# API_常用部分.html#_1-composition-api-常用部分)1. Composition API(常用部分)
文档:
https://composition-api.vuejs.org/zh/api.html
# API_常用部分.html#_1-setup)1) setup
- 新的option, 所有的组合API函数都在此使用, 只在初始化时执行一次
函数如果返回对象, 对象中的属性或方法, 模板中可以直接使用
# API_常用部分.html#_2-ref)2) ref
作用: 定义一个数据的响应式
- 语法: const xxx = ref(initValue):
- 创建一个包含响应式数据的引用(reference)对象
- js中操作数据: xxx.value
- 模板中操作数据: 不需要.value
一般用来定义一个基本类型的响应式数据
<template> <h2>{{count}}</h2> <hr> <button @click="update">更新</button> </template> <script> import { ref } from 'vue' export default { /* 在Vue3中依然可以使用data和methods配置, 但建议使用其新语法实现 */ // data () { // return { // count: 0 // } // }, // methods: { // update () { // this.count++ // } // } /* 使用vue3的composition API */ setup () { // 定义响应式数据 ref对象 const count = ref(1) # 在模板中仍然可以使用一个 没有使用 ref 定义的 变量,但是没有响应式结果,修改值不会 及时更新在模板中,但是数据中的 值 确实被修改了 const gender = 1 console.log(count) // 更新响应式数据的函数 function update () { // alert('update') # 使用 xxx.value 更新 值 count.value = count.value + 1 } return { count, update } } } </script># API_常用部分.html#_3-reactive)3) reactive
作用: 定义多个数据的响应式
- const proxy = reactive(obj): 接收一个普通对象然后返回该普通对象的响应式代理器对象
- 响应式转换是“深层的”:会影响对象内部所有嵌套的属性
内部基于 ES6 的 Proxy 实现,通过代理对象操作源对象内部数据都是响应式的
<template> <h2>name: {{state.name}}</h2> <h2>age: {{state.age}}</h2> <h2>wife: {{state.wife}}</h2> <hr> <button @click="update">更新</button> </template> <script> /* reactive: 作用: 定义多个数据的响应式 const proxy = reactive(obj): 接收一个普通对象然后返回该普通对象的响应式代理器对象 响应式转换是“深层的”:会影响对象内部所有嵌套的属性 内部基于 ES6 的 Proxy 实现,通过代理对象操作源对象内部数据都是响应式的 */ import { reactive, } from 'vue' export default { setup () { /* 定义响应式数据对象 */ const state = reactive({ name: 'tom', age: 25, wife: { name: 'marry', age: 22 }, }) console.log(state, state.wife) const update = () => { state.name += '--' state.age += 1 state.wife.name += '++' state.wife.age += 2 } return { state, update, } } } </script># API_常用部分.html#_4-比较vue2与vue3的响应式-重要)4) 比较Vue2与Vue3的响应式(重要)
# API_常用部分.html#vue2的响应式)vue2的响应式
核心:
- 对象: 通过defineProperty对对象的已有属性值的读取和修改进行劫持(监视/拦截)
- 数组: 通过重写数组更新数组一系列更新元素的方法来实现元素修改的劫持
Object.defineProperty(data, 'count', { get () {}, set () {} })
问题
- 对象直接新添加的属性或删除已有属性, 界面不会自动更新
- 直接通过下标替换元素或更新length, 界面不会自动更新 arr[1] = {}
# API_常用部分.html#vue3的响应式)Vue3的响应式
核心:
- 通过Proxy(代理): 拦截对data任意属性的任意(13种)操作, 包括属性值的读写, 属性的添加, 属性的删除等…
- 通过 Reflect(反射): 动态对被代理对象的相应属性进行特定的操作
文档:
- https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Proxy
- https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Reflect
```js
new Proxy(data, {
// 拦截读取属性值
get (target, prop) {
return Reflect.get(target, prop)
},
// 拦截设置属性值或添加新属性
set (target, prop, value) {
return Reflect.set(target, prop, value)
},
// 拦截删除属性
deleteProperty (target, prop) {
return Reflect.deleteProperty(target, prop)
}
})
proxy.name = ‘tom’
<!DOCTYPE html> ```# API_常用部分.html#_5-setup细节)5) setup细节
setup执行的时机
- 在beforeCreate之前执行(一次), 此时组件对象还没有创建
- this是undefined, 不能通过this来访问data/computed/methods / props
- 其实所有的composition API相关回调函数中也都不可以
- setup的返回值
- 一般都返回一个对象: 为模板提供数据, 也就是模板中可以直接使用此对象中的所有属性/方法
- 返回对象中的属性会与data函数返回对象的属性合并成为组件对象的属性
- 返回对象中的方法会与methods中的方法合并成功组件对象的方法
- 如果有重名, setup优先
- 注意:
- 一般不要混合使用: methods中可以访问setup提供的属性和方法, 但在setup方法中不能访问data和methods
- setup不能是一个async函数: 因为返回值不再是return的对象, 而是promise, 模板看不到return对象中的属性数据
setup的参数
- setup(props, context) / setup(props, {attrs, slots, emit})
- props: 包含props配置声明且传入了的所有属性的对象
- attrs: 包含没有在props配置中声明的属性的对象, 相当于 this.$attrs
- slots: 包含所有传入的插槽内容的对象, 相当于 this.$slots
- emit: 用来分发自定义事件的函数, 相当于 this.$emit
