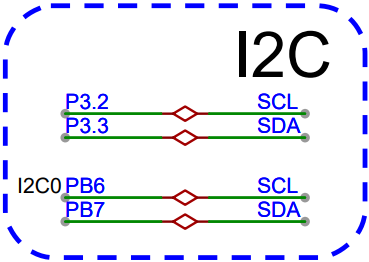
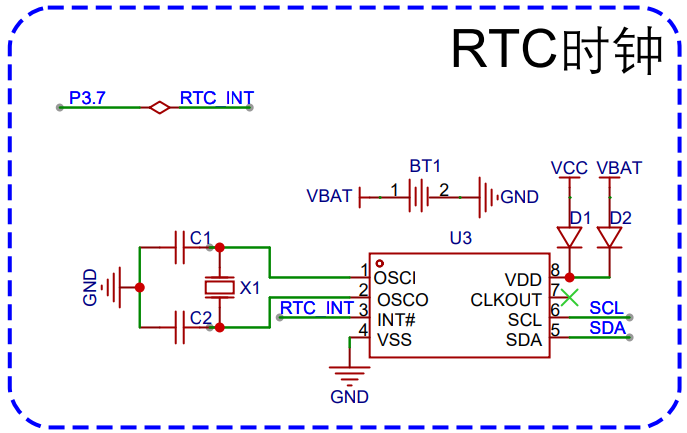
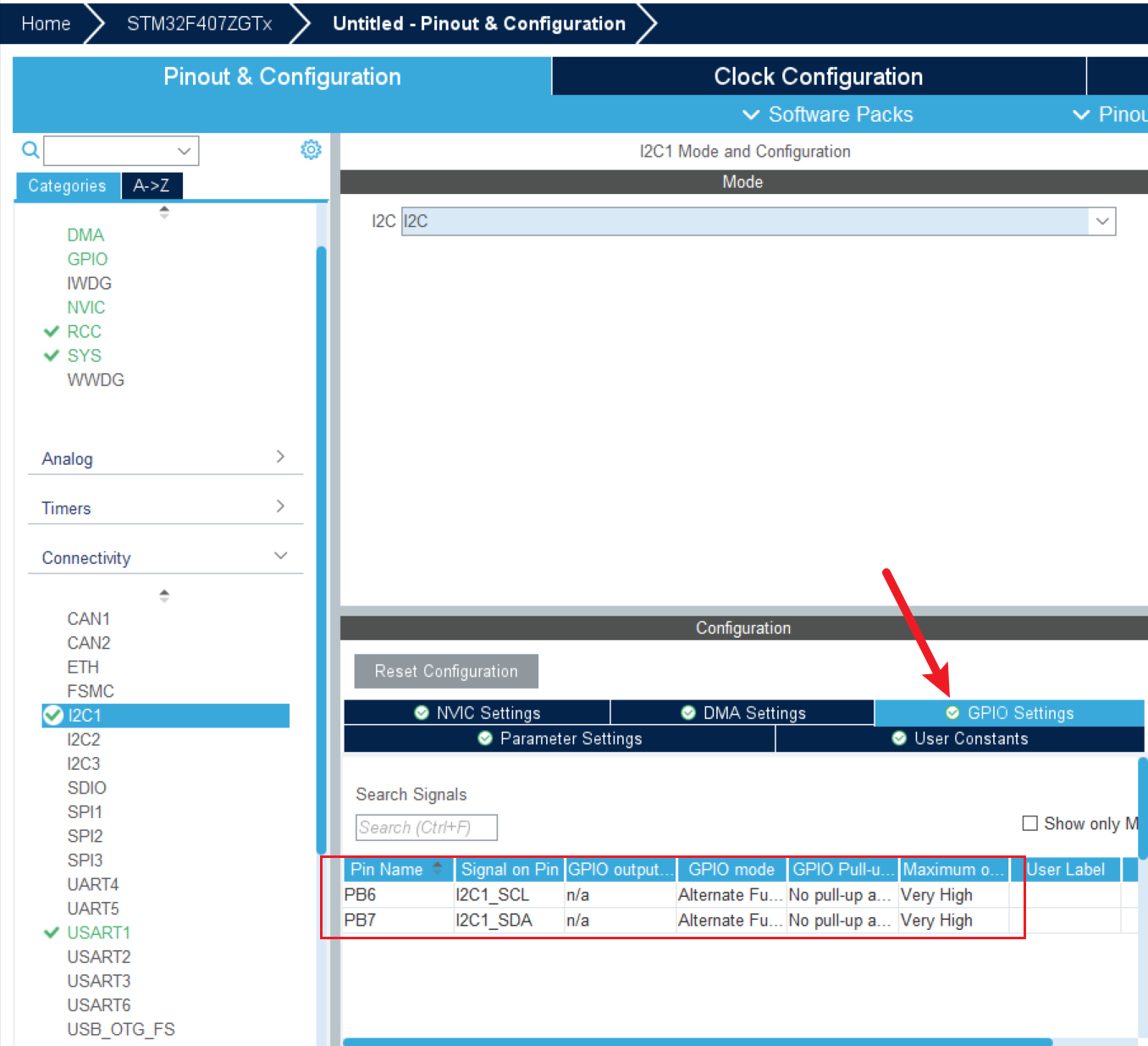
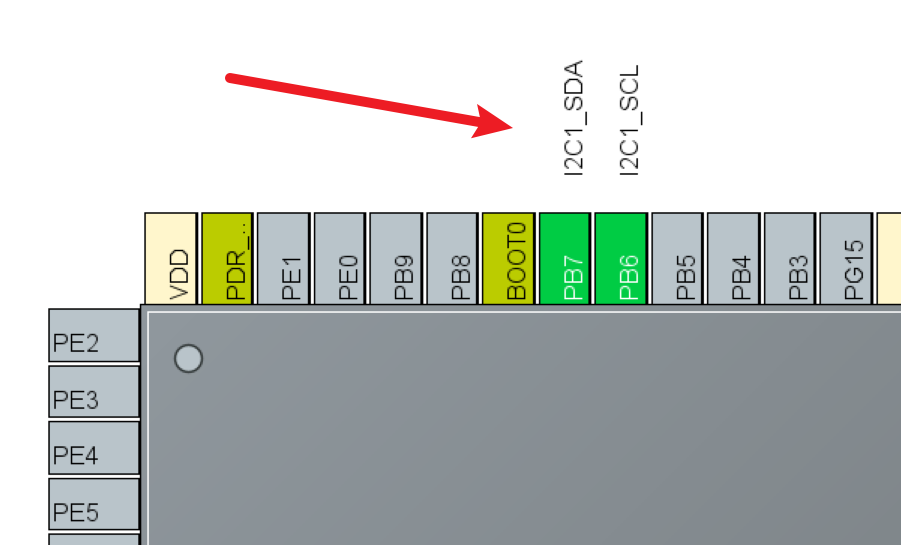
学习目标
I2C编码
移植PCF8563驱动
#ifndef __PCF8563_H__#define __PCF8563_H__#include "stm32f4xx.h"#include "i2c.h"#ifndef u8#define u8 uint8_t#endif#ifndef u16#define u16 uint16_t#endif// 如果定义了该宏,Alarm的相关函数才会被编译并启用,被注释掉就是禁用//#define PCF8563_ALARM_ENABLE// 如果定义了该宏,Timer的相关函数才会被编译并启用,被注释掉就是禁用//#define PCF8563_TIMER_ENABLE// 设备地址#define PCF8563_ADDR 0x51// 存储地址:时间的存储地址开始位置#define PCF8563_REG_TD 0x02// 控制寄存器2#define PCF8563_REG_CS2 0x01// I2C写操作#define I2C_WRITE(a, r, p, n) I2C1_write(a, r, p, n)// I2C读操作#define I2C_READ(a, r, p, n) I2C1_read(a, r, p, n)// 秒、分、时、星期、日、月、年、世纪// year = 2023, month = 2, day = 28, week = 4;// hour = 23, minute = 59, second = 52;typedef struct {u16 year;u8 month;u8 day;u8 week;u8 hour;u8 minute;u8 second;} Clock_t;// 警报、闹铃Alarm结构体typedef struct {u8 minute;u8 hour;u8 day;u8 weekday;} Alarm_t;typedef enum {HZ4096 = 0,HZ64 = 1,HZ1 = 2,HZ1_60 = 3,}TimerFreq;void PCF8563_init();void PCF8563_set_clock(Clock_t c);void PCF8563_get_clock(Clock_t *c);void PCF8563_set_alarm(Alarm_t alarm);void PCF8563_enable_alarm();void PCF8563_disable_alarm();void PCF8563_alarm_clear_flag();void PCF8563_set_timer(TimerFreq freq ,u8 countdown);void PCF8563_enable_timer();void PCF8563_disable_timer();void PCF8563_timer_clear_flag();#ifdef PCF8563_ALARM_ENABLEextern void PCF8563_on_alarm();#endif#ifdef PCF8563_TIMER_ENABLEextern void PCF8563_on_timer();#endif#endif
#include "PCF8563.h"#include <stdio.h>#define NUMBER_TD 7void PCF8563_init() {}void PCF8563_set_clock(Clock_t c) {u8 p[NUMBER_TD]; // 用于存储时间字节数组u8 Cent; // 世纪:0代表本世纪20, 1代表下个世纪,年99->00时交替// 将数值转成一个字节表达 (BCD)// 秒:VL 1 1 1 - 0 0 0 0p[0] = ((c.second / 10) << 4) + (c.second % 10);// 分: X 1 1 1 - 0 0 0 0p[1] = ((c.minute / 10) << 4) + (c.minute % 10);// 时: X X 1 1 - 0 0 0 0p[2] = ((c.hour / 10) << 4) + (c.hour % 10);// 天: X X 1 1 - 0 0 0 0p[3] = ((c.day / 10) << 4) + (c.day % 10);// 周: X X X X - X 0 0 0p[4] = c.week;// 世纪 20xx , 21xxCent = (c.year >= 2100 ? 1 : 0);// 月: C X X 1 - 0 0 0 0p[5] = (Cent << 7) + ((c.month / 10) << 4) + (c.month % 10);// 年: 1 1 1 1 - 0 0 0 0 2023, 2036p[6] = ((c.year % 100 / 10) << 4) + (c.year % 10);// 设置数据WriteI2C_WRITE(PCF8563_ADDR, PCF8563_REG_TD, p, NUMBER_TD);}void PCF8563_get_clock(Clock_t *c) {u8 Cent; // 世纪:0代表本世纪20, 1代表下个世纪,年99->00时交替u8 p[NUMBER_TD]; // 用于存储时间字节数组// 循环读取Read: 秒、分、时、星期、日、月、年、世纪I2C_READ(PCF8563_ADDR, PCF8563_REG_TD, p, NUMBER_TD);// for(i = 0; i < NUMBER; i++){// printf("%d-> %d \n", (int)i, (int)p[i]);// }// printf("----------------\n");// 秒:VL 1 1 1 - 0 0 0 0 转成十进制c->second = ((p[0] >> 4) & 0x07) * 10 + (p[0] & 0x0F);// 分: X 1 1 1 - 0 0 0 0 转成十进制c->minute = ((p[1] >> 4) & 0x07) * 10 + (p[1] & 0x0F);// 时: X X 1 1 - 0 0 0 0 转成十进制c->hour = ((p[2] >> 4) & 0x03) * 10 + (p[2] & 0x0F);// 天: X X 1 1 - 0 