例子;
前提: KEY idx_name_age_position (name,age,position) USING BTREE
1、联合索引第一个字段用范围不会走索引
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM employees WHERE name > 'LiLei' AND age = 22 AND position ='manager';
扫描的rows返回过大,possible_keys有值,但是不会采用,数据量大,回表效率太低,而采用全表
2、强制走索引
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM employees force index(idx_name_age_position) WHERE name > 'LiLei' AND age = 22 AND position ='manager';
强制走了索引,rows少了,但rows少不代表耗时就少,需要回表
3、覆盖索引优化EXPLAIN SELECT name,age,position FROM employees WHERE name > 'LiLei' AND age = 22 AND position ='manager';
4、in和or在表数据量比较大的情况会走索引,在表记录不多的情况下会选择全表扫描
5、like KK% 一般情况都会走索引
like: 会走索引,不区分数据量**
当第一个可能不会走索引,底层计算推算数据可能会很多,就不走索引了
可以强制走索引
强制走索引也不一定更快,
全表走也不一定慢,
建议使用覆盖索引优化,
表优化器会根据表的数据情况会去计算,
数据量小可能全表会快
索引下推:(Index Condition Pushdown,ICP)
联合索引中
5.6以前:根据联合索引先从第一个取出索引id ,取出结果集,在比较后面的索引
5.6之后:下推,先根据联合第一个列比较,在依次比较后面的索引,都符合才会返回这个结果,
过滤不符合条件的记录,回表的记录少了
对于innodb的索引下推只能用于二级索引,innodb主键索引是聚簇索引,叶子节点全是行数据,
所以下推不会起减少查询全行数据的结果
在like 过滤后的结果较小可以走下推,但是如果数据量大,也不一定会走
like会走索引下推
trace工具用法
mysql> set session optimizer_trace="enabled=on",end_markers_in_json=on; ‐‐开启tracemysql> select * from employees where name > 'a' order by position;mysql> SELECT * FROM information_schema.OPTIMIZER_TRACE;查看trace字段:{"steps": [{"join_preparation": { --第一阶段:SQL准备阶段,格式化sql"select#": 1,"steps": [{"expanded_query": "/* select#1 */ select `employees`.`id` AS `id`,`employees`.`name` AS `name`,`employees`.`age` AS `age`,`employees`.`position` AS `position`,`employees`.`hire_time` AS `hire_time` from `employees` where (`employees`.`name` > 'a') order by `employees`.`position`"}] /* steps */} /* join_preparation */},{"join_optimization": { --第二阶段:SQL优化阶段"select#": 1,"steps": [{"condition_processing": { --条件处理"condition": "WHERE","original_condition": "(`employees`.`name` > 'a')","steps": [{"transformation": "equality_propagation","resulting_condition": "(`employees`.`name` > 'a')"},{"transformation": "constant_propagation","resulting_condition": "(`employees`.`name` > 'a')"},{"transformation": "trivial_condition_removal","resulting_condition": "(`employees`.`name` > 'a')"}] /* steps */} /* condition_processing */},{"substitute_generated_columns": {} /* substitute_generated_columns */},{"table_dependencies": [ --表依赖详情{"table": "`employees`","row_may_be_null": false,"map_bit": 0,"depends_on_map_bits": [] /* depends_on_map_bits */}] /* table_dependencies */},{"ref_optimizer_key_uses": [] /* ref_optimizer_key_uses */},{"rows_estimation": [ --预估表的访问成本{"table": "`employees`","range_analysis": {"table_scan": { --全表扫描情况"rows": 10123, --扫描行数"cost": 2054.7 --查询成本} /* table_scan */,"potential_range_indexes": [ --查询可能使用的索引{"index": "PRIMARY", --主键索引"usable": false,"cause": "not_applicable"},{"index": "idx_name_age_position", --辅助索引"usable": true,"key_parts": ["name","age","position","id"] /* key_parts */}] /* potential_range_indexes */,"setup_range_conditions": [] /* setup_range_conditions */,"group_index_range": {"chosen": false,"cause": "not_group_by_or_distinct"} /* group_index_range */,"analyzing_range_alternatives": { --分析各个索引使用成本"range_scan_alternatives": [{"index": "idx_name_age_position","ranges": ["a < name" --索引使用范围] /* ranges */,"index_dives_for_eq_ranges": true,"rowid_ordered": false, --使用该索引获取的记录是否按照主键排序"using_mrr": false,"index_only": false, --是否使用覆盖索引"rows": 5061, --索引扫描行数"cost": 6074.2, --索引使用成本"chosen": false, --是否选择该索引"cause": "cost"}] /* range_scan_alternatives */,"analyzing_roworder_intersect": {"usable": false,"cause": "too_few_roworder_scans"} /* analyzing_roworder_intersect */} /* analyzing_range_alternatives */} /* range_analysis */}] /* rows_estimation */},{"considered_execution_plans": [{"plan_prefix": [] /* plan_prefix */,"table": "`employees`","best_access_path": { --最优访问路径"considered_access_paths": [ --最终选择的访问路径{"rows_to_scan": 10123,"access_type": "scan", --访问类型:为scan,全表扫描"resulting_rows": 10123,"cost": 2052.6,"chosen": true, --确定选择"use_tmp_table": true}] /* considered_access_paths */} /* best_access_path */,"condition_filtering_pct": 100,"rows_for_plan": 10123,"cost_for_plan": 2052.6,"sort_cost": 10123,"new_cost_for_plan": 12176,"chosen": true}] /* considered_execution_plans */},{"attaching_conditions_to_tables": {"original_condition": "(`employees`.`name` > 'a')","attached_conditions_computation": [] /* attached_conditions_computation */,"attached_conditions_summary": [{"table": "`employees`","attached": "(`employees`.`name` > 'a')"}] /* attached_conditions_summary */} /* attaching_conditions_to_tables */},{"clause_processing": {"clause": "ORDER BY","original_clause": "`employees`.`position`","items": [{"item": "`employees`.`position`"}] /* items */,"resulting_clause_is_simple": true,"resulting_clause": "`employees`.`position`"} /* clause_processing */},{"reconsidering_access_paths_for_index_ordering": {"clause": "ORDER BY","steps": [] /* steps */,"index_order_summary": {"table": "`employees`","index_provides_order": false,"order_direction": "undefined","index": "unknown","plan_changed": false} /* index_order_summary */} /* reconsidering_access_paths_for_index_ordering */},{"refine_plan": [{"table": "`employees`"}] /* refine_plan */}] /* steps */} /* join_optimization */},{"join_execution": { --第三阶段:SQL执行阶段"select#": 1,"steps": [] /* steps */} /* join_execution */}] /* steps */}结论:全表扫描的成本低于索引扫描,所以mysql最终选择全表扫描mysql> select * from employees where name > 'zzz' order by position;mysql> SELECT * FROM information_schema.OPTIMIZER_TRACE;查看trace字段可知索引扫描的成本低于全表扫描,所以mysql最终选择索引扫描mysql> set session optimizer_trace="enabled=off"; --关闭trace
Order by group By
orderb by 走索引不体现在key_len 上
前提: KEY idx_name_age_position (name,age,position) USING BTREE 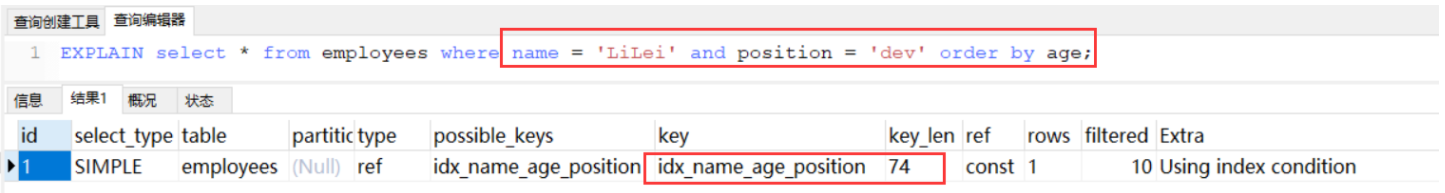
用到了索引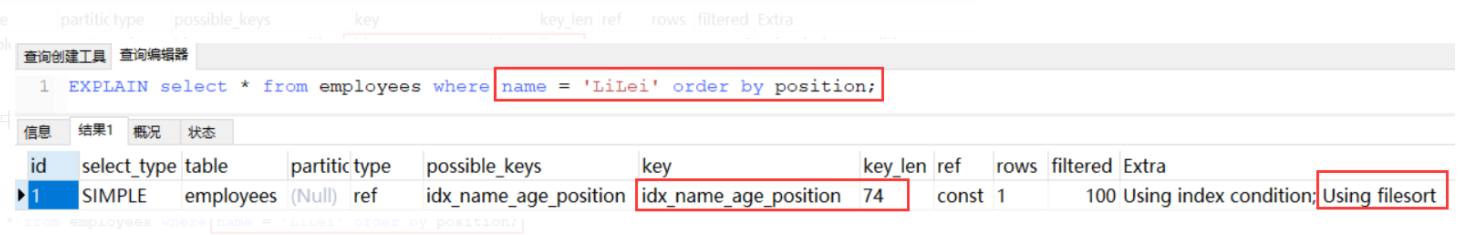
最左匹配,跳过age列,就不走索引了e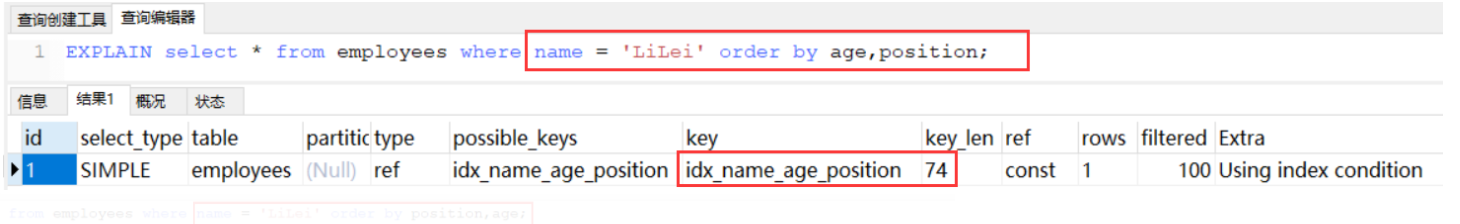
order by 也遵从最左原则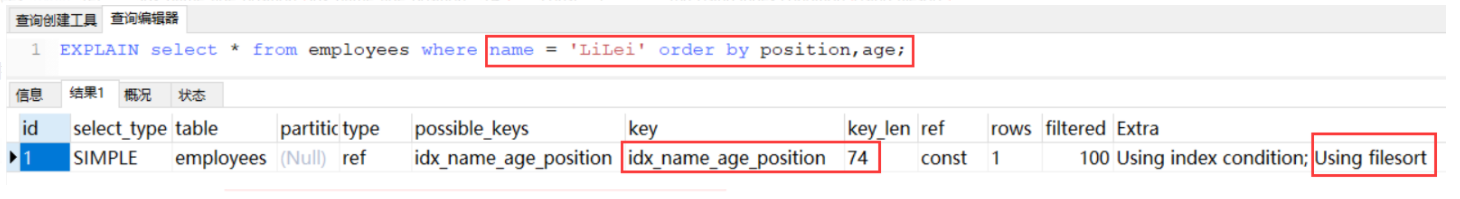
颠换了age, position 的位置也就不走索引了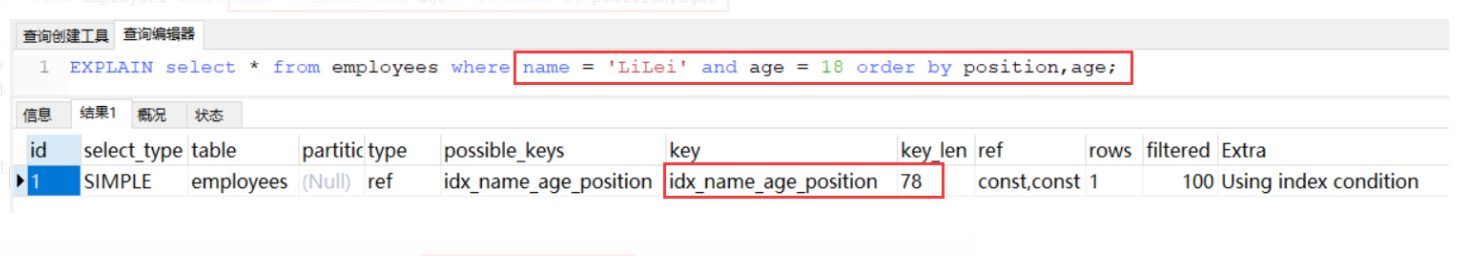
前面的where 中age已经是常量了,order by 颠倒也不影响了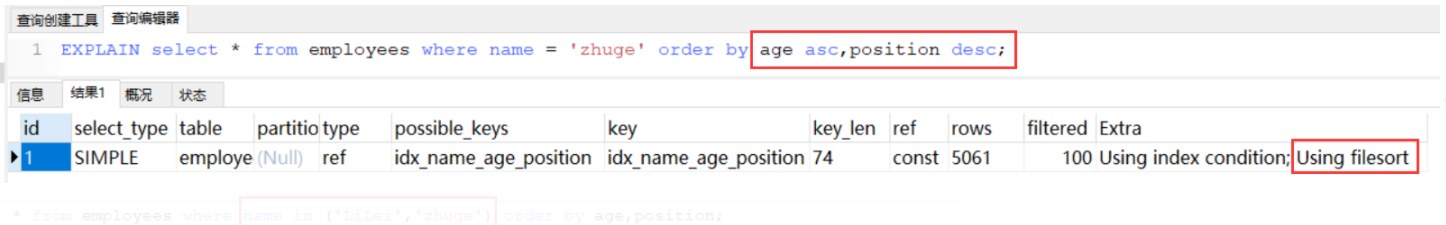 一个正序,一个倒序因为与索引顺序不一致就走不了,8版本以上支持这种了
一个正序,一个倒序因为与索引顺序不一致就走不了,8版本以上支持这种了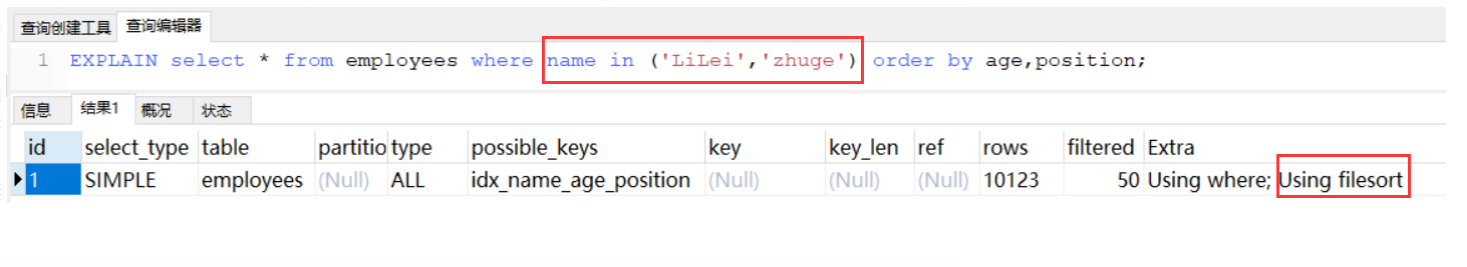
等于了多个name, order by时 age顺序就不确定了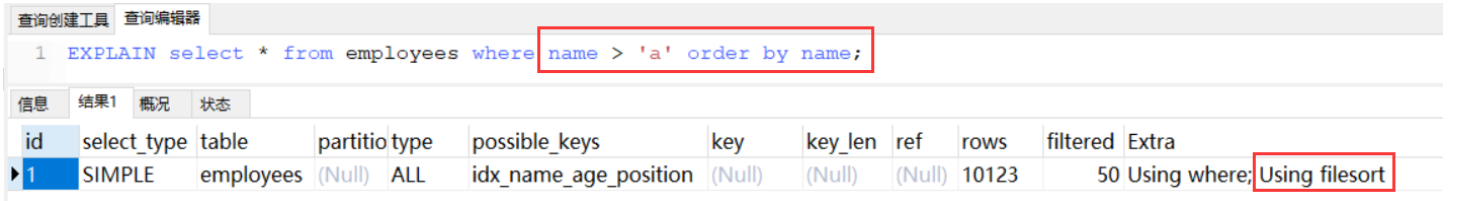
梳理太大,走索引回表效率不高,可以覆盖索引
数据量太大,涉及回表,会采用全表扫描的方式了
总结
1:mysql支持两种 排序:filesort和index
useing index : 扫描索引本身完成排序,效率高
filesort : 需要加载到内存做文件排序,效率不行
2:order by 满足两种情况会用using index
a.order by满足索引最左前列
b. where 子句与order by 子句条件列组合满足最左前列
3:劲量在索引列上排序
4:不行就using filesort
5:有限考虑覆盖索引
6:group by 与 order by 类似,先排序后分组,也遵从最左法则
gropu by 如果不需要排序可以加 order by null 禁止排序
filesort文件排序方式
单路排序,一次性取出所有字段, 在内存中去排序
sort_mode信息里显示< sort_key, additional_fields >
或者< sort_key, packed_additional_fields >
双路排序: 回表模式,只取出结果集中的id ,排序字段取排序,让后在根据ID 回表出对应的数据。
sort_mode信息里显示< sort_key, rowid >
根据max_length_for_sort_data(默认1024字节) 判断是否单路,双路
小于: 单路
大于:双路
单路排序过程
1:找出主键ID
2:根据id取整行,所有字段加入 sort_buffer中
3:找下一个满足条件的Id
4:重复
5:对sort_buffer需求的字段排序
6:return
双路排序过程
1:取满足条件的ID
2:取排序字段,Id,加入到sort_buffer
3:找下一个满足条件的Id
4:重复2 ,3
5:对sort_buffer 按排序字段排序
6:遍历排好序的id回表取值
7:return
MySQL通过 max_length_for_sort_data 这个参数来控制排序,在不同场景使用不同的排序模式,从而提升排序效率
sort_buffer(默认1M) 大小优化,不建议
索引设计原则
需要有具体的场景
1:代码先上,索引后上
2:联合索引尽量覆盖条件
:3:不要在小基数上建立索引
4:长字符串可以采用前缀索引
5:where 与order by冲突有限 where
6:基于具体慢SQL优化
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40884473/article/details/89455740

