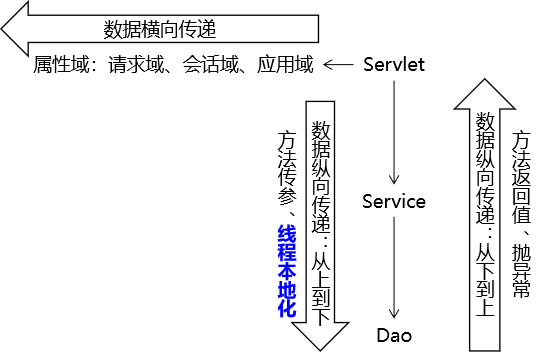
第二节 属性域
1、在整个应用中属性域的重要作用
2、请求域操作方式
①使用 Model 类型的形参
@RequestMapping(“/attr/request/model”)
public String testAttrRequestModel(
// 在形参位置声明Model类型变量,用于存储模型数据<br /> Model model) {// 我们将数据存入模型,SpringMVC 会帮我们把模型数据存入请求域<br /> // 存入请求域这个动作也被称为暴露到请求域<br /> model.addAttribute("requestScopeMessageModel","i am very happy[model]");return "target";<br />}
②使用 ModelMap 类型的形参
@RequestMapping(“/attr/request/model/map”)
public String testAttrRequestModelMap(
// 在形参位置声明ModelMap类型变量,用于存储模型数据<br /> ModelMap modelMap) {
// 我们将数据存入模型,SpringMVC 会帮我们把模型数据存入请求域<br /> // 存入请求域这个动作也被称为暴露到请求域<br /> modelMap.addAttribute("requestScopeMessageModelMap","i am very happy[model map]");
return "target";<br />}
③使用 Map 类型的形参
@RequestMapping(“/attr/request/map”)
public String testAttrRequestMap(
// 在形参位置声明Map类型变量,用于存储模型数据<br /> Map<String, Object> map) {
// 我们将数据存入模型,SpringMVC 会帮我们把模型数据存入请求域<br /> // 存入请求域这个动作也被称为暴露到请求域<br /> map.put("requestScopeMessageMap", "i am very happy[map]");
return "target";<br />}
④使用原生 request 对象
@RequestMapping(“/attr/request/original”)
public String testAttrOriginalRequest(
// 拿到原生对象,就可以调用原生方法执行各种操作<br /> HttpServletRequest request) {
request.setAttribute("requestScopeMessageOriginal", "i am very happy[original]");
return "target";<br />}
⑤使用 ModelAndView 对象
@RequestMapping(“/attr/request/mav”)
public ModelAndView testAttrByModelAndView() {
// 1.创建ModelAndView对象<br /> ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
// 2.存入模型数据<br /> modelAndView.addObject("requestScopeMessageMAV", "i am very happy[mav]");
// 3.设置视图名称<br /> modelAndView.setViewName("target");
return modelAndView;<br />}
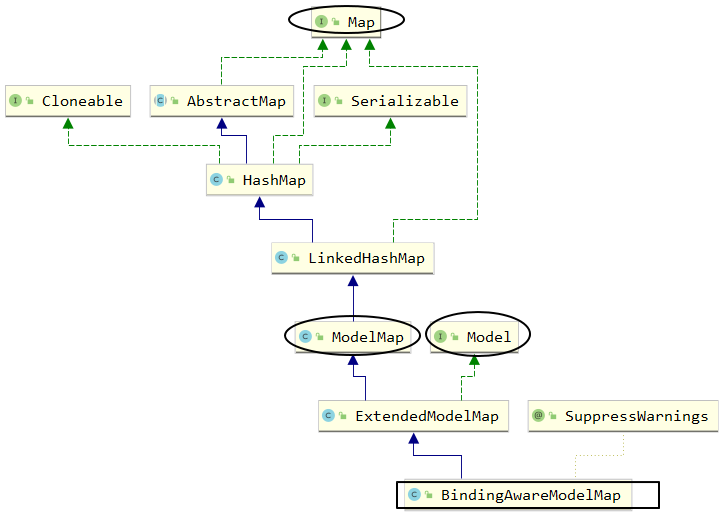
3、模型的本质
①BindingAwareModelMap
SpringMVC 传入的 Model、ModelMap、Map类型的参数其实本质上都是 BindingAwareModelMap 类型的。
②它们之间的关系
4、框架底层将模型存入请求域
①最终找到的源码位置
所在类:org.thymeleaf.context.WebEngineContext
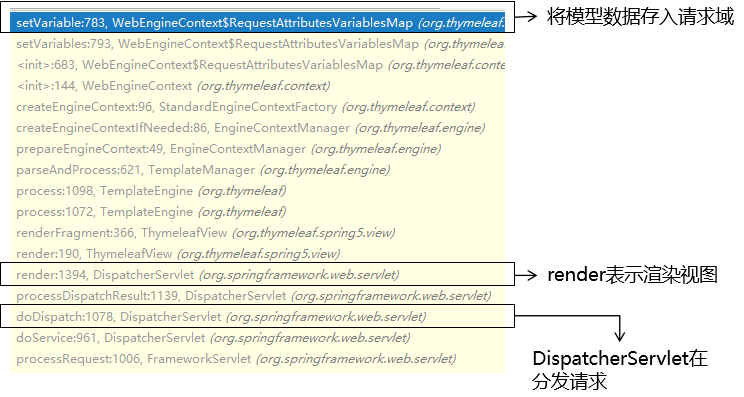
所在方法:setVariable()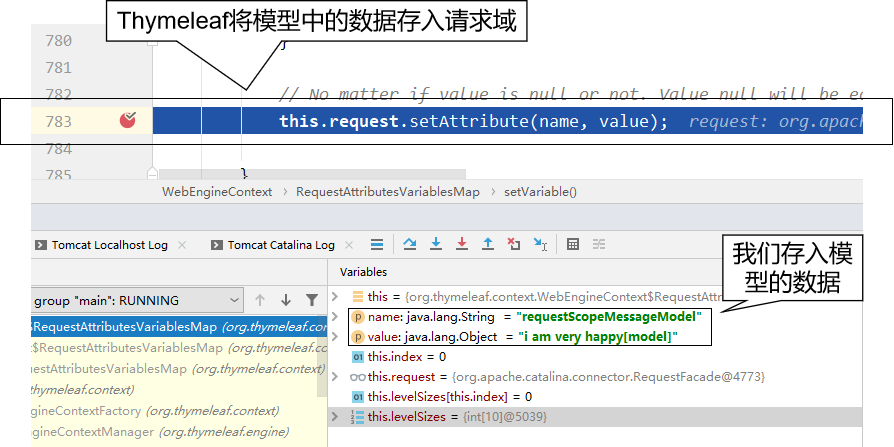
②过程中值得关注的点
5、会话域
使用会话域最简单直接的办法就是使用原生的 HttpSession 对象
@RequestMapping(“/attr/session”)
public String attrSession(
// 使用会话域最简单直接的办法就是使用原生的 HttpSession 对象
HttpSession session) {
session.setAttribute("sessionScopeMessage", "i am haha ...");
return "target";<br />}
6、应用域
应用域同样是使用原生对象来操作:
@Autowired
private ServletContext servletContext;
@RequestMapping(“/attr/application”)
public String attrApplication() {
servletContext.setAttribute("appScopeMsg", "i am hungry...");
return "target";<br />}