数据类型
- 整型
- int/32
- short/16
- long/64
- byte/8
- 浮点类型
- float/32
- double/64
- char 类型
- char/16
boolean 类型
引用类型不能用 == 来比较两个值是否相等,要实用
equals()比较

// 自动装箱(Auto Boxing)Integer n = 100; // 编译器自动使用Integer.valueOf(int)// 自动拆箱(Auto Unboxing)int x = n; // 编译器自动使用Integer.intValue()
缓存池
- new Integer(123) 每次都会新建一个对象
- Integer.valueOf(123) 会使用缓存池中的对象,多次调用会取得同一个对象的引用
Integer x = new Integer(123);Integer y = new Integer(123);System.out.println(x == y); // falseInteger z = Integer.valueOf(123);Integer k = Integer.valueOf(123);System.out.println(z == k); // true
public static Integer valueOf(int i) {if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];return new Integer(i);}
编译器会在缓冲池范围内的基本类型自动装箱过程调用 valueOf() 方法,因此多个 Integer 实例使用自动装箱来创建并且值相同,那么就会引用相同的对象。
Integer m = 123;Integer n = 123;System.out.println(m == n); // true
String
被声明为 final,不可被继承
public final class Stringimplements java.io.Serializable, Comparable<String>, CharSequence {/** The value is used for character storage. */private final char value[];
String.intern()
使用 String.intern() 可以保证相同内容的字符串变量引用同一的内存对象。
String s1 = new String("aaa");String s2 = new String("aaa");System.out.println(s1 == s2); // falseString s3 = s1.intern();System.out.println(s1.intern() == s3); // true// 使用双引号的形式创建字符串实例,会自动地将新建的对象放入 String Pool 中String s4 = "bbb";String s5 = "bbb";System.out.println(s4 == s5); // true
运算
参数传递
Java没有栈上对象,只有堆上对象,Java的引用都是指针
// 第一个例子:基本类型void foo(int value) {value = 100;}foo(num); // num 没有被改变// 第二个例子:没有提供改变自身方法的引用类型void foo(String text) {text = "windows";}foo(str); // str 也没有被改变// 第三个例子:提供了改变自身方法的引用类型StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("iphone");void foo(StringBuilder builder) {builder.append("4");}foo(sb); // sb 被改变了,变成了"iphone4"。// 第四个例子:提供了改变自身方法的引用类型,但是不使用,而是使用赋值运算符。StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("iphone");void foo(StringBuilder builder) {builder = new StringBuilder("ipad");}foo(sb); // sb 没有被改变,还是 "iphone"。
继承
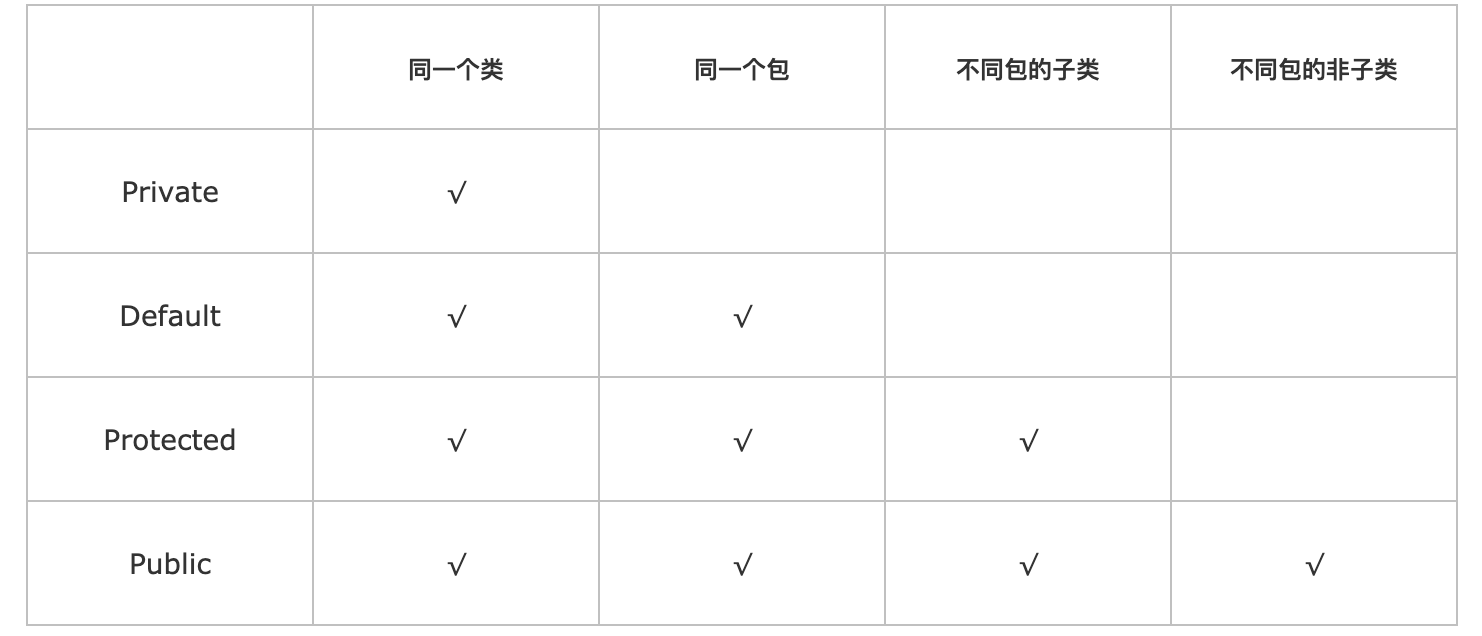
访问权限
抽象类与接口
抽象类
使用 abstract 关键字进行声明,抽象类不能被实例化,需要继承抽象类才能实例化其子类。
public abstract class AbstractClassExample {protected int x;private int y;public abstract void func1();public void func2() {System.out.println("func2");}}public class AbstractExtendClassExample extends AbstractClassExample {@Overridepublic void func1() {System.out.println("func1");}}// AbstractClassExample ac1 = new AbstractClassExample(); // 'AbstractClassExample' is abstract; cannot be instantiatedAbstractClassExample ac2 = new AbstractExtendClassExample();ac2.func1();
