一、阻塞队列是什么?定义:阻塞队列首先是一个队列,当队列是空的时候,从队列获取元素的操作将会被阻塞,当队列是满的时候,从队列插入元素的操作将会被阻塞。
消息中间件底层用的就是阻塞队列。
二、阻塞队列好处
在多线程领域,所谓阻塞,在某些情况下会挂起线程(即阻塞),一旦条件满足,被挂起的线程又会自动被唤醒。
为什么需要使用BlockingQueue? —— 好处是我们不需要关心什么时候去阻塞线程,什么时候需要唤醒线程,因为这一切BlockingQue都给你一手包办了。
在Concurrent包发布以前,在多线程环境下,我们每个程序员都要去控制这些细节,尤其还要兼顾效率与线程安全,这会给我们的程序带来不小的复杂度。
三、阻塞队列BlockingQueue接口架构图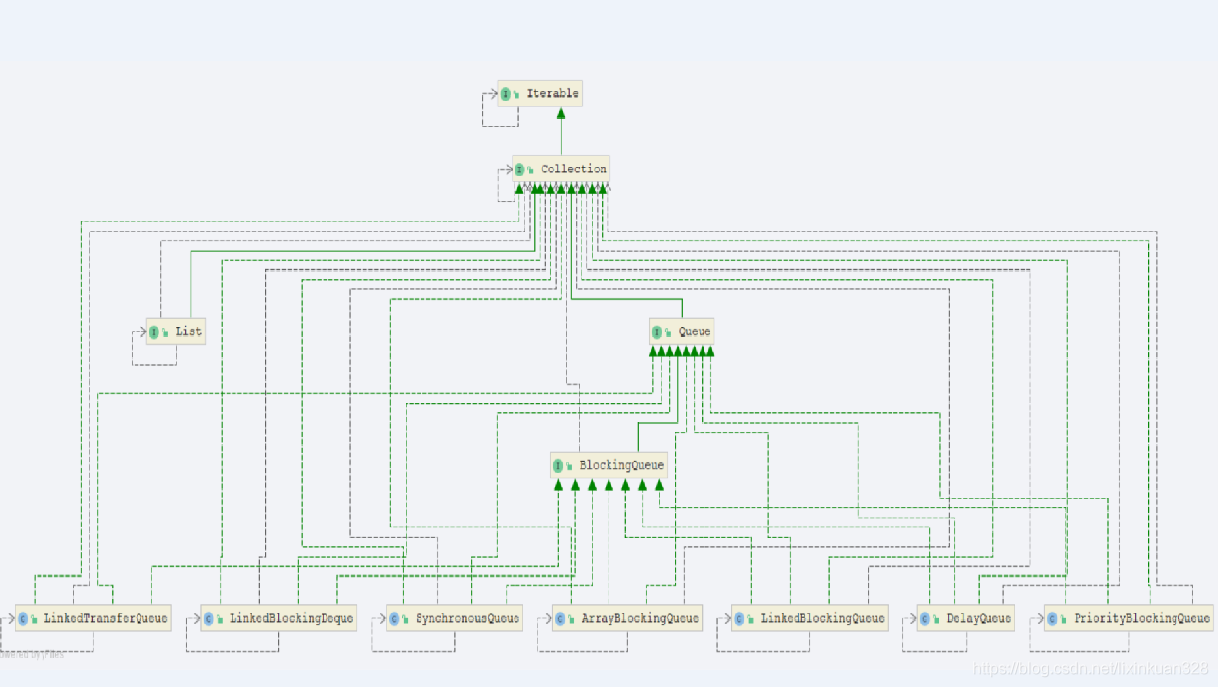
阻塞队列BlockingQueue种类:
(1)ArrayBlockingQueue:由数组结构组成的有界阻塞队列。
(2)LinkedBlockingQueue:由链表结果组成的有界阻塞队列(默认大小Integer.MAX_VALUE)阻塞队列。(接近无界)
(3)SychronousQueue:不存储元素的阻塞队列,也即单个元素队列。(最后代码演示)
(4)PriorityBlockingQueue:支持优先级排序的无界阻塞队列。
(5)DelayQueue:使用优先级队列实现的延迟无界阻塞队列。
(6)LinkedTransferQueue:由链表结构组成的无界阻塞队列。
(7)LinkedBlockingDeque:由链表结构组成的双端阻塞队列。
四、阻塞队列BlockingQueue核心方法
共同点:插入成功或者删除成功都返回true(除了put和take),区别在于处理异常情况
Queue 中 element() 和 peek()都是用来返回队列的头元素,不删除。在队列元素为空的情况下,element() 方法会抛出NoSuchElementException异常,peek() 方法只会返回 null。
(1)抛出异常的方法
当阻塞队列满时,再往队列里add元素会抛出IllegalStateException:Queue full;
当阻塞队列空时,再从队列里remove移除元素会抛NoSuchElementException。
(2)返回特殊值(boolean值)的方法
插入成功,返回true;插入失败,返回false;
删除成功返回出队列元素;删除失败返回null;
(3)阻塞的方法(添加无返回值)
当阻塞队列满时,生产者线程继续往队列里put元素,队列会一直阻塞生产线程直到put数据or响应中断退出。
当阻塞队列空时,消费者线程试图take队列里的元素,队列会一直阻塞消费者线程直到队列有可用元素。
(4)超时的方法
当向阻塞队列offer元素时候,时间超过了设定的值,就会出现超时中断;
当向阻塞队列poll元素时候,时间超过了设定的值,就会出现超时中断。
五、阻塞队列BlockingQueue核心方法代码验证
5.1、抛出异常的方法代码验证:
add方法抛出异常
package com.lxk.juc;import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;/*** 当阻塞队列满时,再往队列里add元素会抛出IllegalStateException:Queue full.* 当阻塞队列空时,再往队列里remove元素会抛出NoSuchElementException.*/public class BlockingQueueDemoOne {public static void main(String[] args) {BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<String>(5);System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("吴用"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("宋江"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("李逵"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("卢俊义"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("高俅"));// 再往阻塞队列添加一个元素就会抛出I了legalStateException:Queue full.System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("武松"));}}
程序执行结果: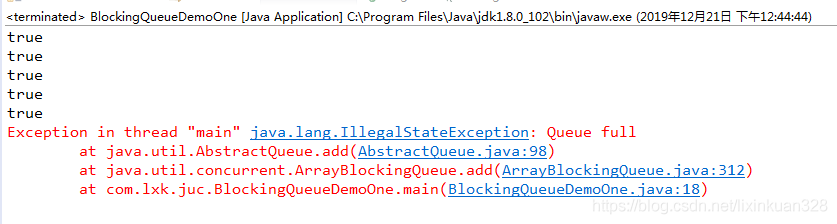
remove方法抛出异常
/ * 当阻塞队列空时,再往队列里remove元素会抛出NoSuchElementException.*/public class BlockingQueueDemoOne {public static void main(String[] args) {BlockingQueue blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue(5);// 阻塞队列add方法抛出异常演示System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("吴用"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("宋江"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("李逵"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("卢俊义"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.add(123));// 再往阻塞队列添加一个元素就会抛出I了legalStateException:Queue full.// System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("武松"));// 阻塞队列remove方法抛出异常演示System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());// 再往阻塞队列里remove一个元素就会抛出NoSuchElementExceptionSystem.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());}}