<template> <h2>App</h2> <p>msg: {{msg}}</p> <button @click="fn('--')">更新</button> <child :msg="msg" msg2="cba" @fn="fn"/> </template> <script lang="ts"> import { reactive, ref, } from 'vue' import child from './child.vue' export default { components: { child }, setup () { const msg = ref('abc') function fn (content: string) { msg.value += content } return { msg, fn } } } </script> <template> <div> <h3>{{n}}</h3> <h3>{{m}}</h3> <h3>msg: {{msg}}</h3> <h3>msg2: {{$attrs.msg2}}</h3> <slot name="xxx"></slot> <button @click="update">更新</button> </div> </template> <script lang="ts"> import { ref, defineComponent } from 'vue' export default defineComponent({ name: 'child', props: ['msg'], emits: ['fn'], // 可选的, 声明了更利于程序员阅读, 且可以对分发的事件数据进行校验 data () { console.log('data', this) return { // n: 1 } }, beforeCreate () { console.log('beforeCreate', this) }, methods: { // update () { // this.n++ // this.m++ // } }, // setup (props, context) { setup (props, {attrs, emit, slots}) { console.log('setup', this) console.log(props.msg, attrs.msg2, slots, emit) const m = ref(2) const n = ref(3) function update () { // console.log('--', this) // this.n += 2 // this.m += 2 m.value += 2 n.value += 2 // 分发自定义事件 emit('fn', '++') } return { m, n, update, } }, }) </script># API_常用部分.html#_6-reactive与ref-细节)6) reactive与ref-细节
是Vue3的 composition API中2个最重要的响应式API
- ref用来处理基本类型数据, reactive用来处理对象(递归深度响应式)
- 如果用ref对象/数组, 内部会自动将对象/数组转换为reactive的代理对象
- ref内部: 通过给value属性添加getter/setter来实现对数据的劫持
- reactive内部: 通过使用Proxy来实现对对象内部所有数据的劫持, 并通过Reflect操作对象内部数据
ref的数据操作: 在js中要.value, 在模板中不需要(内部解析模板时会自动添加.value)
<template> <h2>App</h2> <p>m1: {{m1}}</p> <p>m2: {{m2}}</p> <p>m3: {{m3}}</p> <button @click="update">更新</button> </template> <script lang="ts"> import { reactive, ref } from 'vue' export default { setup () { const m1 = ref('abc') const m2 = reactive({x: 1, y: {z: 'abc'}}) // 使用ref处理对象 ==> 对象会被自动reactive为proxy对象 const m3 = ref({a1: 2, a2: {a3: 'abc'}}) console.log(m1, m2, m3) console.log(m3.value.a2) // 也是一个proxy对象 function update() { m1.value += '--' m2.x += 1 m2.y.z += '++' m3.value = {a1: 3, a2: {a3: 'abc---'}} m3.value.a2.a3 += '==' // reactive对对象进行了深度数据劫持 console.log(m3.value.a2) } return { m1, m2, m3, update } } } </script># API_常用部分.html#_7-计算属性与监视)7) 计算属性与监视
computed函数:
- 与computed配置功能一致
- 只有getter
- 有getter和setter
- watch函数
- 与watch配置功能一致
- 监视指定的一个或多个响应式数据, 一旦数据变化, 就自动执行监视回调
- 默认初始时不执行回调, 但可以通过配置immediate为true, 来指定初始时立即执行第一次
- 通过配置deep为true, 来指定深度监视
- watchEffect函数
- 不用直接指定要监视的数据, 回调函数中使用的哪些响应式数据就监视哪些响应式数据
- 默认初始时就会执行第一次, 从而可以收集需要监视的数据
- 监视数据发生变化时回调
```vue
App
fistName:
lastName:
fullName1:
fullName2:
fullName3:
```# API_常用部分.html#_8-生命周期)8) 生命周期
vue2.x的生命周期
vue3的生命周期
与 2.x 版本生命周期相对应的组合式 API beforeCreate-> 使用setup()created-> 使用setup()beforeMount->onBeforeMountmounted->onMountedbeforeUpdate->onBeforeUpdateupdated->onUpdatedbeforeDestroy->onBeforeUnmountdestroyed->onUnmountederrorCaptured->onErrorCaptured- onRenderTracked
onRenderTriggered
<template> <div class="about"> <h2>msg: {{msg}}</h2> <hr> <button @click="update">更新</button> </div> </template> <script lang="ts"> import { ref, onMounted, onUpdated, onUnmounted, onBeforeMount, onBeforeUpdate, onBeforeUnmount } from "vue" export default { beforeCreate () { console.log('beforeCreate()') }, created () { console.log('created') }, beforeMount () { console.log('beforeMount') }, mounted () { console.log('mounted') }, beforeUpdate () { console.log('beforeUpdate') }, updated () { console.log('updated') }, beforeUnmount () { console.log('beforeUnmount') }, unmounted () { console.log('unmounted') }, setup() { const msg = ref('abc') const update = () => { msg.value += '--' } onBeforeMount(() => { console.log('--onBeforeMount') }) onMounted(() => { console.log('--onMounted') }) onBeforeUpdate(() => { console.log('--onBeforeUpdate') }) onUpdated(() => { console.log('--onUpdated') }) onBeforeUnmount(() => { console.log('--onBeforeUnmount') }) onUnmounted(() => { console.log('--onUnmounted') }) return { msg, update } } } </script> <template> <h2>App</h2> <button @click="isShow=!isShow">切换</button> <hr> <Child v-if="isShow"/> </template> <script lang="ts"> import Child from './Child.vue' export default { data () { return { isShow: true } }, components: { Child } } </script># API_常用部分.html#_09-自定义hook函数)09) 自定义hook函数
使用Vue3的组合API封装的可复用的功能函数
- 自定义hook的作用类似于vue2中的mixin技术
- 自定义Hook的优势: 很清楚复用功能代码的来源, 更清楚易懂
需求1: 收集用户鼠标点击的页面坐标
