[[toc]]
第四节 数据输入
1、Mybatis总体机制概括

2、概念说明
这里数据输入具体是指上层方法(例如Service方法)调用Mapper接口时,数据传入的形式。
- 简单类型:只包含一个值的数据类型
- 基本数据类型:int、byte、short、double、……
- 基本数据类型的包装类型:Integer、Character、Double、……
- 字符串类型:String
- 复杂类型:包含多个值的数据类型
- 实体类类型:Employee、Department、……
- 集合类型:List、Set、Map、……
- 数组类型:int[]、String[]、……
- 复合类型:List
、实体类中包含集合……
3、单个简单类型参数
①Mapper接口中抽象方法的声明
Employee selectEmployee(Integer empId);
②SQL语句
4、实体类类型参数
①Mapper接口中抽象方法的声明
int insertEmployee(Employee employee);
②SQL语句
insert into t_emp(emp_name,emp_salary) values(#{empName},#{empSalary})
③对应关系
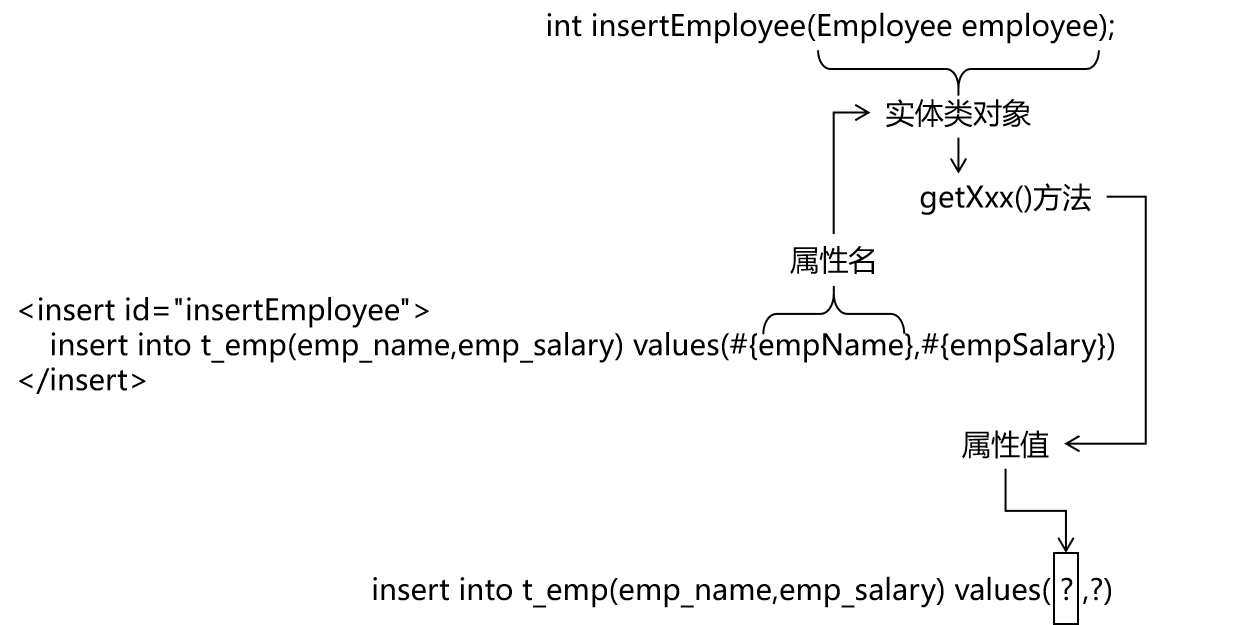
④结论
Mybatis会根据#{}中传入的数据,加工成getXxx()方法,通过反射在实体类对象中调用这个方法,从而获取到对应的数据。填充到#{}这个位置。
5、零散的简单类型数据
①Mapper接口中抽象方法的声明
int updateEmployee(@Param(“empId”) Integer empId,@Param(“empSalary”) Double empSalary);
②SQL语句
<update id="updateEmployee"><br /> update t_emp set emp_salary=#{empSalary} where emp_id=#{empId}<br /> </update>
③对应关系
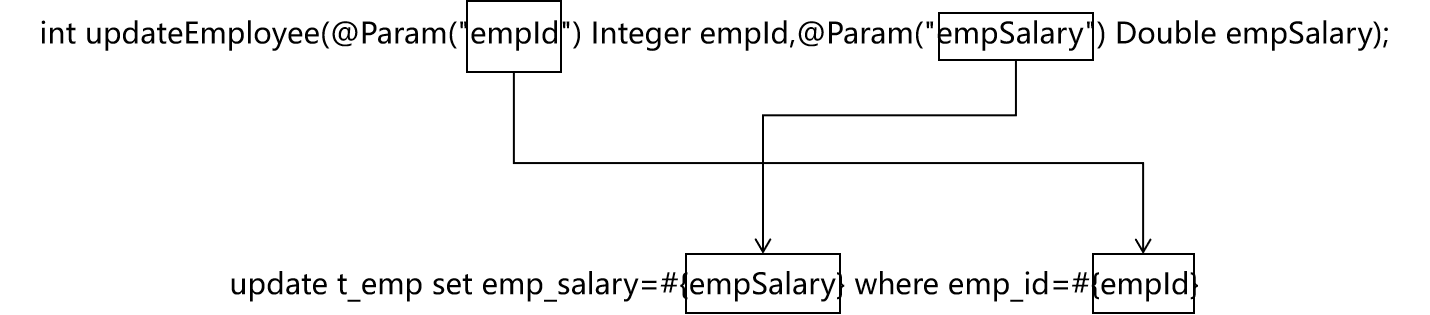
6、Map类型参数
①Mapper接口中抽象方法的声明
int updateEmployeeByMap(Map
②SQL语句
<update id="updateEmployeeByMap"><br /> update t_emp set emp_salary=#{empSalaryKey} where emp_id=#{empIdKey}<br /> </update>
③junit测试
@Test
public void testUpdateEmpNameByMap() {
EmployeeMapper mapper = session.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);Map<String, Object> paramMap = new HashMap<>();paramMap.put("empSalaryKey", 999.99);<br /> paramMap.put("empIdKey", 5);int result = mapper.updateEmployeeByMap(paramMap);System.out.println("result = " + result);<br />}
④对应关系
{}中写Map中的key
⑤使用场景
有很多零散的参数需要传递,但是没有对应的实体类类型可以使用。使用@Param注解一个一个传入又太麻烦了。所以都封装到Map中。