程序执行结果: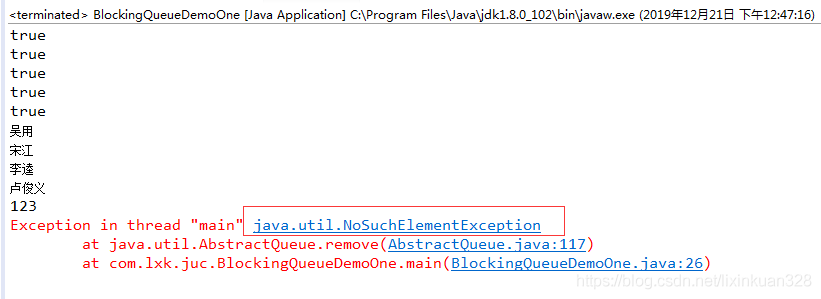
element检查方法:(底层调用了 peek()方法)
package com.lxk.juc;import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;/*** 当阻塞队列满时,再往队列里add元素会抛出IllegalStateException:Queue full.* 当阻塞队列空时,再往队列里remove元素会抛出NoSuchElementException.*/public class BlockingQueueDemoOne {public static void main(String[] args) {BlockingQueue blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue(5);// 阻塞队列add方法抛出异常演示System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("吴用"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("宋江"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("李逵"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("卢俊义"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("高俅"));// 检查队列队首元素是啥?或者检查队列是否为空。System.err.println(blockingQueue.element());}}
程序执行结果:(不存在,会抛NoSuchElementException异常)
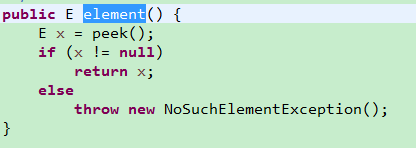
5.2、返回特殊值的方法(boolean值返回)
Demo One:阻塞队列offer方法的使用
package com.lxk.juc;import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;/*** 当阻塞队列满时,再往队列里offer元素会返回false.* 当阻塞队列空时,再往队列里poll元素会返回null.*/public class BlockingQueueDemoTwo {public static void main(String[] args) {BlockingQueue blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue(5);// 当阻塞队列满时,offer方法返回false演示System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("吴用"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("宋江"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("李逵"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("卢俊义"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("高俅"));// 此时再往阻塞队列offer一个元素就会返回falseSystem.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("武松"));}}
程序执行结果: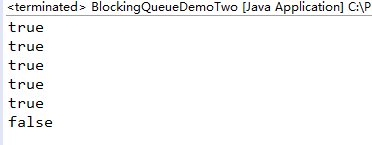
Demo Two:阻塞队列poll方法的使用
package com.lxk.juc;import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;/*** 当阻塞队列满时,再往队列里offer元素会返回false.* 当阻塞队列空时,再往队列里poll元素会返回null.*/public class BlockingQueueDemoTwo {public static void main(String[] args) {BlockingQueue blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue(5);// 当阻塞队列满时,offer方法返回false演示System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("吴用"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("宋江"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("李逵"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("卢俊义"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("高俅"));// 此时再往阻塞队列offer一个元素就会返回falseSystem.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("武松"));// 当阻塞队列为空时,poll方法返回null演示System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());// 此时再往阻塞队列执行poll一个元素就会返回nullSystem.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());}}
程序执行结果:
Demo Three:(peek()方法常用)
