源码优化
代码管理方式: monorepo
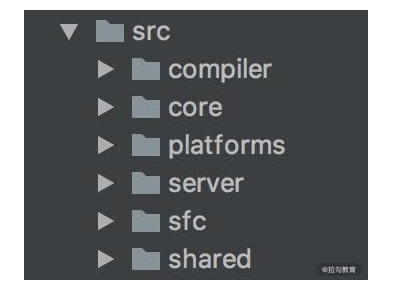
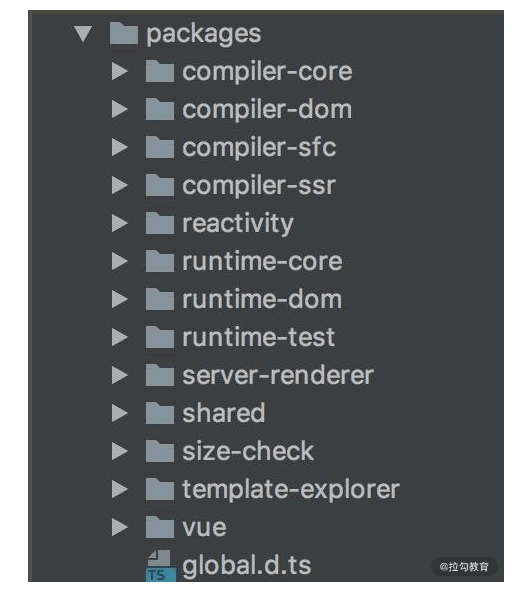
使用 monorepo 把各个功能模块拆分到不同的 package 中
- compiler:模板编译的相关代码
- core:与平台无关的通用运行时代码
- platforms:平台专有代码
- serve:服务端渲染的相关代码
- sfc:vue 单文件解析相关代码
-
Ts
性能优化
源码体积优化
移除冷门 feature (filter、inline-template 等)
- 引入 tree-shaking 的技术,减少打包体积
tree-shaking 依赖 ES2015 模块语法的静态结构(即 import 和 export),通过编译阶段的静态分析,找到没有引入的模块并打上标记
export function square(x) {return x * x}export function cube(x) {return x * x * x}
import { cube } from './math.js'// do something with cube
/* 1 *//***/ (function(module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {'use strict';/* unused harmony export square *//* harmony export (immutable) */ __webpack_exports__['a'] = cube;function square(x) {return x * x;}function cube(x) {return x * x * x;}});
未被引入的模块被标记,在压缩阶段会利用如 uglify-js、terser 等压缩工具删除无用代码
数据劫持优化
数据响应式:DOM 是数据的一种映射,数据发生变化后可以自动更新 DOM,用户只需要专注于数据的修改,没有其余的心智负担。 通过劫持数据的访问和更新来实现
Object.defineProperty(data, 'a',{get(){// track},set(){// trigger}})
Vue2 中使用 Object.defineProperty 存在的缺陷:需要预先知道要拦截的 key 值,所以不能监测对象属性的添加和删除。(使用 $set 和 $delete 处理)
export default {data: {a: {b: {c: {d: 1}}}}}
多层嵌套数据要劫持内部深层次的对象变化,需要递归遍历这个对象,执行 Object.defineProperty 把每一层对象数据变成响应式,所以有较大的性能负担
observed = new Proxy(data, {get() {// track},set() {// trigger}})
Vue3 使用 Proxy 做数据劫持,能够劫持整个对象,相应的属性增删就能监测到
但 Proxy 也不能监听内部深层次的对象变化,Vue3 是在 getter 中去递归响应式,这样只有当使用到该数据时才会变成响应式,提高了性能
编译优化
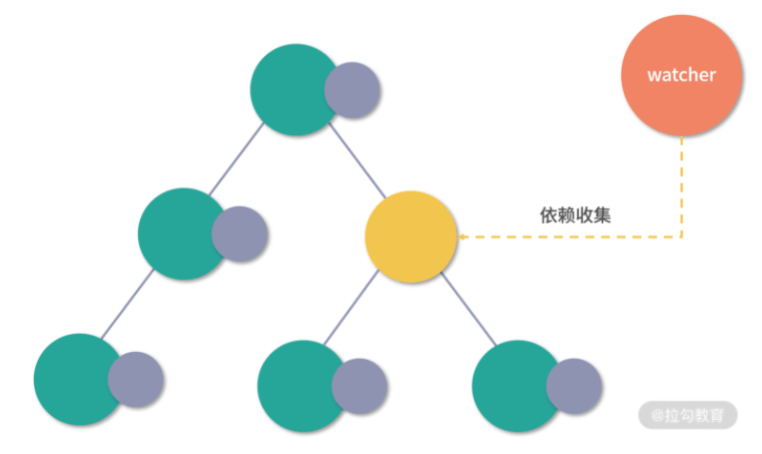
Vue 能保证触发更新的组件最小化,但在单个组件内部依然需要遍历该组件的整个 vnode 树
<template><div id="content"><p class="text">static text</p><p class="text">static text</p><p class="text">{{message}}</p><p class="text">static text</p><p class="text">static text</p></div></template>
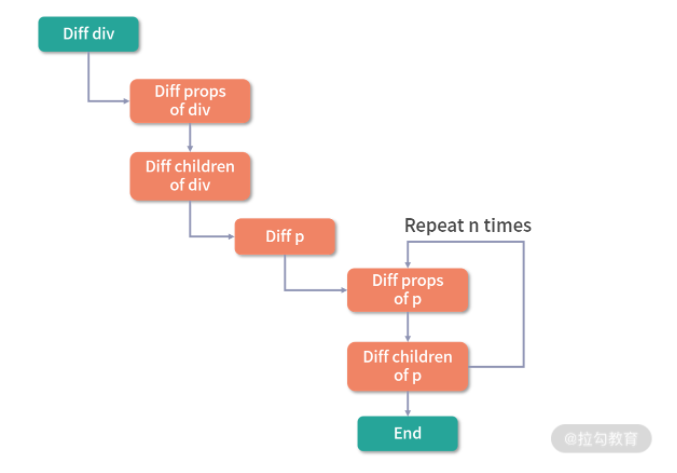
因为这段代码中只有一个动态节点,所以这里有很多 diff 和遍历其实都是不需要的,这就会导致 vnode 的性能跟模版大小正相关,跟动态节点的数量无关,当一些组件的整个模版内只有少量动态节点时,这些遍历都是性能的浪费。
Vue.js 3.0 通过编译阶段对静态模板的分析,编译生成了 Block tree。Block tree 是一个将模版基于动态节点指令切割的嵌套区块,每个区块内部的节点结构是固定的,而且每个区块只需要以一个 Array 来追踪自身包含的动态节点。借助 Block tree,Vue.js 将 vnode 更新性能由与模版整体大小相关提升为与动态内容的数量相关。
语法 API 优化:Composition API
优化逻辑组织
将某个逻辑关注点相关的代码全都放在一个函数里
优化逻辑复用
Vue2 中使用 mixins 复用逻辑,存在大量 mixins 时,会导致命名冲突和数据来源不清晰问题
const mousePositionMixin = {data() {return {x: 0,y: 0}},mounted() {window.addEventListener('mousemove', this.update)},destroyed() {window.removeEventListener('mousemove', this.update)},methods: {update(e) {this.x = e.pageXthis.y = e.pageY}}}export default mousePositionMixin
<template><div>Mouse position: x {{ x }} / y {{ y }}</div></template><script>import mousePositionMixin from './mouse'export default {mixins: [mousePositionMixin]}</script>
使用 hook 写法
import { ref, onMounted, onUnmounted } from 'vue'export default function useMousePosition() {const x = ref(0)const y = ref(0)const update = e => {x.value = e.pageXy.value = e.pageY}onMounted(() => {window.addEventListener('mousemove', update)})onUnmounted(() => {window.removeEventListener('mousemove', update)})return { x, y }}
<template><div>Mouse position: x {{ x }} / y {{ y }}</div></template><script>import useMousePosition from './mouse'export default {setup() {const { x, y } = useMousePosition()return { x, y }}}</script>