hooks/useMousePosition.tsimport { ref, onMounted, onUnmounted } from 'vue' /* 收集用户鼠标点击的页面坐标 */ export default function useMousePosition () { // 初始化坐标数据 const x = ref(-1) const y = ref(-1) // 用于收集点击事件坐标的函数 const updatePosition = (e: MouseEvent) => { x.value = e.pageX y.value = e.pageY } // 挂载后绑定点击监听 onMounted(() => { document.addEventListener('click', updatePosition) }) // 卸载前解绑点击监听 onUnmounted(() => { document.removeEventListener('click', updatePosition) }) return {x, y} } <template> <div> <h2>x: {{x}}, y: {{y}}</h2> </div> </template> <script> import { ref } from "vue" /* 在组件中引入并使用自定义hook 自定义hook的作用类似于vue2中的mixin技术 自定义Hook的优势: 很清楚复用功能代码的来源, 更清楚易懂 */ import useMousePosition from './hooks/useMousePosition' export default { setup() { const {x, y} = useMousePosition() return { x, y, } } } </script>利用TS泛型强化类型检查
需求2: 封装发ajax请求的hook函数
hooks/useRequest.tsimport { ref } from 'vue' import axios from 'axios' /* 使用axios发送异步ajax请求 */ export default function useUrlLoader<T>(url: string) { const result = ref<T | null>(null) const loading = ref(true) const errorMsg = ref(null) axios.get(url) .then(response => { loading.value = false result.value = response.data }) .catch(e => { loading.value = false errorMsg.value = e.message || '未知错误' }) return { loading, result, errorMsg, } } <template> <div class="about"> <h2 v-if="loading">LOADING...</h2> <h2 v-else-if="errorMsg">{{errorMsg}}</h2> <!-- <ul v-else> <li>id: {{result.id}}</li> <li>name: {{result.name}}</li> <li>distance: {{result.distance}}</li> </ul> --> <ul v-for="p in result" :key="p.id"> <li>id: {{p.id}}</li> <li>title: {{p.title}}</li> <li>price: {{p.price}}</li> </ul> <!-- <img v-if="result" :src="result[0].url" alt=""> --> </div> </template> <script lang="ts"> import { watch } from "vue" import useRequest from './hooks/useRequest' // 地址数据接口 interface AddressResult { id: number; name: string; distance: string; } // 产品数据接口 interface ProductResult { id: string; title: string; price: number; } export default { setup() { // const {loading, result, errorMsg} = useRequest<AddressResult>('/data/address.json') const {loading, result, errorMsg} = useRequest<ProductResult[]>('/data/products.json') watch(result, () => { if (result.value) { console.log(result.value.length) // 有提示 } }) return { loading, result, errorMsg } } } </script># API_常用部分.html#_10-torefs)10) toRefs
把一个响应式对象转换成普通对象,该普通对象的每个 property 都是一个 ref
应用: 当从合成函数返回响应式对象时,toRefs 非常有用,这样消费组件就可以在不丢失响应式的情况下对返回的对象进行分解使用
问题: reactive 对象取出的所有属性值都是非响应式的
解决: 利用 toRefs 可以将一个响应式 reactive 对象的所有原始属性转换为响应式的 ref 属性<template> <h2>App</h2> <h3>foo: {{foo}}</h3> <h3>bar: {{bar}}</h3> <h3>foo2: {{foo2}}</h3> <h3>bar2: {{bar2}}</h3> </template> <script lang="ts"> import { reactive, toRefs } from 'vue' /* toRefs: 将响应式对象中所有属性包装为ref对象, 并返回包含这些ref对象的普通对象 应用: 当从合成函数返回响应式对象时,toRefs 非常有用, 这样消费组件就可以在不丢失响应式的情况下对返回的对象进行分解使用 */ export default { setup () { const state = reactive({ foo: 'a', bar: 'b', }) const stateAsRefs = toRefs(state) setTimeout(() => { state.foo += '++' state.bar += '++' }, 2000); const {foo2, bar2} = useReatureX() return { // ...state, ...stateAsRefs, foo2, bar2 } }, } function useReatureX() { const state = reactive({ foo2: 'a', bar2: 'b', }) setTimeout(() => { state.foo2 += '++' state.bar2 += '++' }, 2000); return toRefs(state) } </script># API_常用部分.html#_11-ref获取元素)11) ref获取元素
利用ref函数获取组件中的标签元素
功能需求: 让输入框自动获取焦点<template> <h2>App</h2> <input type="text">--- <input type="text" ref="inputRef"> </template> <script lang="ts"> import { onMounted, ref } from 'vue' /* ref获取元素: 利用ref函数获取组件中的标签元素 功能需求: 让输入框自动获取焦点 */ export default { setup() { const inputRef = ref<HTMLElement|null>(null) onMounted(() => { inputRef.value && inputRef.value.focus() }) return { inputRef } }, } </script># API_其它部分.html#_2-composition-api-其它部分)2. Composition API(其它部分)
# API_其它部分.html#_1-shallowreactive-与-shallowref)1) shallowReactive 与 shallowRef
shallowReactive : 只处理了对象内最外层属性的响应式(也就是浅响应式)
- shallowRef: 只处理了value的响应式, 不进行对象的reactive处理
什么时候用浅响应式呢?
