initMixin:定义原型上的 init 方法(内部方法)
function initMixin (Vue) {Vue.prototype._init = function (options) {}}
stateMixin:定义原型上跟数据相关的属性方法
function stateMixin (Vue) {var dataDef = {};dataDef.get = function () { return this._data };var propsDef = {};propsDef.get = function () { return this._props };{dataDef.set = function () {warn('Avoid replacing instance root $data. ' +'Use nested data properties instead.',this);};propsDef.set = function () {warn("$props is readonly.", this);};}// 代理了_data,_props的访问Object.defineProperty(Vue.prototype, '$data', dataDef);Object.defineProperty(Vue.prototype, '$props', propsDef);// $set, $delVue.prototype.$set = set;Vue.prototype.$delete = del;// $watchVue.prototype.$watch = function (expOrFn,cb,options) {};}
eventsMixin:定义原型上跟事件相关的属性方法
function eventsMixin(Vue) {// 自定义事件监听Vue.prototype.$on = function (event, fn) {};// 自定义事件监听,只触发一次Vue.prototype.$once = function (event, fn) {}// 自定义事件解绑Vue.prototype.$off = function (event, fn) {}// 自定义事件通知Vue.prototype.$emit = function (event, fn) {}
lifecycleMixin:定义原型上跟生命周期相关的方法
function lifecycleMixin (Vue) {Vue.prototype._update = function (vnode, hydrating) {};Vue.prototype.$forceUpdate = function () {};Vue.prototype.$destroy = function () {}}
renderMixin:定义渲染相关的函数
function renderMixin (Vue) {Vue.prototype.$nextTick = function (fn) {};// _render函数,后面会着重讲Vue.prototype._render = function () {};}
常规选项的合并
data 合并
Vue 组件的 data 为什么是一个函数
组件设计的目的是为了复用,每次通过函数创建相当于在一个独立的内存空间中生成一个 data 副本,这样每个组件之间的数据不会互相影响。
strats.data = function (parentVal, childVal, vm) {// vm代表是否为Vue创建的实例,否则是子父类的关系if (!vm) {if (childVal && typeof childVal !== 'function') { // 必须保证子类的data类型是一个函数而不是一个对象warn('The "data" option should be a function ' + 'that returns a per-instance value in component ' + 'definitions.',vm);return parentVal}return mergeDataOrFn(parentVal, childVal)}return mergeDataOrFn(parentVal, childVal, vm); // vue实例时需要传递vm作为函数的第三个参数};
