 概述:Koa 是一个新的 web 框架, 致力于成为 web 应用和 API 开发领域中的一个更小、更富有表现力、更健壮的基石。
概述:Koa 是一个新的 web 框架, 致力于成为 web 应用和 API 开发领域中的一个更小、更富有表现力、更健壮的基石。
- koa是Express的下一代基于Node.js的web框架
- koa2完全使用Promise并配合 async 来实现异步
举例:
const Koa = require('koa')const app = new Koa()app.use((ctx, next) =>{ctx.body = [ { name: 'tom' } ]next()})//日志app.use(async (ctx,next) =>{const start = Date.now()await next()const end = Date.now()console.log(`请求${ctx.url} 耗时${parseInt(end - start)}ms`)})app.listen(3000)
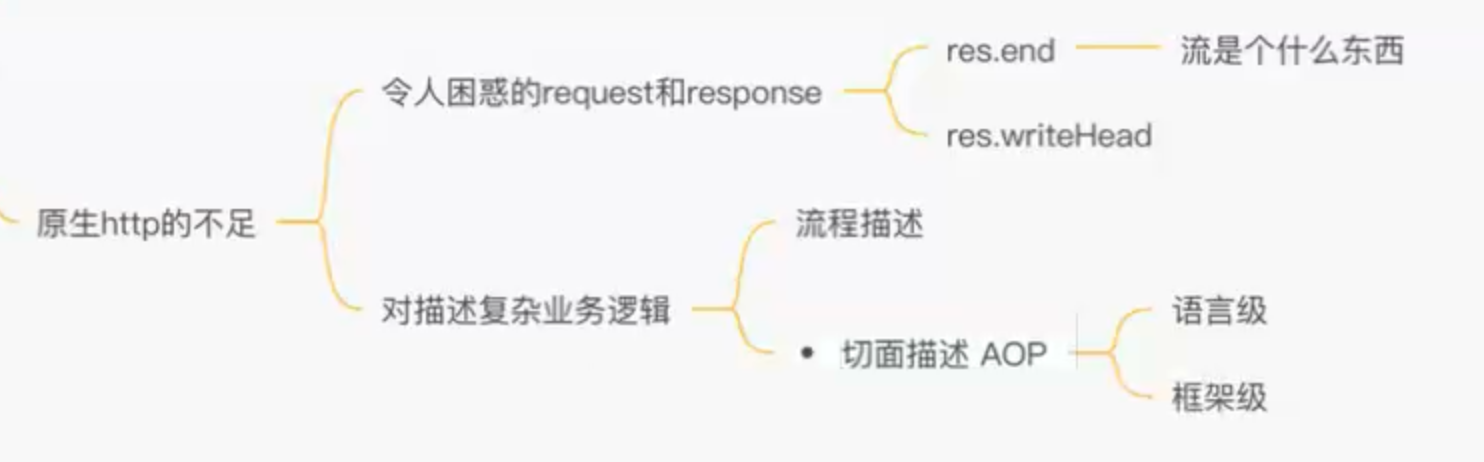
koa 原理:
一个基于nodejs的入门级http服务,类似下面代码:
const http = require('http')const server = http.createServer((req, res)=>{res.writeHead(200)res.end('hi kaikeba')})server.listen(3000,()=>{console.log('监听端口3000')})
koa的目标是用更简单化、流程化、模块化的方式实现回调部分
const http = require("http");class KKB {listen(...args) {const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {this.callback(req, res);});server.listen(...args);}use(callback) {this.callback = callback;}}module.exports = KKB;
// 调用,index.jsconst KKB = require("./kkb");const app = new KKB();app.use((req, res) => {res.writeHead(200);res.end("hi kaikeba");});app.listen(3000, () => {console.log("监听端口3000");});
koa为了能够简化API,引入上下文context概念,将原始请求对象req和响应对象res封装并挂载到 context上,并且在context上设置getter和setter,从而简化操作
// request.jsmodule.exports = {get url() {return this.req.url;},get method(){return this.req.method.toLowerCase()}};// response.jsmodule.exports = {get body() {return this._body;},set body(val) {this._body = val;}};// context.jsmodule.exports = {get url() {return this.request.url;},get body() {return this.response.body;},set body(val) {this.response.body = val;},get method() {return this.request.method}};
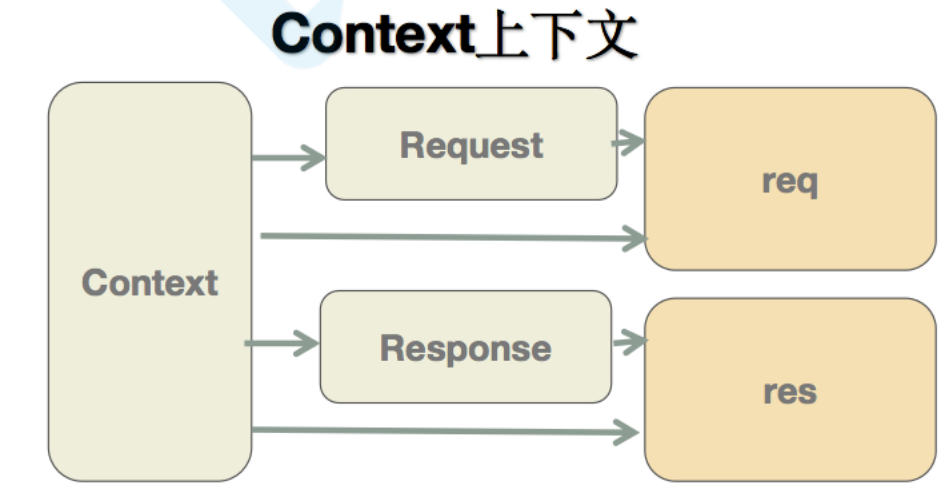
