给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2]
输出:[2,1]
示例 3:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
可以遍历链表时,依次取出一个结点,放到新链表中,每次取出的结点都放在 dummy 节点和 头结点之间: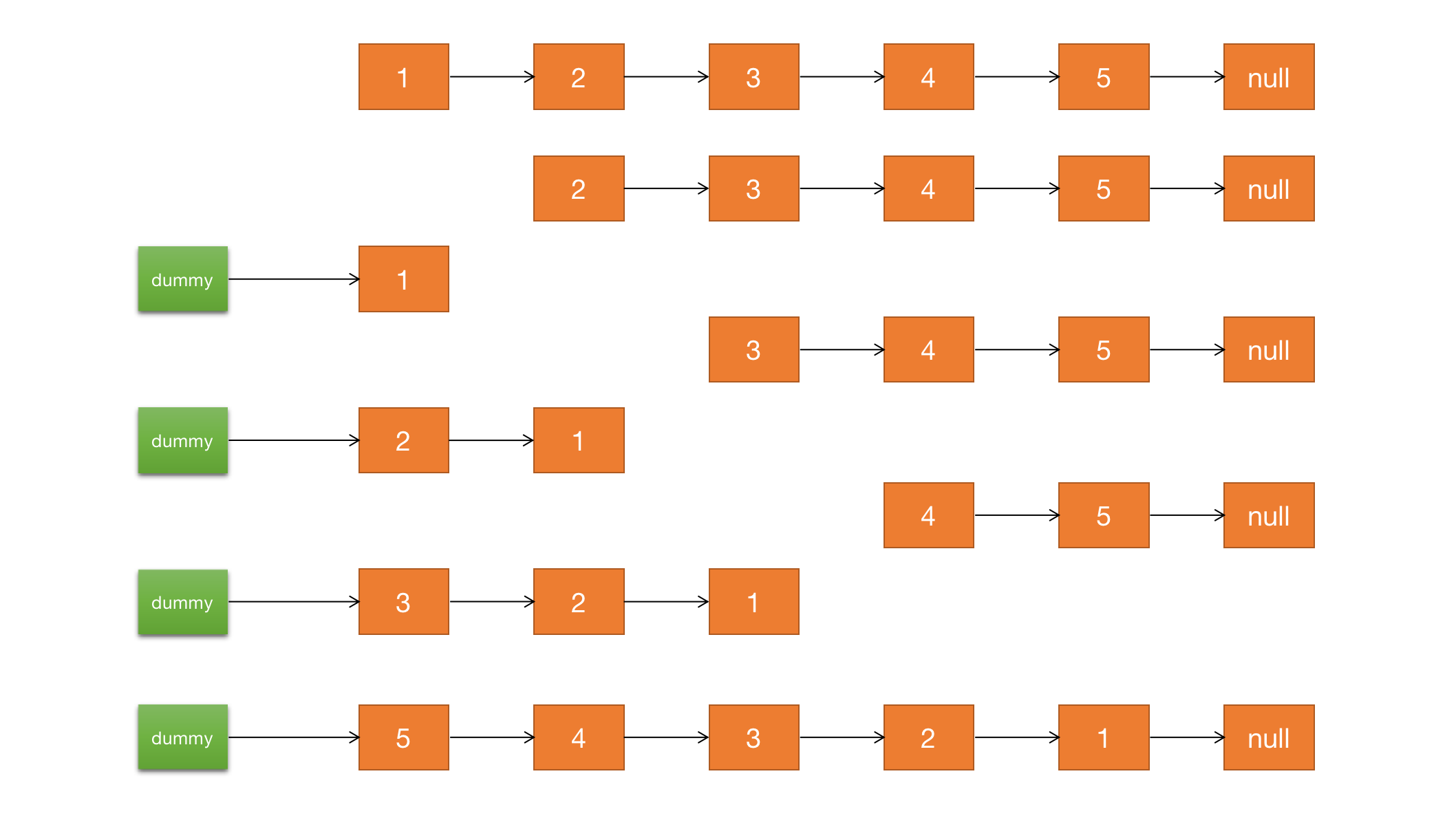
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {ListNode dummy = new ListNode();ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {// 记录 cur 下一次循环的指向结点ListNode nextNode = cur.next;// 将 cur 结点插入 dummy 和 头结点之间// 让 cur 的下一个结点指向 dummy 的下一个结点cur.next = dummy.next;// 让 dummy 的下一个节点指向 cur 节点dummy.next = cur;// cur 指向下一次循环的结点cur = nextNode;}return dummy.next;}
官方还提供了一种递归的思路!
假设需要反转链表: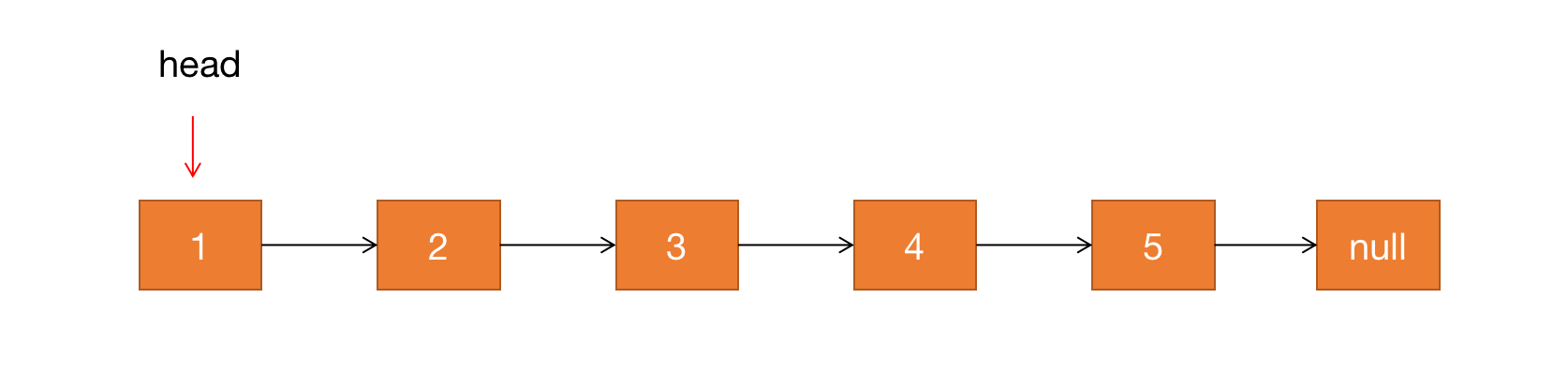
递归算法基础框架:
public ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {ListNode last = reverse(head.next);return last;}
代码 reverse(head.next);的效果是什么呢?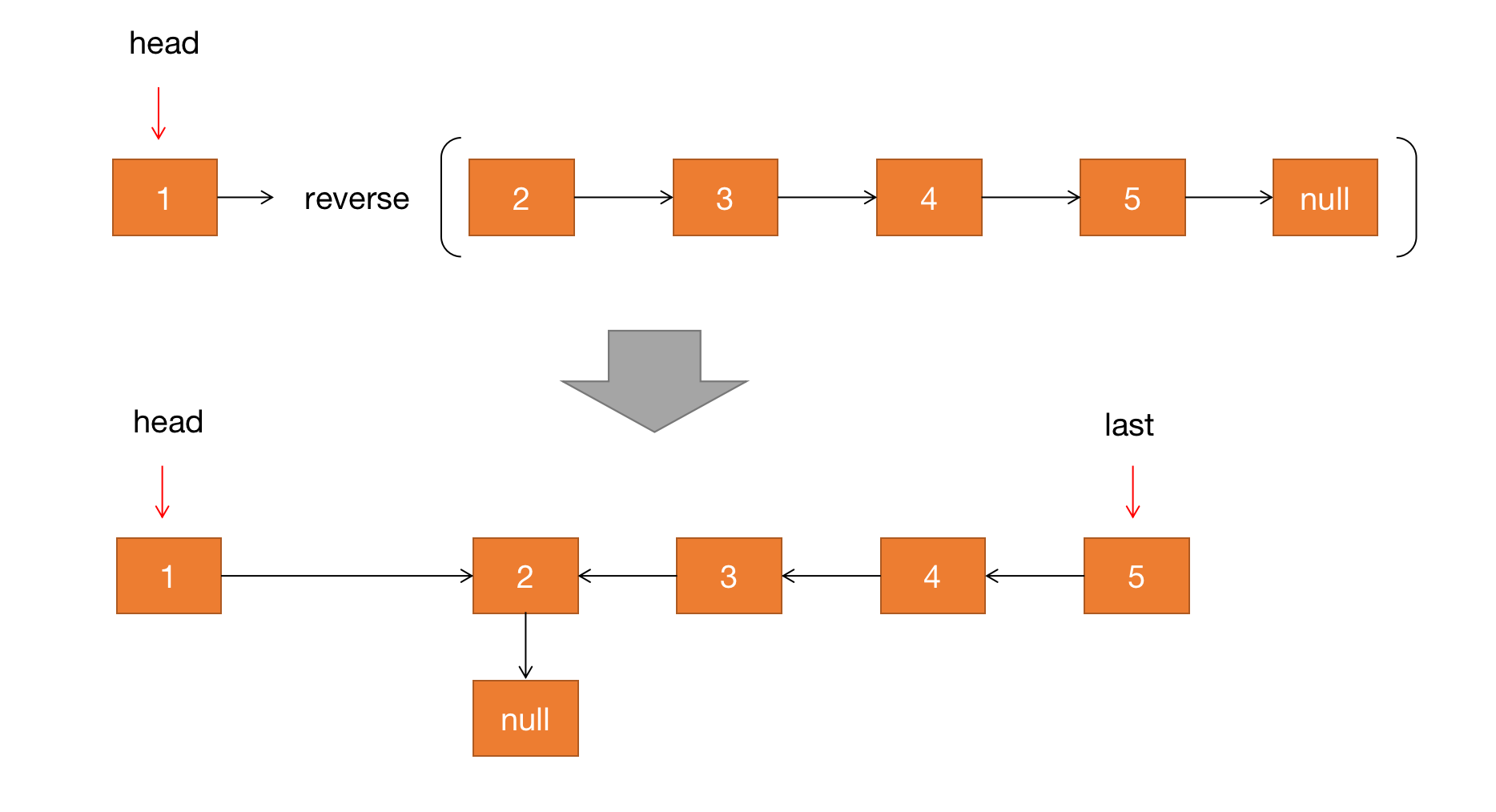
但是我们最终期望的结果是: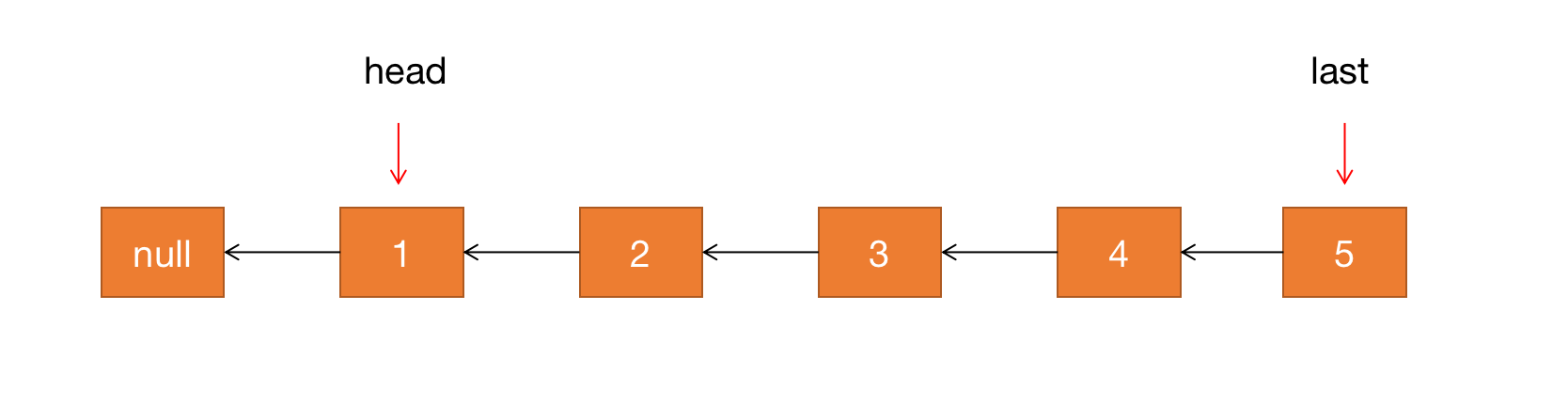
怎么才能变成最终期望的结果呢?
第一步:让 head 节点的下一个节点的 next 指针从指向 null 变成指向 head 节点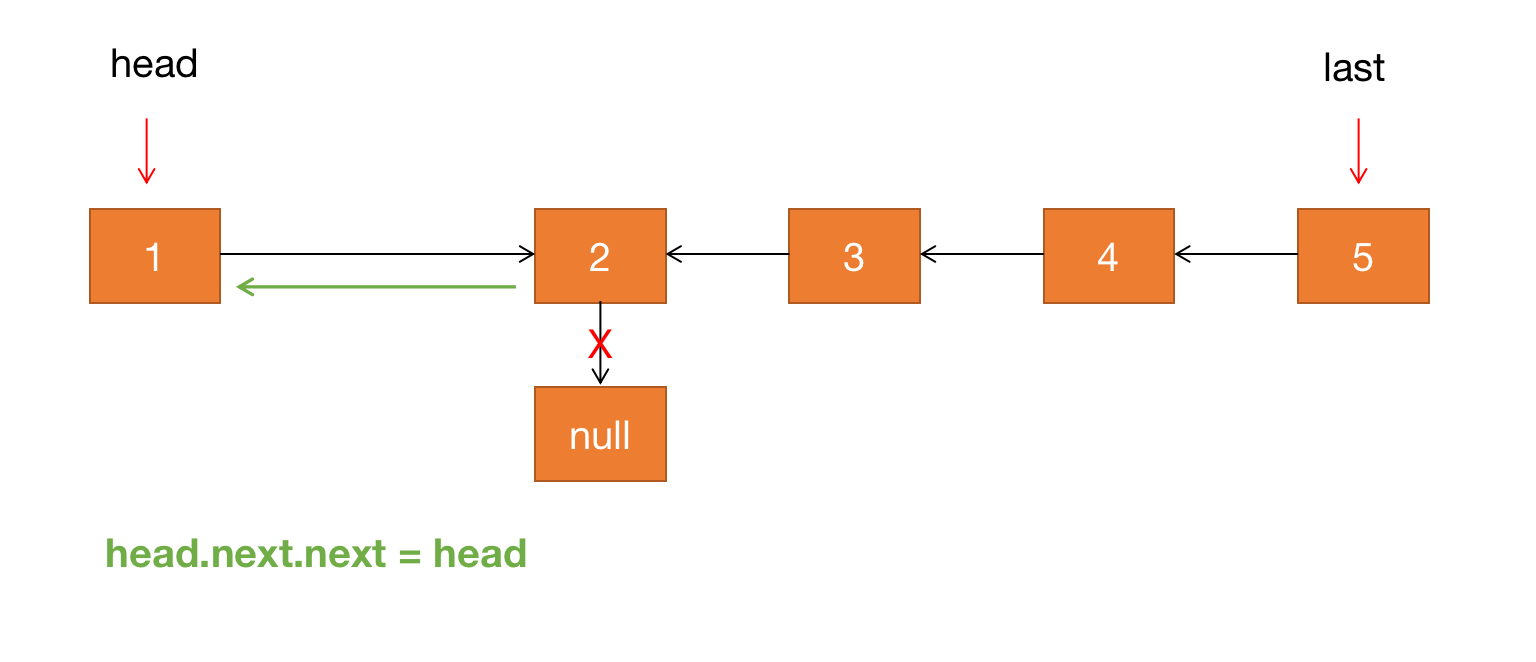
第二步:让 head 节点的 next 指针指向 null 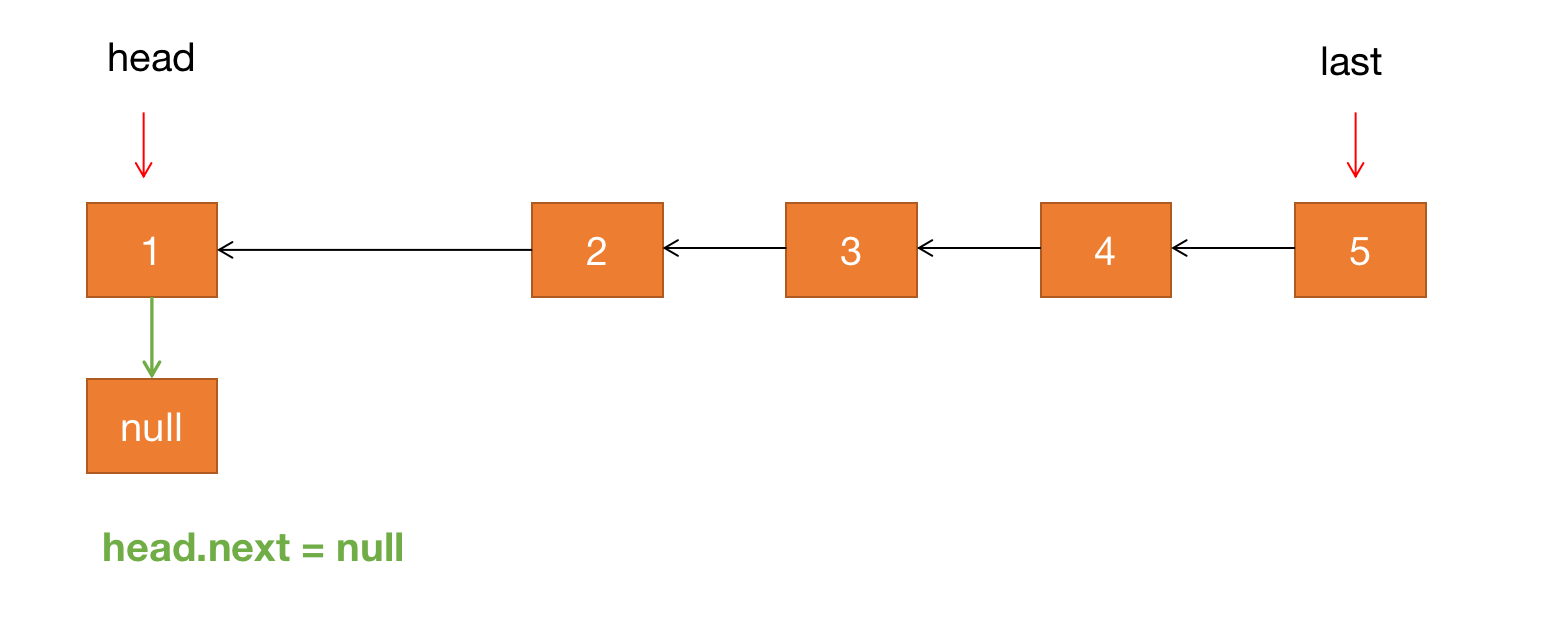
递归算法框架:
public ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {ListNode last = reverse(head.next);head.next.next = head;head.next = null;return last;}
那递归结束条件是什么呢?
如果 head 是空节点,那么肯定递归就结束了。
特别需要注意的是,如果链表只有一个节点,那么也无需进行反转,递归也可以结束
完整地递归算法:
public ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {if (head == null || head.next == null) {return head;}ListNode last = reverse(head.next);head.next.next = head;head.next = null;return last;}