function mergeDataOrFn ( parentVal, childVal, vm ) {// 子父类if (!vm) {if (!childVal) { // 子类不存在data选项,则合并结果为父类data选项return parentVal}if (!parentVal) { // 父类不存在data选项,则合并结果为子类data选项return childVal}return function mergedDataFn () { // data选项在父类和子类同时存在的情况下返回的是一个函数// 子类实例和父类实例,分别将子类和父类实例中data函数执行后返回的对象传递给mergeData函数做数据合并return mergeData(typeof childVal === 'function' ? childVal.call(this, this) : childVal,typeof parentVal === 'function' ? parentVal.call(this, this) : parentVal)}} else {// Vue实例// vue构造函数实例对象return function mergedInstanceDataFn () {var instanceData = typeof childVal === 'function'? childVal.call(vm, vm): childVal;var defaultData = typeof parentVal === 'function'? parentVal.call(vm, vm): parentVal;if (instanceData) {// 当实例中传递data选项时,将实例的data对象和Vm构造函数上的data属性选项合并return mergeData(instanceData, defaultData)} else {// 当实例中不传递data时,默认返回Vm构造函数上的data属性选项return defaultData}}}}
将父类数据整合到字类数据选项中,出现冲突时,选择字类数据。嵌套数据,递归处理。
function mergeData (to, from) {if (!from) { return to }var key, toVal, fromVal;// Reflect.ownKeys可以拿到Symbol属性var keys = hasSymbol? Reflect.ownKeys(from): Object.keys(from);for (var i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {key = keys[i];toVal = to[key];fromVal = from[key];if (!hasOwn(to, key)) {// 子的数据父没有,则将新增的数据加入响应式系统中。set(to, key, fromVal);} else if (toVal !== fromVal &&isPlainObject(toVal) &&isPlainObject(fromVal)) {// 处理深层对象,当合并的数据为多层嵌套对象时,需要递归调用mergeData进行比较合并mergeData(toVal, fromVal);}}return to}
数据代理
代理使得数据在访问时进行依赖收集,在修改更新时对依赖进行更新
- Object.defineProperty:无法对数组中新添加的数据进行拦截,因为添加的索引值没有预先加入到数据拦截中
- Proxy:针对目标对象会创建一个新的实例对象,并将目标对象代理到新的实例对象上
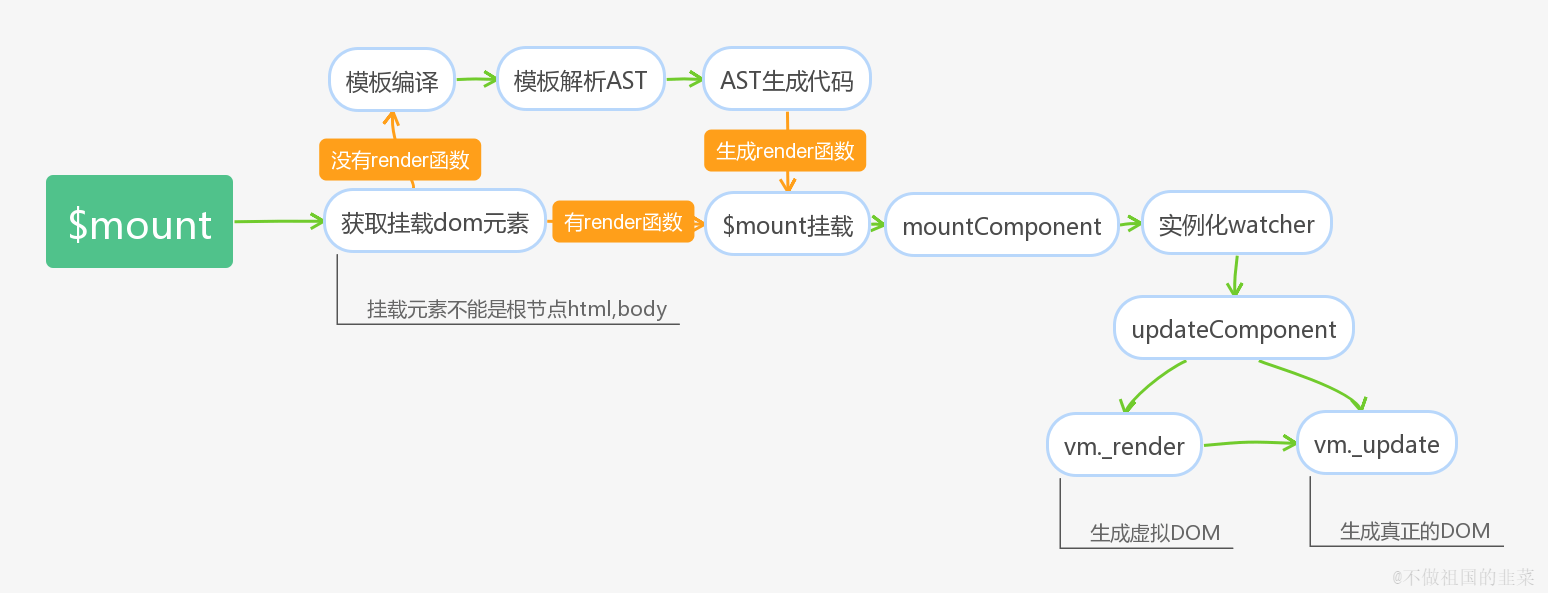
实例挂载流程和模板编译
实例挂载
 ```javascript
// 内部真正实现挂载的方法
Vue.prototype.$mount = function (el, hydrating) {
el = el && inBrowser ? query(el) : undefined;
// 调用mountComponent方法挂载