// kkb.js// 导入这三个类const context = require("./context");const request = require("./request");const response = require("./response");class KKB {listen(...args) {const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {// 创建上下文let ctx = this.createContext(req, res);this.callback(ctx)// 响应res.end(ctx.body);});// ...}// 构建上下文, 把res和req都挂载到ctx之上,并且在ctx.req 和ctx.request.req同时保存createContext(req, res) {const ctx = Object.create(context);ctx.request = Object.create(request);ctx.response = Object.create(response);ctx.req = ctx.request.req = req;ctx.res = ctx.response.res = res;return ctx;}}
中间件
Koa中间件机制:Koa中间件机制就是函数式 组合概念 Compose的概念,将一组需要顺序执行的函数复合为一个函数,外层函数的参数实际是内层函数的返回值。洋葱圈模型可以形象表示这种机制,是源码中的精髓和难点。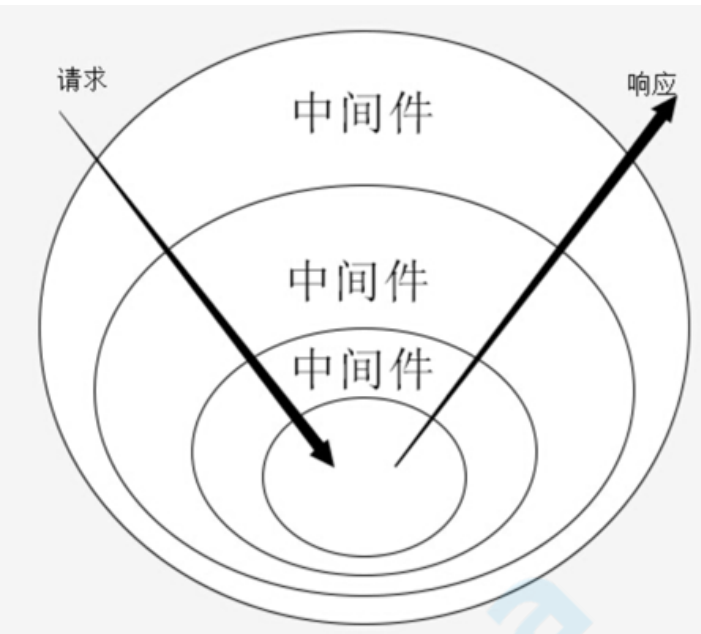
多个函数组合
const compose = (fn1, fn2) => (...args) => fn2(fn1(...args))const fn = compose(add,square)const compose = (...[first,...other]) => (...args) => {let ret = first(...args)other.forEach(fn => {ret = fn(ret)})return ret}const fn = compose(add,square)console.log(fn(1, 2))
异步中间件:上面的函数都是同步的,挨个遍历执行即可,如果是异步的函数呢,是一个 promise,我们要支持async + await的中间件,所以我们要等异步结束后,再执行下一个中间件。
function compose(middlewares) {return function() {return dispatch(0);// 执行第0个function dispatch(i) {let fn = middlewares[i];if (!fn) {return Promise.resolve();}return Promise.resolve(fn(function next() {// promise完成后,再执行下一个return dispatch(i + 1);}));}};}async function fn1(next) {console.log("fn1");await next();console.log("end fn1");}async function fn2(next) {console.log("fn2");await delay();await next();console.log("end fn2");}function fn3(next) {console.log("fn3");}function delay() {return new Promise((reslove, reject) => {setTimeout(() => {reslove();}, 2000);});}const middlewares = [fn1, fn2, fn3];const finalFn = compose(middlewares);finalFn();
compose用在koa中,kkb.js
const http = require("http");const context = require("./context");const request = require("./request");const response = require("./response");class KKB {// 初始化中间件数组constructor() {this.middlewares = [];}listen(...args) {const server = http.createServer(async (req, res) => {const ctx = this.createContext(req, res);// 中间件合成const fn = this.compose(this.middlewares);// 执行合成函数并传入上下文await fn(ctx);res.end(ctx.body);});server.listen(...args);}use(middleware) {// 将中间件加到数组里this.middlewares.push(middleware);}// 合成函数compose(middlewares) {return function(ctx) { // 传入上下文return dispatch(0);function dispatch(i) {let fn = middlewares[i];if (!fn) {return Promise.resolve();}return Promise.resolve(fn(ctx, function next() {// 将上下文传入中间件,mid(ctx,next)return dispatch(i + 1);}));}};createContext(req, res) {let ctx = Object.create(context);ctx.request = Object.create(request);ctx.response = Object.create(response);ctx.req = ctx.request.req = req;ctx.res = ctx.response.res = res;return ctx;}}module.exports = KKB;
常见koa中间件的实现
koa中间件的规范:
一个async函数
接收ctx和next两个参数
任务结束需要执行next
const mid = async (ctx, next) => {// 来到中间件,洋葱圈左边next() // 进入其他中间件// 再次来到中间件,洋葱圈右边};
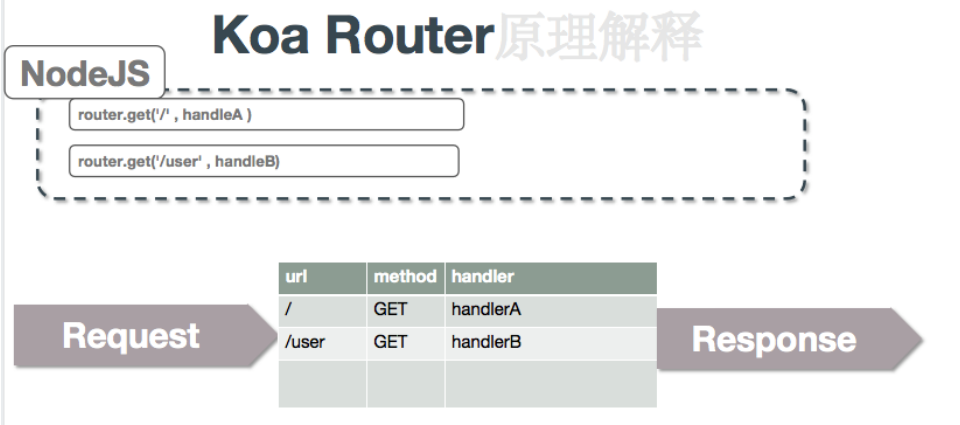
const Koa = require('./kkb')const Router = require('./router')const app = new Koa()const router = new Router();router.get('/index', async ctx => { ctx.body = 'index page'; });// 路由实例输出父中间件 router.routes()app.use(router.routes());
class Router {constructor() {this.stack = [];}register(path, methods, middleware) {let route = {path, methods, middleware}this.stack.push(route);}// 现在只支持get和post,其他的同理get(path,middleware){this.register(path, 'get', middleware);}post(path,middleware){this.register(path, 'post', middleware);}routes() {let stock = this.stack;return async function(ctx, next) {let currentPath = ctx.url;let route;for (let i = 0; i < stock.length; i++) {let item = stock[i];if (currentPath === item.path && item.methods.indexOf(ctx.method) >=0) {// 判断path和methodroute = item.middleware;break;}}if (typeof route === 'function') {route(ctx, next);return;}await next();};}}module.exports = Router;