0 0 0 转成十进制c->day = ((p[3] >> 4) & 0x03) * 10 + (p[3] & 0x0F);// 周: X X X X - X 0 0 0 转成十进制c->week = p[4] & 0x07;// 世纪// 月: C X X 1 - 0 0 0 0c->month = ((p[5] >> 4) & 0x01) * 10 + (p[5] & 0x0F);Cent = p[5] >> 7; // 0->20xx年 1->21xx年// 年: 1 1 1 1 - 0 0 0 0 1969, 2023c->year = ((p[6] >> 4) & 0x0F) * 10 + (p[6] & 0x0F);c->year += Cent == 0 ? 2000 : 2100;}void PCF8563_set_alarm(Alarm_t alarm){// 想将某个类型关闭掉,传一个负数// 或者多传1个字段,低4位,根据01决定是否启动对应类型 0000 0011u8 a[4];// a = 0; // 分钟// I2C_WRITE(PCF8563_ADDR, 0x09, &a, 1);//// a = 0; // 小时// I2C_WRITE(PCF8563_ADDR, 0x0A, &a, 1);// 分 M 1 1 1 - 0 0 0 0 enable->0, diabled->0x80a[0] = ((alarm.minute / 10) << 4) + (alarm.minute % 10) + 0;// 时 H x 1 1 - 0 0 0 0 enable->0, diabled->0x80a[1] = ((alarm.hour / 10) << 4) + (alarm.hour % 10) + 0;// 天 D x 1 1 - 0 0 0 0 enable->0, diabled->0x80a[2] = ((alarm.day / 10) << 4) + (alarm.day % 10) + 0;// 周 W x x x - x 0 0 0 enable->0, diabled->0x80a[3] = alarm.weekday + 0;I2C_WRITE(PCF8563_ADDR, 0x09, a, 4);}void PCF8563_enable_alarm(){u8 cs2 = 0; // 控制状态寄存器2// 配置 cs2 寄存器以启用Alarm -------------------------------------------------I2C_READ(PCF8563_ADDR, 0x01, &cs2, 1);// printf("cs2: %d \n", (int)cs2);// 清除Alarm标记,AF设置为0,下一次闹钟到点时,才能触发cs2 &= ~0x08;// 开启Alarm中断, AIE为1,启用Alarm闹钟cs2 |= 0x02;I2C_WRITE(PCF8563_ADDR, 0x01, &cs2, 1);}void PCF8563_disable_alarm(){u8 cs2 = 0; // 控制状态寄存器2// 配置 cs2 寄存器以启用Alarm -------------------------------------------------I2C_READ(PCF8563_ADDR, 0x01, &cs2, 1);// printf("cs2: %d \n", (int)cs2);// 清除Alarm标记,AF设置为0,下一次闹钟到点时,才能触发cs2 &= ~0x08;// 开启Alarm中断, AIE为0,禁用Alarm闹钟cs2 &= ~0x02;I2C_WRITE(PCF8563_ADDR, 0x01, &cs2, 1);}void PCF8563_alarm_clear_flag(){u8 cs2 = 0; // 控制状态寄存器2// 01H寄存器中AF位,会在Alarm触发时,被置为1.// 必须手动置为0,下一个Alarm才能触发。// 配置 cs2 寄存器I2C_READ(PCF8563_ADDR, 0x01, &cs2, 1);// printf("cs2: %d \n", (int)cs2);// 清除Alarm标记,AF设置为0,下一次闹钟到点时,才能触发cs2 &= ~0x08;I2C_WRITE(PCF8563_ADDR, 0x01, &cs2, 1);}void PCF8563_set_timer(TimerFreq freq ,u8 countdown){u8 p = 0;// 设置Timer运行频率、启用timer source clockp = 0x80 + freq; // 64HzI2C_WRITE(PCF8563_ADDR, 0x0E, &p, 1);// 设置Timer计数值(每个周期)p = countdown;I2C_WRITE(PCF8563_ADDR, 0x0F, &p, 1);}void PCF8563_enable_timer(){u8 cs2 = 0; // 控制状态寄存器2// 通过cs2启用TimerI2C_READ(PCF8563_ADDR, 0x01, &cs2, 1);// 开启Timer中断: TIEcs2 |= 0x01;// 清除Timer flag; TFcs2 &= ~0x04;I2C_WRITE(PCF8563_ADDR, 0x01, &cs2, 1);}void PCF8563_disable_timer(){u8 cs2 = 0; // 控制状态寄存器2// 通过cs2启用TimerI2C_READ(PCF8563_ADDR, 0x01, &cs2, 1);// 开启Timer中断: TIEcs2 &= ~0x01;// 清除Timer flag; TFcs2 &= ~0x04;I2C_WRITE(PCF8563_ADDR, 0x01, &cs2, 1);}void PCF8563_timer_clear_flag(){u8 cs2 = 0; // 控制状态寄存器2// 通过cs2启用TimerI2C_READ(PCF8563_ADDR, 0x01, &cs2, 1);// 清除Timer flag; TFcs2 &= ~0x04;I2C_WRITE(PCF8563_ADDR, 0x01, &cs2, 1);}// 当中断触发时,此函数会执行(Alarm、Timer)void ext_int3_call() {u8 cs2;I2C_READ(PCF8563_ADDR, PCF8563_REG_CS2, &cs2, 1);// printf("cs2: %d \n", (int) cs2);#ifdef PCF8563_TIMER_ENABLE// Alarm Flag && AIEif((cs2 & 0x08) && (cs2 & 0x02)){// 清除Alarm标记,避免下次无法触发PCF8563_alarm_clear_flag();// 事件触发PCF8563_on_alarm();}#endif#ifdef PCF8563_TIMER_ENABLE// Timer Flag && TIEif((cs2 & 0x04) && (cs2 & 0x01)){// 清除Timer标记,避免下次无法触发PCF8563_timer_clear_flag();// 事件触发PCF8563_on_timer();}#endif}
只需要实现 i2c_write和i2c_read,驱动就可以正常运行。
/* USER CODE BEGIN WHILE */// pcf8563初始化PCF8563_init();Clock_t c;c.year = 2023;c.month = 3;c.day = 10;c.week = 2;c.hour = 23;c.minute = 59;c.second = 55;PCF8563_set_clock(c);while (1){PCF8563_get_clock(&c);printf("%d-%d-%d %d %d:%d:%d\r\n", c.year, c.month, c.day, c.week, c.hour, c.minute,c.second);HAL_Delay(1000);/* USER CODE END WHILE *//* USER CODE BEGIN 3 */}/* USER CODE END 3 */
I2C读写实现
添加头定义
/* USER CODE BEGIN Prototypes */void I2C1_write(uint8_t addr, uint8_t reg, uint8_t* data, uint32_t len);void I2C1_read(uint8_t addr, uint8_t reg, uint8_t* data, uint32_t len);/* USER CODE END Prototypes */
添加c实现
/* USER CODE BEGIN 1 */#include "string.h"void I2C1_write(uint8_t addr, uint8_t reg, uint8_t* data, uint32_t len) {uint8_t buff[len + 1];buff[0] = reg;memcpy(&buff[1], data, len);HAL_I2C_Master_Transmit(&hi2c1, addr << 1, buff, len + 1, HAL_MAX_DELAY);}void I2C1_read(uint8_t addr, uint8_t reg, uint8_t* data, uint32_t len) {HAL_I2C_Master_Transmit(&hi2c1, addr << 1, ®, 1, HAL_MAX_DELAY);HAL_I2C_Master_Receive(&hi2c1, (addr << 1) | 0x01, data, len, HAL_MAX_DELAY);}/* USER CODE END 1 */
- 使用HAL库读写PCF8563芯片