Using filesort文件排序原理详解
filesort文件排序方式
- 单路排序:是一次性取出满足条件行的所有字段,然后在sort buffer中进行排序;用trace工具可以看到sort_mode信息里显示< sort_key, additional_fields >或者< sort_key, packed_additional_fields >
- 双路排序(又叫回表排序模式):是首先根据相应的条件取出相应的排序字段和可以直接定位行数据的行 ID,然后在 sort buffer 中进行排序,排序完后需要再次取回其它需要的字段;用trace工具可以看到sort_mode信息里显示< sort_key, rowid >
MySQL 通过比较系统变量 max_length_for_sort_data(默认1024字节) 的大小和需要查询的字段总大小来判断使用哪种排序模式。
- 如果 字段的总长度小于max_length_for_sort_data ,那么使用 单路排序模式;
- 如果 字段的总长度大于max_length_for_sort_data ,那么使用 双路排序模·式。
示例验证下各种排序方式: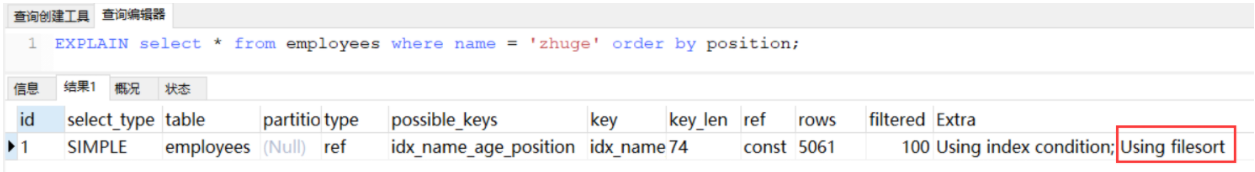
查看下这条sql对应trace结果如下(只展示排序部分):
mysql> set session optimizer_trace=”enabled=on”,end_markers_in_json=on; —开启trace
mysql> select from employees where name = ‘zhuge’ order by position;
mysql> select from information_schema.OPTIMIZER_TRACE;
trace排序部分结果:
“join_execution”: { —Sql执行阶段
“select#”: 1,
“steps”: [
{
“filesort_information”: [
{
“direction”: “asc”,
“table”: “employees“,
“field”: “position”
}
] / filesort_information /,
“filesort_priority_queue_optimization”: {
“usable”: false,
“cause”: “not applicable (no LIMIT)”
} / filesort_priority_queue_optimization /,
“filesort_execution”: [
] / filesort_execution /,
“filesort_summary”: { —文件排序信息
“rows”: 10000, —预计扫描行数
“examined_rows”: 10000, —参与排序的行
“number_of_tmp_files”: 3, —使用临时文件的个数,这个值如果为0代表全部使用的sort_buffer内存排序,否则使用的磁盘文件排序
“sort_buffer_size”: 262056, —排序缓存的大小,单位Byte
“sort_mode”: “
} / filesort_summary /
}
] / steps /
} / join_execution /
mysql> set max_length_for_sort_data = 10; —employees表所有字段长度总和肯定大于10字节
mysql> select from employees where name = ‘zhuge’ order by position;
mysql> select from information_schema.OPTIMIZER_TRACE;
trace排序部分结果:
“join_execution”: {
“select#”: 1,
“steps”: [
{
“filesort_information”: [
{
“direction”: “asc”,
“table”: “employees“,
“field”: “position”
}
] / filesort_information /,
“filesort_priority_queue_optimization”: {
“usable”: false,
“cause”: “not applicable (no LIMIT)”
} / filesort_priority_queue_optimization /,
“filesort_execution”: [
] / filesort_execution /,
“filesort_summary”: {
“rows”: 10000,
“examined_rows”: 10000,
“number_of_tmp_files”: 2,
“sort_buffer_size”: 262136,
“sort_mode”: “
} / filesort_summary /
}
] / steps /
} / join_execution /
mysql> set session optimizer_trace=”enabled=off”; —关闭trace
我们先看单路排序的详细过程:
- 从索引name找到第一个满足 name = ‘zhuge’ 条件的主键 id
- 根据主键 id 取出整行,取出所有字段的值,存入 sort_buffer 中
- 从索引name找到下一个满足 name = ‘zhuge’ 条件的主键 id
- 重复步骤 2、3 直到不满足 name = ‘zhuge’
- 对 sort_buffer 中的数据按照字段 position 进行排序
- 返回结果给客户端
我们再看下双路排序的详细过程:
- 从索引 name 找到第一个满足 name = ‘zhuge’ 的主键id
- 根据主键 id 取出整行,把排序字段 position 和主键 id 这两个字段放到 sort buffer 中
- 从索引 name 取下一个满足 name = ‘zhuge’ 记录的主键 id
- 重复 3、4 直到不满足 name = ‘zhuge’
- 对 sort_buffer 中的字段 position 和主键 id 按照字段 position 进行排序
- 遍历排序好的 id 和字段 position,按照 id 的值回到原表中取出 所有字段的值返回给客户端
其实对比两个排序模式,单路排序会把所有需要查询的字段都放到 sort buffer 中,而双路排序只会把主键和需要排序的字段放到 sort buffer 中进行排序,然后再通过主键回到原表查询需要的字段。
如果 MySQL 排序内存 sort_buffer配置的比较小并且没有条件继续增加了,可以适当把 max_length_for_sort_data 配置小点,让优化器选择使用双路排序算法,可以在sort_buffer 中一次排序更多的行,只是需要再根据主键回到原表取数据。
如果 MySQL 排序内存有条件可以配置比较大,可以适当增大 max_length_for_sort_data 的值,让优化器优先选择全字段排序(单路排序),把需要的字段放到 sort_buffer 中,这样排序后就会直接从内存里返回查询结果了。
所以,MySQL通过 max_length_for_sort_data 这个参数来控制排序,在不同场景使用不同的排序模式,从而提升排序效率。
注意,如果全部使用sort_buffer内存排序一般情况下效率会高于磁盘文件排序,但不能因为这个就随便增大sort_buffer(默认1M),mysql很多参数设置都是做过优化的,不要轻易调整。