package com.lxk.juc;import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;/*** 当阻塞队列满时,再往队列里offer元素会返回false.* 当阻塞队列空时,再往队列里poll元素会返回null.*/public class BlockingQueueDemoTwo {public static void main(String[] args) {BlockingQueue blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue(5);System.out.println(blockingQueue.peek());// 当阻塞队列满时,offer方法返回false演示System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("吴用"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("宋江"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("李逵"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("卢俊义"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("高俅"));// peek方法返回阻塞队列队首元素,如果此阻塞队列为空,则返回为nullSystem.out.println(blockingQueue.peek());}}
测试结果: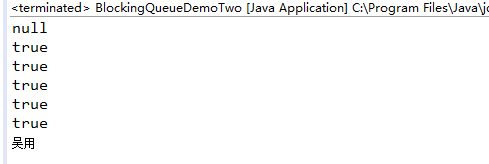
5.3、阻塞队列的方法
Demo One:阻塞队列put方法使用
package com.lxk.juc;import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;/*** 当阻塞队列满时,再往队列里put元素会阻塞队列.* 当阻塞队列空时,再往队列里take元素会阻塞队列.*/public class BlockingQueueDemoThree {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {BlockingQueue blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue(5);// 当阻塞队列满时,put方法会阻塞队列演示blockingQueue.put("吴用");blockingQueue.put("宋江");blockingQueue.put("李逵");blockingQueue.put("卢俊义");blockingQueue.put("高俅");//此时再往阻塞队列put一个元素时,会阻塞队列blockingQueue.put("武松");}}
程序执行结果:
Demo Two:阻塞队列take方法使用
package com.lxk.juc;import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;/*** * 当阻塞队列满时,再往队列里put元素会阻塞队列. * 当阻塞队列空时,再往队列里take元素会阻塞队列.*/public class BlockingQueueDemoThree {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {BlockingQueue blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue(5);// 当阻塞队列满时,put方法会阻塞队列演示blockingQueue.put("吴用");blockingQueue.put("宋江");blockingQueue.put("李逵");blockingQueue.put("卢俊义");blockingQueue.put("高俅");// 此时再往阻塞队列put一个元素时,会阻塞队列// blockingQueue.put("武松");// 当阻塞队列空时,take方法会阻塞队列演示System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());// 此时再往阻塞队列take一个元素时,会阻塞队列System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());}}
程序执行结果: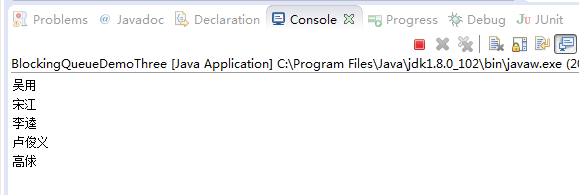
5.4、超时中断的方法
Demo One:阻塞队列offer超时中断演示
package com.lxk.juc;import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;/*** 当阻塞队列满时,再往队列里offer元素阻塞队列会超时中断.* 当阻塞队列空时,再往队列里poll元素阻塞队列会超时中断.*/public class BlockingQueueDemoFour {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {BlockingQueue blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue(5);// 当阻塞队列满时,offer方法执行超过3秒,阻塞队列会超时中断演示System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("吴用", 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS));System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("宋江", 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS));System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("李逵", 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS));System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("卢俊义", 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS));System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("高俅", 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS));//此时再往阻塞队列offer一个元素时,阻塞队列3秒后会超时中断System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("武松", 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS));}}
程序执行结果如下:当往阻塞队列添加第六个元素的时候,队列添加不进去,3秒后会超时中断。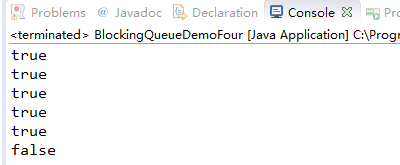
Demo Two:阻塞队列poll超时中断演示