- 一般情况下使用ref和reactive即可
- 如果有一个对象数据, 结构比较深, 但变化时只是外层属性变化 ===> shallowReactive
- 如果有一个对象数据, 后面会产生新的对象来替换 ===> shallowRef
<template> <h2>App</h2> <h3>m1: {{m1}}</h3> <h3>m2: {{m2}}</h3> <h3>m3: {{m3}}</h3> <h3>m4: {{m4}}</h3> <button @click="update">更新</button> </template> <script lang="ts"> import { reactive, ref, shallowReactive, shallowRef } from 'vue' /* shallowReactive与shallowRef shallowReactive: 只处理了对象内最外层属性的响应式(也就是浅响应式) shallowRef: 只处理了value的响应式, 不进行对象的reactive处理 总结: reactive与ref实现的是深度响应式, 而shallowReactive与shallowRef是浅响应式 什么时候用浅响应式呢? 一般情况下使用ref和reactive即可, 如果有一个对象数据, 结构比较深, 但变化时只是外层属性变化 ===> shallowReactive 如果有一个对象数据, 后面会产生新的对象来替换 ===> shallowRef */ export default { setup () { const m1 = reactive({a: 1, b: {c: 2}}) const m2 = shallowReactive({a: 1, b: {c: 2}}) const m3 = ref({a: 1, b: {c: 2}}) const m4 = shallowRef({a: 1, b: {c: 2}}) const update = () => { // m1.b.c += 1 // m2.b.c += 1 // m3.value.a += 1 m4.value.a += 1 } return { m1, m2, m3, m4, update, } } } </script># API_其它部分.html#_2-readonly-与-shallowreadonly)2) readonly 与 shallowReadonly
readonly:
- 深度只读数据
- 获取一个对象 (响应式或纯对象) 或 ref 并返回原始代理的只读代理。
- 只读代理是深层的:访问的任何嵌套 property 也是只读的。
- shallowReadonly
- 浅只读数据
- 创建一个代理,使其自身的 property 为只读,但不执行嵌套对象的深度只读转换
应用场景:
在某些特定情况下, 我们可能不希望对数据进行更新的操作, 那就可以包装生成一个只读代理对象来读取数据, 而不能修改或删除
<template> <h2>App</h2> <h3>{{state}}</h3> <button @click="update">更新</button> </template> <script lang="ts"> import { reactive, readonly, shallowReadonly } from 'vue' /* readonly: 深度只读数据 获取一个对象 (响应式或纯对象) 或 ref 并返回原始代理的只读代理。 只读代理是深层的:访问的任何嵌套 property 也是只读的。 shallowReadonly: 浅只读数据 创建一个代理,使其自身的 property 为只读,但不执行嵌套对象的深度只读转换 应用场景: 在某些特定情况下, 我们可能不希望对数据进行更新的操作, 那就可以包装生成一个只读代理对象来读取数据, 而不能修改或删除 */ export default { setup () { const state = reactive({ a: 1, b: { c: 2 } }) // const rState1 = readonly(state) const rState2 = shallowReadonly(state) const update = () => { // rState1.a++ // error // rState1.b.c++ // error // rState2.a++ // error rState2.b.c++ } return { state, update } } } </script># API_其它部分.html#_3-toraw-与-markraw)3) toRaw 与 markRaw
toRaw
- 返回由
reactive或readonly方法转换成响应式代理的普通对象。 - 这是一个还原方法,可用于临时读取,访问不会被代理/跟踪,写入时也不会触发界面更新。
- 返回由
markRaw
- 标记一个对象,使其永远不会转换为代理。返回对象本身
- 应用场景:
- 有些值不应被设置为响应式的,例如复杂的第三方类实例或 Vue 组件对象。
- 当渲染具有不可变数据源的大列表时,跳过代理转换可以提高性能。
<template> <h2>{{state}}</h2> <button @click="testToRaw">测试toRaw</button> <button @click="testMarkRaw">测试markRaw</button> </template> <script lang="ts"> /* toRaw: 得到reactive代理对象的目标数据对象 */ import { markRaw, reactive, toRaw, } from 'vue' export default { setup () { const state = reactive<any>({ name: 'tom', age: 25, }) const testToRaw = () => { const user = toRaw(state) user.age++ // 界面不会更新 } const testMarkRaw = () => { const likes = ['a', 'b'] // state.likes = likes state.likes = markRaw(likes) // likes数组就不再是响应式的了 setTimeout(() => { state.likes[0] += '--' }, 1000) } return { state, testToRaw, testMarkRaw, } } } </script># API_其它部分.html#_4-toref)4) toRef
为源响应式对象上的某个属性创建一个 ref对象, 二者内部操作的是同一个数据值, 更新时二者是同步的
- 区别ref: 拷贝了一份新的数据值单独操作, 更新时相互不影响
应用: 当要将 某个prop 的 ref 传递给复合函数时,toRef 很有用
<template> <h2>App</h2> <p>{{state}}</p> <p>{{foo}}</p> <p>{{foo2}}</p> <button @click="update">更新</button> <Child :foo="foo"/> </template> <script lang="ts"> /* toRef: 为源响应式对象上的某个属性创建一个 ref对象, 二者内部操作的是同一个数据值, 更新时二者是同步的 区别ref: 拷贝了一份新的数据值单独操作, 更新时相互不影响 应用: 当要将某个 prop 的 ref 传递给复合函数时,toRef 很有用 */ import { reactive, toRef, ref, } from 'vue' import Child from './Child.vue' export default { setup () { const state = reactive({ foo: 1, bar: 2 }) const foo = toRef(state, 'foo') const foo2 = ref(state.foo) const update = () => { state.foo++ // foo.value++ // foo2.value++ // foo和state中的数据不会更新 } return { state, foo, foo2, update, } }, components: { Child } } </script> <template> <h2>Child</h2> <h3>{{foo}}</h3> <h3>{{length}}</h3> </template> <script lang="ts"> import { computed, defineComponent, Ref, toRef } from 'vue' const component = defineComponent({ props: { foo: { type: Number, require: true } }, setup (props, context) { const length = useFeatureX(toRef(props, 'foo')) return { length } } }) function useFeatureX(foo: Ref) { const lenth = computed(() => foo.value.length) return lenth } export default component </script># API_其它部分.html#_5-customref)5) customRef
创建一个自定义的 ref,并对其依赖项跟踪和更新触发进行显式控制
需求: 使用 customRef 实现 debounce 的示例
<template> <h2>App</h2> <input v-model="keyword" placeholder="搜索关键字"/> <p>{{keyword}}</p> </template> <script lang="ts"> /* customRef: 创建一个自定义的 ref,并对其依赖项跟踪和更新触发进行显式控制 需求: 使用 customRef 实现 debounce 的示例 */ import { ref, customRef } from 'vue' export default { setup () { const keyword = useDebouncedRef('', 500) console.log(keyword) return { keyword } }, } /* 实现函数防抖的自定义ref */ function useDebouncedRef<T>(value: T, delay = 200) { let timeout: number return customRef((track, trigger) => { return { get() { // 告诉Vue追踪数据 track() return value }, set(newValue: T) { clearTimeout(timeout) timeout = setTimeout(() => { value = newValue // 告诉Vue去触发界面更新 trigger() }, delay) } } }) } </script># API_其它部分.html#_6-provide-与-inject)6) provide 与 inject
provide