接口
接口的成员(字段 + 方法)默认都是 public 的,并且不允许定义为 private 或者 protected。
接口的字段默认都是 static 和 final 的。
public interface InterfaceExample {void func1();default void func2(){System.out.println("func2");}int x = 123;// int y; // Variable 'y' might not have been initializedpublic int z = 0; // Modifier 'public' is redundant for interface fields// private int k = 0; // Modifier 'private' not allowed here// protected int l = 0; // Modifier 'protected' not allowed here// private void fun3(); // Modifier 'private' not allowed here}public class InterfaceImplementExample implements InterfaceExample {@Overridepublic void func1() {System.out.println("func1");}}// InterfaceExample ie1 = new InterfaceExample(); // 'InterfaceExample' is abstract; cannot be instantiatedInterfaceExample ie2 = new InterfaceImplementExample();ie2.func1();System.out.println(InterfaceExample.x);
关键字
final
- 数据:相当于常量
- 基本类型:数值不变
- 引用类型:引用不变
- 方法:不能被子类重写
- 类:不能被继承 ```javascript final int x = 1; // x = 2; // cannot assign value to final variable ‘x’ final A y = new A(); y.a = 1;
<a name="T4pKG"></a>## static- 静态变量:类的所有实例共享静态变量```javascriptpublic class A {private int x; // 实例变量private static int y; // 静态变量public static void main(String[] args) {// int x = A.x; // Non-static field 'x' cannot be referenced from a static contextA a = new A();int x = a.x;int y = A.y;}}
静态方法:方法中不能有 this 和 super 关键字。 ```javascript public class A { private static int x; private int y;
public static void func1(){
int a = x;// int b = y; // Non-static field 'y' cannot be referenced from a static context// int b = this.y; // 'A.this' cannot be referenced from a static context
} }
- 静态内部类:不能访问外部类的非静态的变量和方法。```javascriptpublic class OuterClass {class InnerClass {}static class StaticInnerClass {}public static void main(String[] args) {// InnerClass innerClass = new InnerClass(); // 'OuterClass.this' cannot be referenced from a static contextOuterClass outerClass = new OuterClass();InnerClass innerClass = outerClass.new InnerClass();StaticInnerClass staticInnerClass = new StaticInnerClass();}}
反射(reflective)
JAVA反射机制是在运行状态中,对于任意一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法;对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意一个方法和属性;这种动态获取的信息以及动态调用对象的方法的功能称为java语言的反射机制。