package com.lxk.juc;import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;/*** 当阻塞队列满时,再往队列里offer元素阻塞队列会超时中断.* 当阻塞队列空时,再往队列里poll元素阻塞队列会超时中断.*/public class BlockingQueueDemoFour {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {BlockingQueue blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue(5);// 当阻塞队列满时,offer方法执行超过3秒,阻塞队列会超时中断演示System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("吴用", 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS));System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("宋江", 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS));System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("李逵", 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS));System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("卢俊义", 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS));System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("高俅", 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS));//此时再往阻塞队列offer一个元素时,阻塞队列3秒后会超时中断System.out.println("延时3秒。。。");System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("武松", 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS));// 当阻塞队列空时,poll方法执行超过3秒,阻塞队列会超时中断演示System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll(3,TimeUnit.SECONDS));System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll(3,TimeUnit.SECONDS));System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll(3,TimeUnit.SECONDS));System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll(3,TimeUnit.SECONDS));System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll(3,TimeUnit.SECONDS));// 此时再往阻塞队列poll一个元素时,超过3秒,阻塞队列会超时中断System.out.println("延时3秒。。。");System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll(3,TimeUnit.SECONDS));}}
程序执行结果: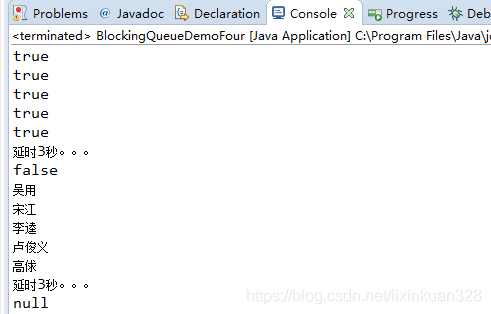
六、SychronousQueue类阻塞队列代码验证
程序执行结果如下:因为消费者线程每隔5秒钟取一个元素,所以生产者线程也是每隔5秒钟往Synchronous阻塞队列中添加一个元素。
package com.lxk.juc;import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;import java.util.concurrent.SynchronousQueue;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;/*** SynchronousBlocking是一个不存储元素的阻塞队列,即单个元素队列*/public class SynchronousQueueDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new SynchronousQueue<>();// 生产者线程进行put操作new Thread(() -> {try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t put one");blockingQueue.put("one");System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t put two");blockingQueue.put("two");System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t put three");blockingQueue.put("three");} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}, "t1").start();// 消费者线程进行take操作new Thread(()->{try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t take one");blockingQueue.take();TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t take two");blockingQueue.take();TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t take three");blockingQueue.take();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}},"t2").start();}}
测试结果:

