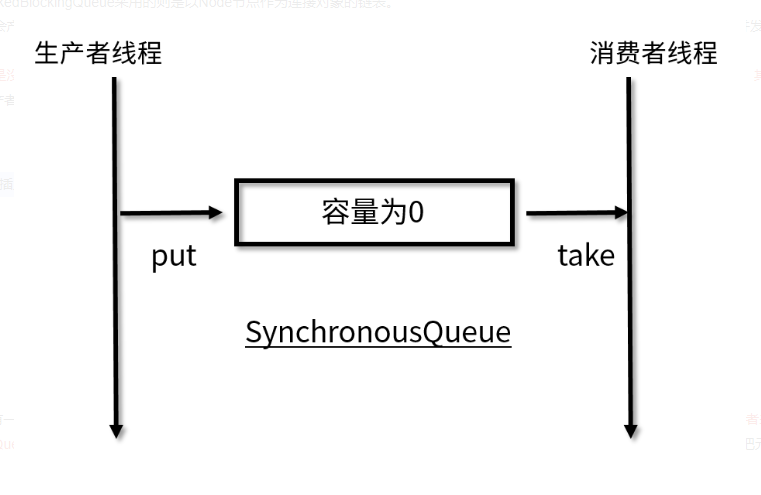
容量为0
每次取数据都会先阻塞,直到数据被放入,同理:每次放输入也会等消费者来取
所做的就是直接传递(direct handoff)
不需要存储,
应用场景
适合传递性场景做交换工作,生产者的线程和消费者的线程同步传递某些信息、事件或者任务。
Executors.newCachedThreadPool()就使用了SynchronousQueue,有根据需求创建新的线程,如果有空闲就会重复使用
线程空闲60秒,会被回收
不确定来自生产者请求数量,但这些请求需要很快处理掉,适合为每一个生产者请求分配一个消费线程的处理高效的方法
SynchronousQueue使用
BlockingQueue<Integer> synchronousQueue = new SynchronousQueue<>();
公平非公平,一个是队列结构,一个是栈结构
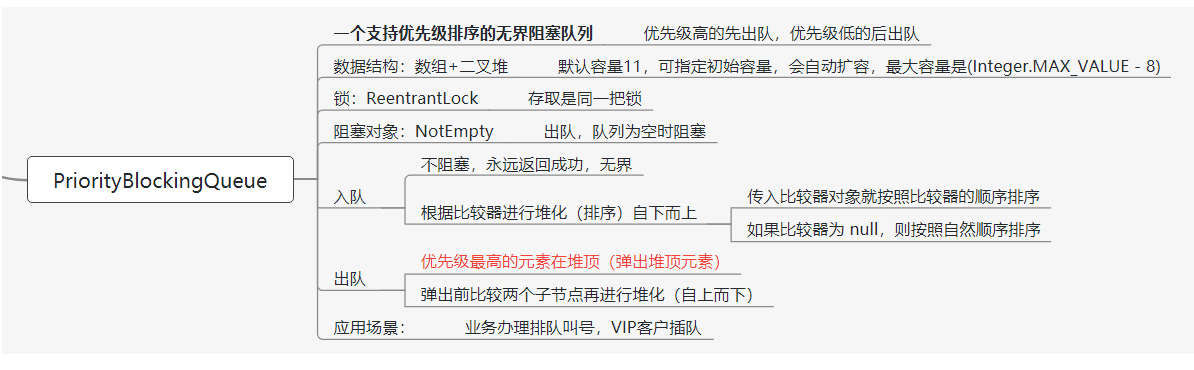
PriorityBlockingQueue使用
//创建优先级阻塞队列 Comparator为null,自然排序PriorityBlockingQueue<Integer> queue=new PriorityBlockingQueue<Integer>(5);//自定义ComparatorPriorityBlockingQueue queue=new PriorityBlockingQueue<Integer>(5, new Comparator<Integer>() {// 重写比较方法@Overridepublic int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {return o2-o1;}}
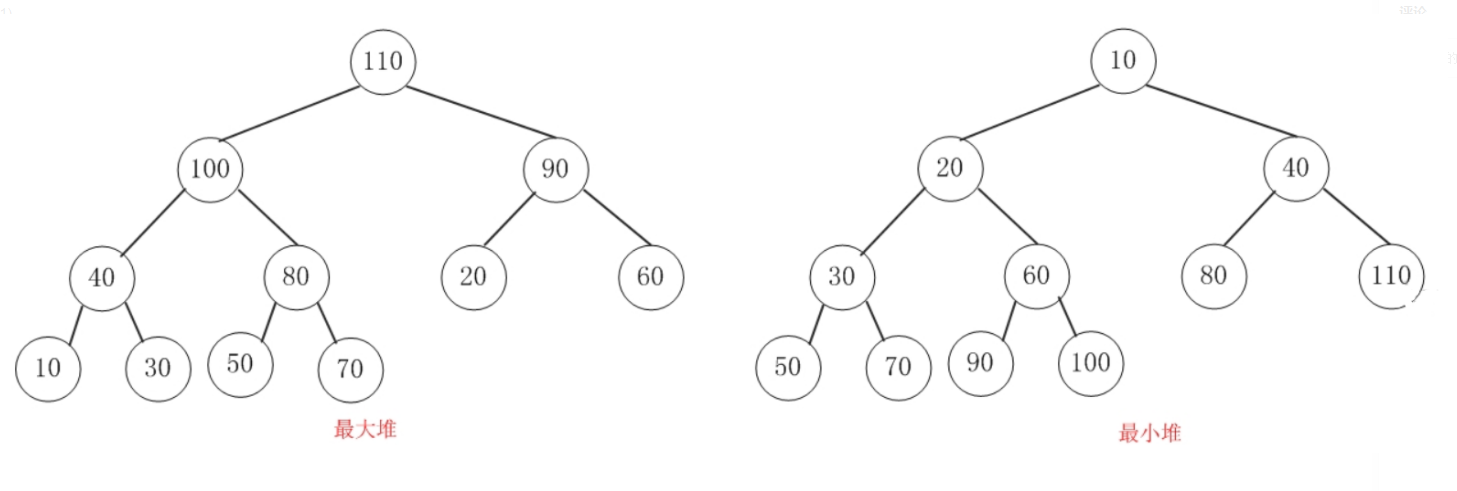
底层实现:二叉堆
完全二叉树:除了最后一行,其他行都满的二叉树,而且最后一行所有叶子节点都从左向右开始排序。
二叉堆:完全二叉树的基础上,加以一定的条件约束的一种特殊的二叉树。根据约束条件的不同,
二叉堆又可以分为两个类型:
- 大顶堆:父结点的键值大于或等于任何一个子结点的键值
- 小顶堆:父结点的键值小于或等于任何一个子结点的键值
//Inserts the specified element into this priority queue.public boolean offer(E e) {if (e == null)throw new NullPointerException();final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;lock.lock();int n, cap;Object[] array;while ((n = size) >= (cap = (array = queue).length))//Tries to grow array to accommodate at least one more elementtryGrow(array, cap);try {Comparator<? super E> cmp = comparator;if (cmp == null)//没有定义comparator 就走默认的排序规定siftUpComparable(n, e, array);else//走自定义的比较规则siftUpUsingComparator(n, e, array, cmp);size = n + 1;notEmpty.signal();} finally {lock.unlock();}return true;}private void tryGrow(Object[] array, int oldCap) {lock.unlock(); // must release and then re-acquire main lockObject[] newArray = null;if (allocationSpinLock == 0 &&UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, allocationSpinLockOffset,0, 1)) {try {int newCap = oldCap + ((oldCap < 64) ?(oldCap + 2) : // grow faster if small(oldCap >> 1));if (newCap - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) { // possible overflowint minCap = oldCap + 1;if (minCap < 0 || minCap > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE)throw new OutOfMemoryError();newCap = MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;}if (newCap > oldCap && queue == array)newArray = new Object[newCap];} finally {allocationSpinLock = 0;}}if (newArray == null) // back off if another thread is allocatingThread.yield();lock.lock();if (newArray != null && queue == array) {queue = newArray;System.arraycopy(array, 0, newArray, 0, oldCap);}}
应用场景
根据客户优先级的排队
DelayQueue
支持延时获取元素的阻塞队列, 采用优先队列 PriorityQueue 存储元素,
同时元素必须实现 Delayed 接口。设置延迟时间
延迟队列的特点是:不是先进先出,而是会按照延迟时间的长短来排序,下一个即将执行的任务会排到队列的最前面。
无界队列
public class DelayQueue<E extends Delayed> extends AbstractQueue<E>implements BlockingQueue<E> {private final transient ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();\//采用priorityQueue存储元素private final PriorityQueue<E> q = new PriorityQueue<E>();}
public interface Delayed extends Comparable<Delayed> {//getDelay 方法返回的是“还剩下多长的延迟时间才会被执行”,//如果返回 0 或者负数则代表任务已过期。//元素会根据延迟时间的长短被放到队列的不同位置,越靠近队列头代表越早过期。long getDelay(TimeUnit unit);}
DelayQueue使用
DelayQueue<OrderInfo> queue = new DelayQueue<OrderInfo>();// 对象需要实现delayed 接口class OrderInfo implements Delayed {private String name;private long time; //延时时间@Overridepublic long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {long diff = time - System.currentTimeMillis();return unit.convert(diff, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);}@Overridepublic int compareTo(Delayed obj) {if (this.time < ((DelayObject) obj).time) {return -1;}if (this.time > ((DelayObject) obj).time) {return 1;}return 0;}}
DelayQueue的原理
数据结构
//用于保证队列操作的线程安全private final transient ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();// 优先级队列,存储元素,用于保证延迟低的优先执行private final PriorityQueue<E> q = new PriorityQueue<E>();// 用于标记当前是否有线程在排队(仅用于取元素时) leader 指向的是第一个从队列获取元素阻塞的线程private Thread leader = null;// 条件,用于表示现在是否有可取的元素 当新元素到达,或新线程可能需要成为leader时被通知private final Condition available = lock.newCondition();public DelayQueue() {}public DelayQueue(Collection<? extends E> c) {this.addAll(c);}
入队put方法
public void put(E e) {offer(e);}public boolean offer(E e) {final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;lock.lock();try {// 入队q.offer(e);if (q.peek() == e) {// 若入队的元素位于队列头部,说明当前元素延迟最小// 将 leader 置空leader = null;// available条件队列转同步队列,准备唤醒阻塞在available上的线程available.signal();}return true;} finally {lock.unlock(); // 解锁,真正唤醒阻塞的线程}}入队put方法
出队take方法
public E take() throws InterruptedException {final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;lock.lockInterruptibly();try {for (;;) {E first = q.peek();// 取出堆顶元素( 最早过期的元素,但是不弹出对象)if (first == null)// 如果堆顶元素为空,说明队列中还没有元素,直接阻塞等待available.await();//当前线程无限期等待,直到被唤醒,并且释放锁。else {long delay = first.getDelay(NANOSECONDS);// 堆顶元素的到期时间if (delay <= 0)// 如果小于0说明已到期,直接调用poll()方法弹出堆顶元素return q.poll();// 如果delay大于0 ,则下面要阻塞了// 将first置为空方便gcfirst = null;// 如果有线程争抢的Leader线程,则进行无限期等待。if (leader != null)available.await();else {// 如果leader为null,把当前线程赋值给它Thread thisThread = Thread.currentThread();leader = thisThread;try {// 等待剩余等待时间available.awaitNanos(delay);} finally {// 如果leader还是当前线程就把它置为空,让其它线程有机会获取元素if (leader == thisThread)leader = null;}}}}} finally {// 成功出队后,如果leader为空且堆顶还有元素,就唤醒下一个等待的线程if (leader == null && q.peek() != null)// available条件队列转同步队列,准备唤醒阻塞在available上的线程available.signal();// 解锁,真正唤醒阻塞的线程lock.unlock();}}
- 获取锁
- 获取最早过期的元素,先不弹出元素素。
- 判断最早是否为空,如果是空就无线等吧,
- 如果为不为空,判断剩余的过期时间,
- 如果已经过期则直接返回当前元素
- 如果没有过期,也就是说剩余时间还存在,则先获取Leader对象,如果Leader已经有线程在处理,就是说还轮不到当前的线程执行,当前线程需要进行无限期等待,如果Leader为空,就可以只需等待剩余的时间就ok了
- 如果Leader已经为空,并且队列有内容则唤醒一个等待的队列。
总结就是:如果获取的对象以及过期就直接出队,如果哦没有就等下剩余的时间
如何选择适合的阻塞队列
线程池对于阻塞队列的选择
- FixedThreadPool———> LinkedBlockingQueue
- SingleThreadExecutor ———> LinkedBlockingQueue
- CachedThreadPool ———> SynchronousQueue
- ScheduledThreadPool ——->DelayQueue
- SingleThreadScheduledExecutor ——->DelayQueue
选择策略
通常我们可以从以下 5 个角度考虑,来选择合适的阻塞队列:
- 功能:
需要排序?延迟? - 容量:
考虑并发量,和业务需求是否有大量的任务
固定容量的:ArrayBlockingQueue
无界队列:LinkedBlockingQueue,DelayQueue - 是否扩容
看业务是否稳定类型,还是高并发类型
不能自动扩容:ArrayBlockingQueue
会自动扩容:PriorityBlockingQueue - 内存结构:
考虑内存利用率的性能
ArrayBlockingQueue:数据实现,没有所谓的结点,利用率高
LinkedBlockingQueue :链表实现,多了一层结点 - 性能:
ArrayBlockingQueue :一把锁,读写都会
LinkedBlockingQueue :两把锁,读写分离
SynchronousQueue :数据直传,没有存储的过程