return mountComponent(this, el, hydrating)
};
// 缓存了原型上的 $mount 方法
var mount = Vue.prototype.$mount;
```javascript
// 内部真正实现挂载的方法
Vue.prototype.$mount = function (el, hydrating) {
el = el && inBrowser ? query(el) : undefined;
// 调用mountComponent方法挂载
return mountComponent(this, el, hydrating)
};
// 缓存了原型上的 $mount 方法
var mount = Vue.prototype.$mount;
// 重新定义$mount,为包含编译器和不包含编译器的版本提供不同封装,最终调用的是缓存原型上的$mount方法 Vue.prototype.$mount = function (el, hydrating) { // 获取挂载元素 el = el && query(el); // 挂载元素不能为跟节点 if (el === document.body || el === document.documentElement) { warn( “Do not mount Vue to or - mount to normal elements instead.” ); return this } var options = this.$options; // 需要编译 or 不需要编译 // render选项不存在,代表是template模板的形式,此时需要进行模板的编译过程 if (!options.render) { ··· // 使用内部编译器编译模板 } // 无论是template模板还是手写render函数最终调用缓存的$mount方法 return mount.call(this, el, hydrating) } // mountComponent方法思路 function mountComponent(vm, el, hydrating) { // 定义updateComponent方法,在watch回调时调用。 updateComponent = function () { // render函数渲染成虚拟DOM, 虚拟DOM渲染成真实的DOM vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating); }; // 实例化渲染watcher new Watcher(vm, updateComponent, noop, {}) }
<a name="T5W2s"></a># Virtual DOM 的创建> 挂载的过程是调用 Vue 实例上 $mount 方法,而 $mount 的核心是 mountComponent 函数。> 如果传递的是 template 模板,模板会先经过编译器的解析,并最终根据不同平台生成对于代码,此时对应的就是将 with 语句封装好的 render 函数;> 如果传递的是 render 函数,则跳过模板编译过程,直接进入下一个阶段。> 下一个阶段是拿到 render 函数,调用 vm._render() 方法将 render 函数转化为 Virtual DOM,并最终通过 vm._update() 方法将 Virtual DOM 渲染为真实的 DOM 节点<a name="vVKkp"></a># 组件<a name="Qnz1Z"></a>## Vnode 创建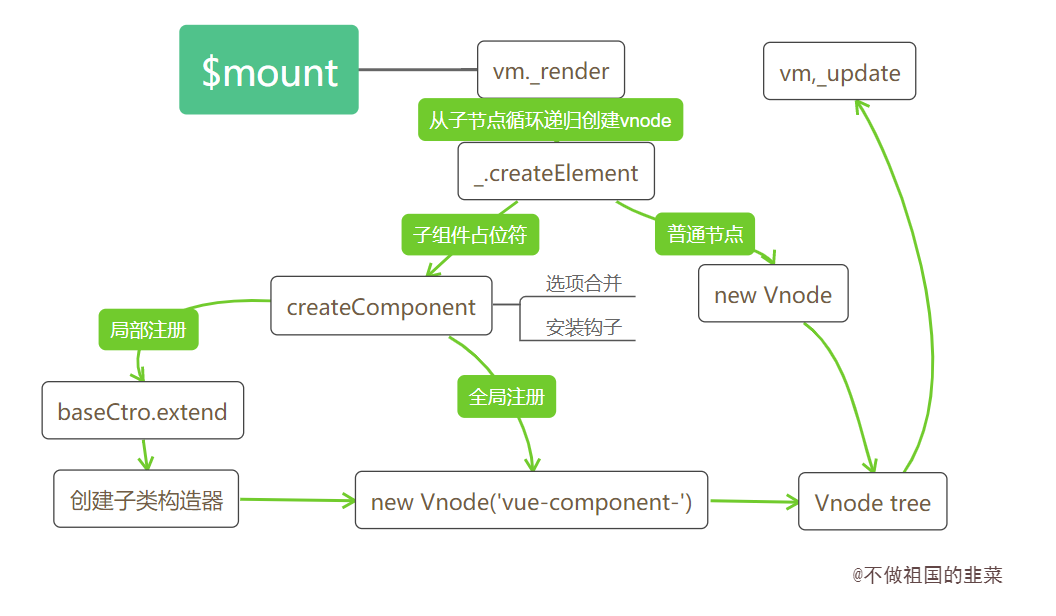1. 局部注册添加的对象配置是在某个组件下,而全局注册添加的子组件是在根实例下1. 局部注册添加的是一个子组件的配置对象,而全局注册添加的是一个字类构造器<a name="yXxzj"></a>## 真实节点渲染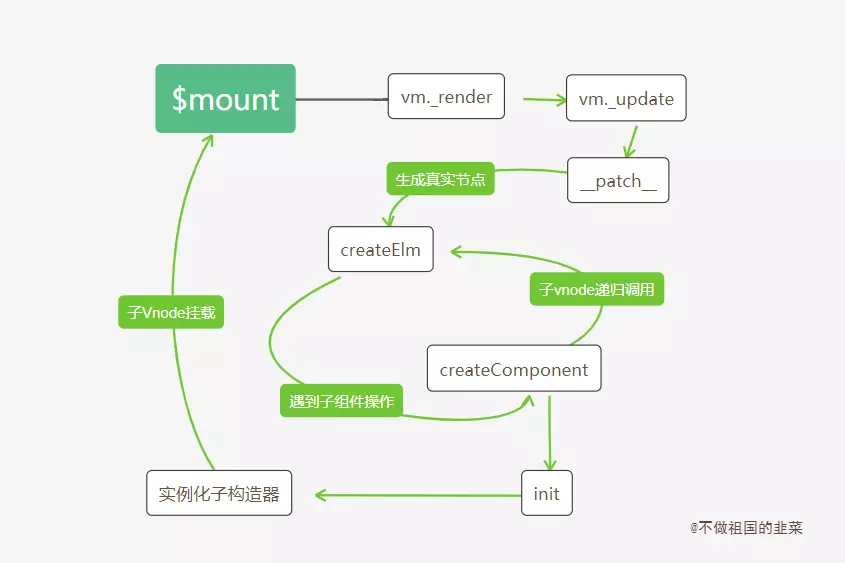<br />不管是父实例还是子实例,在初始化实例阶段有一个 initLifecycle 的过程。这个过程会把当前实例添加到父实例的 $children 属性中,并设置自身的 $parent 属性指向父实例。```javascriptfunction initLifecycle (vm) {var options = vm.$options;// 子组件注册时,会把父组件的实例挂载到自身选项的parent上var parent = options.parent;// 如果是子组件,并且该组件不是抽象组件时,将该组件的实例添加到父组件的$parent属性上,如果父组件是抽象组件,则一直往上层寻找,直到该父级组件不是抽象组件,并将,将该组件的实例添加到父组件的$parent属性if (parent && !options.abstract) {while (parent.$options.abstract && parent.$parent) {parent = parent.$parent;}parent.$children.push(vm);}// 将自身的$parent属性指向父实例。vm.$parent = parent;vm.$root = parent ? parent.$root : vm;vm.$children = [];vm.$refs = {};vm._watcher = null;vm._inactive = null;vm._directInactive = false;// 该实例是否挂载vm._isMounted = false;// 该实例是否被销毁vm._isDestroyed = false;// 该实例是否正在被销毁vm._isBeingDestroyed = false;}
异步组件
异步组件实现的本质是 2 次渲染,除了 0 delay 的高级异步组件第一次直接渲染成 loading 组件外,其他都是第一次渲染生成一个注释节点,当异步获取组件成功后,再通过 forceRender 强制重新渲染。
export function createComponent (Ctor: Class<Component> | Function | Object | void,data: ?VNodeData,context: Component,children: ?Array<VNode>,tag?: string): VNode | Array<VNode> | void {if (isUndef(Ctor)) {return}const baseCtor = context.$options._base// plain options object: turn it into a constructorif (isObject(Ctor)) {Ctor = baseCtor.extend(Ctor)}// if at this stage it's not a constructor or an async component factory,// reject.if (typeof Ctor !== 'function') {if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {warn(`Invalid Component definition: ${String(Ctor)}`, context)}return}// async component 异步组件处理// Ctor不是对象,不会走上面那一套,Ctor.cid未定义let asyncFactoryif (isUndef(Ctor.cid)) {asyncFactory = CtorCtor = resolveAsyncComponent(asyncFactory, baseCtor)if (Ctor === undefined) {// return a placeholder node for async component, which is rendered// as a comment node but preserves all the raw information for the node.// the information will be used for async server-rendering and hydration.return createAsyncPlaceholder(asyncFactory,data,context,children,tag)}}...return vnode}