和inject提供依赖注入,功能类似 2.x 的provide/inject实现跨层级组件(祖孙)间通信 ```vue
父组件
当前颜色: {{color}}
子组件
孙子组件: {{color}}
<a name="xQ6bo"></a> ## [#]([https://24kcs.github.io/vue3_study/chapter4/02_Composition](https://24kcs.github.io/vue3_study/chapter4/02_Composition) API_其它部分.html#_7-响应式数据的判断)7) 响应式数据的判断 - isRef: 检查一个值是否为一个 ref 对象 - isReactive: 检查一个对象是否是由 `reactive` 创建的响应式代理 - isReadonly: 检查一个对象是否是由 `readonly` 创建的只读代理 - isProxy: 检查一个对象是否是由 `reactive` 或者 `readonly` 方法创建的代理 <a name="t7IU2"></a> # [#](https://24kcs.github.io/vue3_study/chapter4/03_%E6%89%8B%E5%86%99%E7%BB%84%E5%90%88API.html#_3-%E6%89%8B%E5%86%99%E7%BB%84%E5%90%88api)3. 手写组合API <a name="IdKk9"></a> ## [#](https://24kcs.github.io/vue3_study/chapter4/03_%E6%89%8B%E5%86%99%E7%BB%84%E5%90%88API.html#_1-shallowreactive-%E4%B8%8E-reactive)1) shallowReactive 与 reactive ```js const reactiveHandler = { get (target, key) { if (key==='_is_reactive') return true return Reflect.get(target, key) }, set (target, key, value) { const result = Reflect.set(target, key, value) console.log('数据已更新, 去更新界面') return result }, deleteProperty (target, key) { const result = Reflect.deleteProperty(target, key) console.log('数据已删除, 去更新界面') return result }, } /* 自定义shallowReactive */ function shallowReactive(obj) { return new Proxy(obj, reactiveHandler) } /* 自定义reactive */ function reactive (target) { if (target && typeof target==='object') { if (target instanceof Array) { // 数组 target.forEach((item, index) => { target[index] = reactive(item) }) } else { // 对象 Object.keys(target).forEach(key => { target[key] = reactive(target[key]) }) } const proxy = new Proxy(target, reactiveHandler) return proxy } return target } /* 测试自定义shallowReactive */ const proxy = shallowReactive({ a: { b: 3 } }) proxy.a = {b: 4} // 劫持到了 proxy.a.b = 5 // 没有劫持到 /* 测试自定义reactive */ const obj = { a: 'abc', b: [{x: 1}], c: {x: [11]}, } const proxy = reactive(obj) console.log(proxy) proxy.b[0].x += 1 proxy.c.x[0] += 1#2) shallowRef 与 ref
/* 自定义shallowRef */ function shallowRef(target) { const result = { _value: target, // 用来保存数据的内部属性 _is_ref: true, // 用来标识是ref对象 get value () { return this._value }, set value (val) { this._value = val console.log('set value 数据已更新, 去更新界面') } } return result } /* 自定义ref */ function ref(target) { if (target && typeof target==='object') { target = reactive(target) } const result = { _value: target, // 用来保存数据的内部属性 _is_ref: true, // 用来标识是ref对象 get value () { return this._value }, set value (val) { this._value = val console.log('set value 数据已更新, 去更新界面') } } return result } /* 测试自定义shallowRef */ const ref3 = shallowRef({ a: 'abc', }) ref3.value = 'xxx' ref3.value.a = 'yyy' /* 测试自定义ref */ const ref1 = ref(0) const ref2 = ref({ a: 'abc', b: [{x: 1}], c: {x: [11]}, }) ref1.value++ ref2.value.b[0].x++ console.log(ref1, ref2)#3) shallowReadonly 与 readonly
const readonlyHandler = { get (target, key) { if (key==='_is_readonly') return true return Reflect.get(target, key) }, set () { console.warn('只读的, 不能修改') return true }, deleteProperty () { console.warn('只读的, 不能删除') return true }, } /* 自定义shallowReadonly */ function shallowReadonly(obj) { return new Proxy(obj, readonlyHandler) } /* 自定义readonly */ function readonly(target) { if (target && typeof target==='object') { if (target instanceof Array) { // 数组 target.forEach((item, index) => { target[index] = readonly(item) }) } else { // 对象 Object.keys(target).forEach(key => { target[key] = readonly(target[key]) }) } const proxy = new Proxy(target, readonlyHandler) return proxy } return target } /* 测试自定义readonly */ /* 测试自定义shallowReadonly */ const objReadOnly = readonly({ a: { b: 1 } }) const objReadOnly2 = shallowReadonly({ a: { b: 1 } }) objReadOnly.a = 1 objReadOnly.a.b = 2 objReadOnly2.a = 1 objReadOnly2.a.b = 2#4) isRef, isReactive 与 isReadonly
/* 判断是否是ref对象 */ function isRef(obj) { return obj && obj._is_ref } /* 判断是否是reactive对象 */ function isReactive(obj) { return obj && obj._is_reactive } /* 判断是否是readonly对象 */ function isReadonly(obj) { return obj && obj._is_readonly } /* 是否是reactive或readonly产生的代理对象 */ function isProxy (obj) { return isReactive(obj) || isReadonly(obj) } /* 测试判断函数 */ console.log(isReactive(reactive({}))) console.log(isRef(ref({}))) console.log(isReadonly(readonly({}))) console.log(isProxy(reactive({}))) console.log(isProxy(readonly({})))# VS Option.html#_4-composition-api-vs-option-api)4. Composition API VS Option API
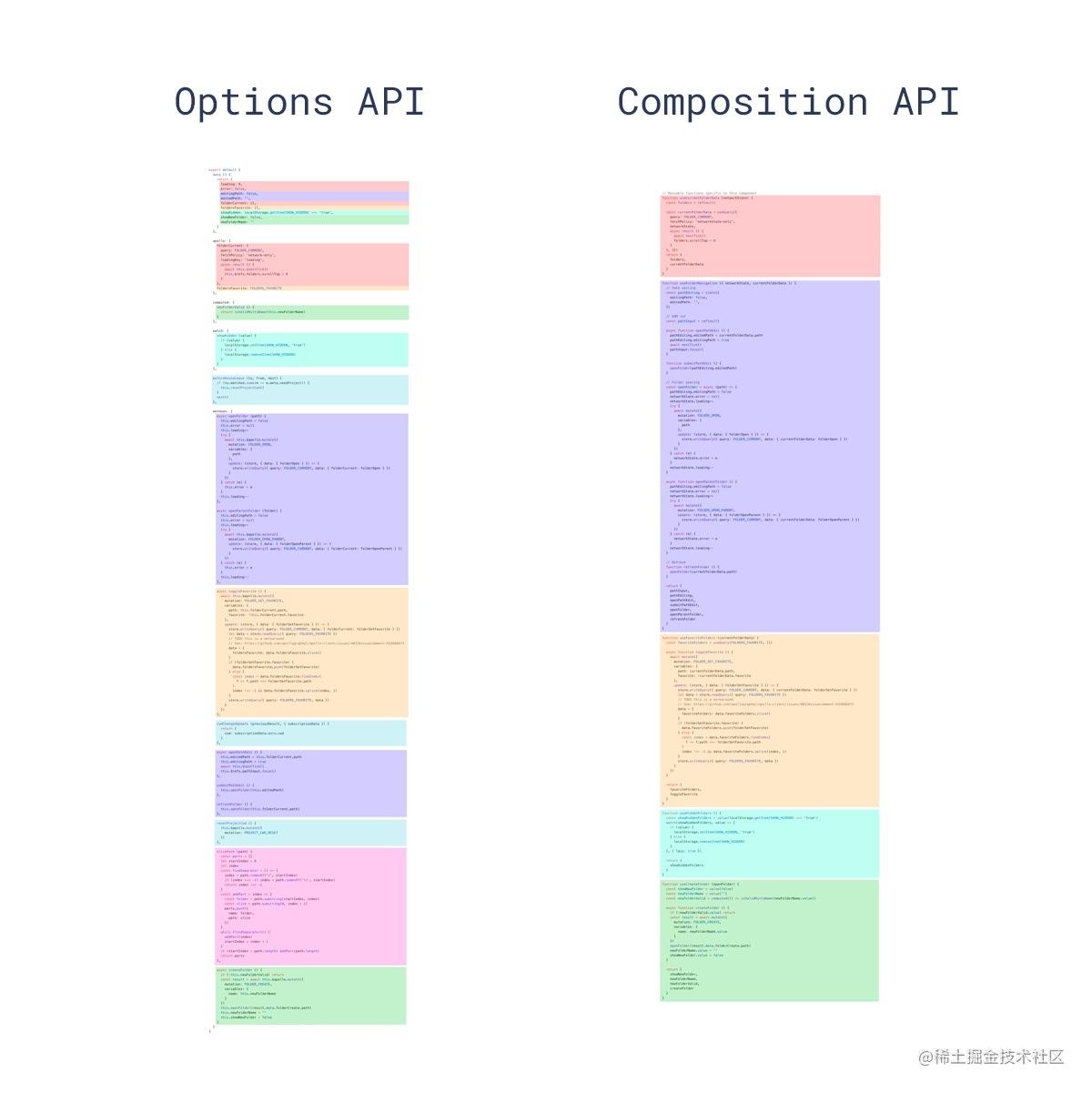
# VS Option.html#_1-option-api的问题)1) Option API的问题
- 在传统的Vue OptionsAPI中,新增或者修改一个需求,就需要分别在data,methods,computed里修改 ,滚动条反复上下移动
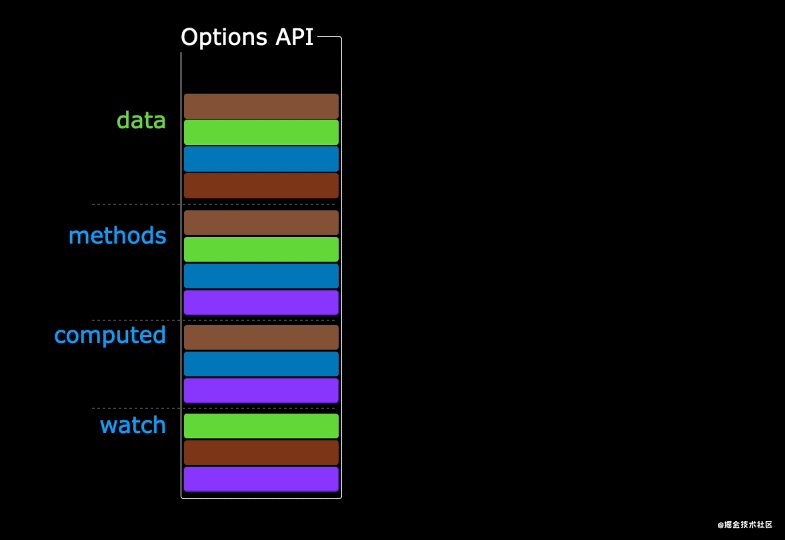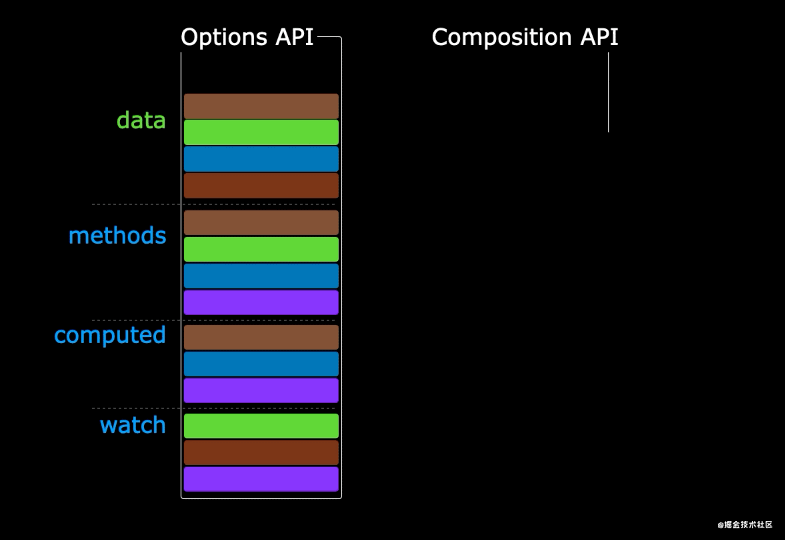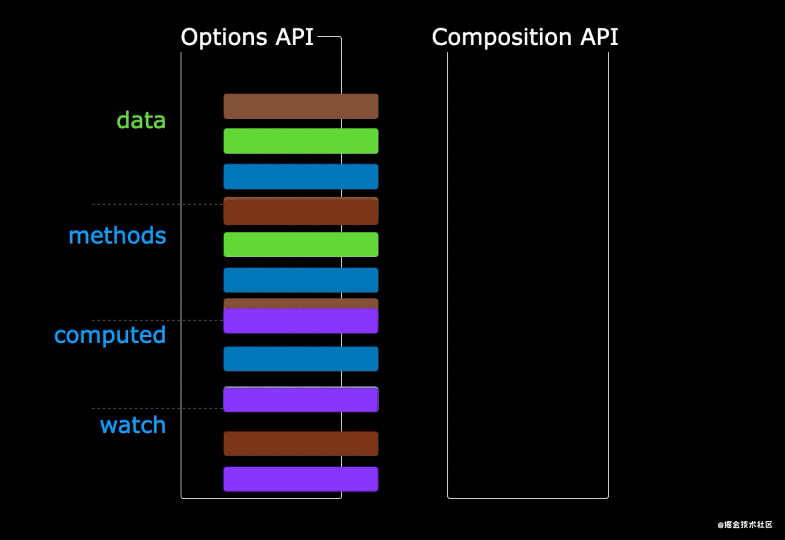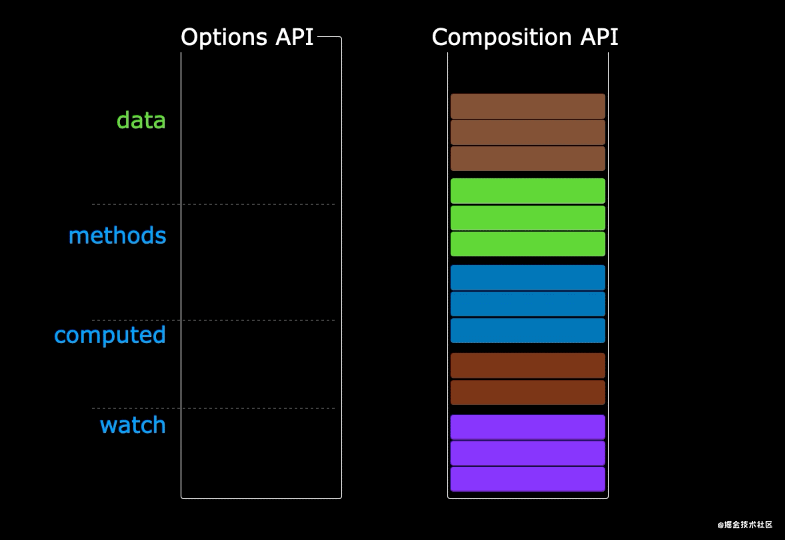
# VS Option.html#_2-使用compisition-api)2) 使用Compisition API
我们可以更加优雅的组织我们的代码,函数。让相关功能的代码更加有序的组织在一起

#1. 新组件
#1) Fragment(片断)
- 在Vue2中: 组件必须有一个根标签
- 在Vue3中: 组件可以没有根标签, 内部会将多个标签包含在一个Fragment虚拟元素中
好处: 减少标签层级, 减小内存占用
<template> <h2>aaaa</h2> <h2>aaaa</h2> </template>#2) Teleport(瞬移)
Teleport 提供了一种干净的方法, 让组件的html在父组件界面外的特定标签(很可能是body)下插入显示
ModalButton.vue
<template> <button @click="modalOpen = true"> Open full screen modal! (With teleport!) </button> <teleport to="body"> <div v-if="modalOpen" class="modal"> <div> I'm a teleported modal! (My parent is "body") <button @click="modalOpen = false"> Close </button> </div> </div> </teleport> </template> <script> import { ref } from 'vue' export default { name: 'modal-button', setup () { const modalOpen = ref(false) return { modalOpen } } } </script> <style> .modal { position: absolute; top: 0; right: 0; bottom: 0; left: 0; background-color: rgba(0,0,0,.5); display: flex; flex-direction: column; align-items: center; justify-content: center; } .modal div { display: flex; flex-direction: column; align-items: center; justify-content: center; background-color: white; width: 300px; height: 300px; padding: 5px; } </style>App.vue
<template> <h2>App</h2> <modal-button></modal-button> </template> <script lang="ts"> import ModalButton from './ModalButton.vue' export default { setup() { return { } }, components: { ModalButton } } </script>#3) Suspense(不确定的)
它们允许我们的应用程序在等待异步组件时渲染一些后备内容,可以让我们创建一个平滑的用户体验
<template> <Suspense> <template v-slot:default> <AsyncComp/> <!-- <AsyncAddress/> --> </template> <template v-slot:fallback> <h1>LOADING...</h1> </template> </Suspense> </template> <script lang="ts"> /* 异步组件 + Suspense组件 */ // import AsyncComp from './AsyncComp.vue' import AsyncAddress from './AsyncAddress.vue' import { defineAsyncComponent } from 'vue' const AsyncComp = defineAsyncComponent(() => import('./AsyncComp.vue')) export default { setup() { return { } }, components: { AsyncComp, AsyncAddress } } </script>AsyncComp.vue
<template> <h2>AsyncComp22</h2> <p>{{msg}}</p> </template> <script lang="ts"> export default { name: 'AsyncComp', setup () { // return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { // setTimeout(() => { // resolve({ // msg: 'abc' // }) // }, 2000) // }) return { msg: 'abc' } } } </script>AsyncAddress.vue
<template> <h2>{{data}}</h2> </template> <script lang="ts"> import axios from 'axios' export default { async setup() { const result = await axios.get('/data/address.json') return { data: result.data } } } </script>#2. 其他新的API
#全新的全局API
createApp()
- defineProperty()
- defineAsyncComponent()
-
#将原来的全局API转移到应用对象
app.component()
- app.config()
- app.directive()
- app.mount()
- app.unmount()
-
#模板语法变化
v-model的本质变化
- prop:value -> modelValue;
- event:input -> update:modelValue;
- .sync修改符已移除, 由v-model代替
- v-if优先v-for解析
新增的钩子函数
组合式 API 还提供了以下调试钩子函数:



