介绍
Vue的单项数据流:
“单向数据流”理念的简单示意: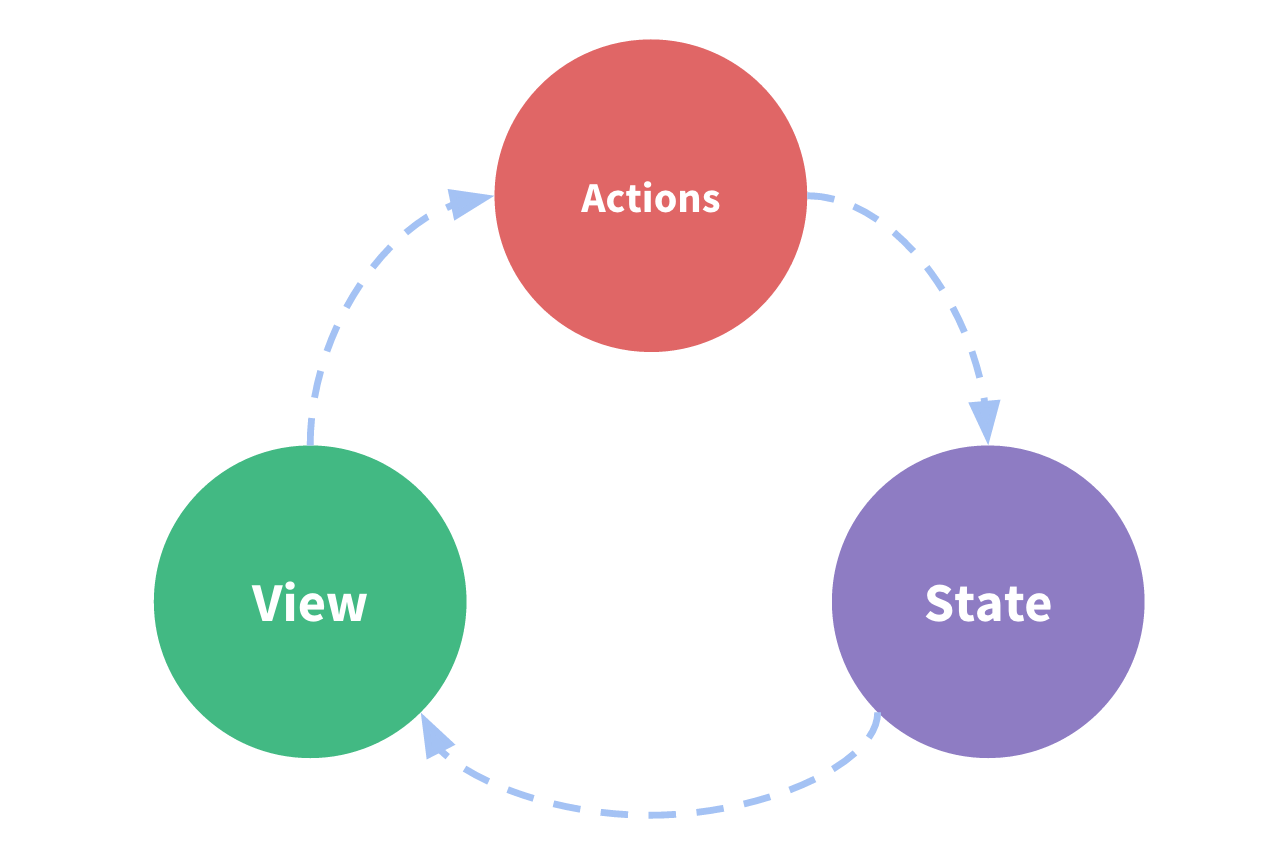
当我们的应用遇到多个组件共享状态时,单向数据流的简洁性很容易被破坏:
- 多个视图依赖于同一状态。
- 来自不同视图的行为需要变更同一状态。
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式。它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。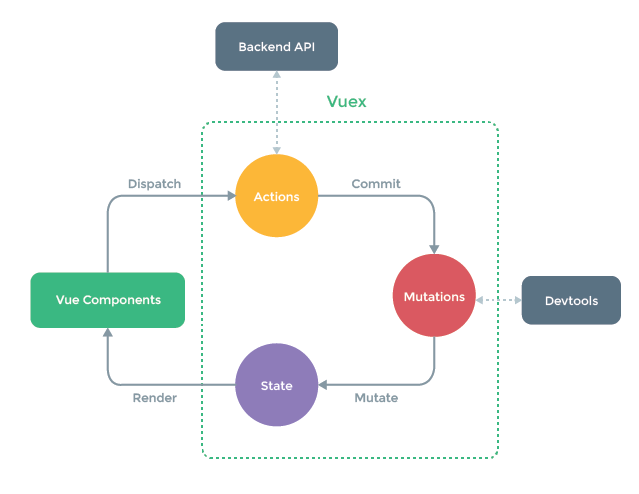
- 每一个 Vuex 应用的核心就是 store(仓库)。“
store”基本上就是一个容器,它包含着你的应用中大部分的状态 (state)。Vuex 和单纯的全局对象有以下两点不同: - Vuex 的状态存储是响应式的。当 Vue 组件从
store中读取状态的时候,若store中的状态发生变化,那么相应的组件也会相应地得到高效更新。 - 你不能直接改变
store中的状态。改变store中的状态的唯一途径就是显式地提交 (commit)mutation。这样使得我们可以方便地跟踪每一个状态的变化,从而让我们能够实现一些工具帮助我们更好地了解我们的应用。
import Vue from 'vue'import Vuex from 'vuex'Vue.use(Vuex)const store = new Vuex.Store({state: {count: 0},mutations: {increment (state) {state.count++}}})//store.state 来获取状态对象,通过 store.commit 方法触发状态变更store.commit('increment')/输出结果console.log(store.state.count) // -> 1==================================//挂载到Vue实例上(ES6)new Vue({el: '#app',store})//在方法上提交变更methods: {increment() {this.$store.commit('increment')console.log(this.$store.state.count)}}
action和mutation:
- action 异步操作,mutation同步操作
- action 提交的是 mutation,而不是直接变更状态
mapState
有时候需要获取多个状态,但是使用计算属性会调用多次,显得麻烦,这里借助mapState方法来获取state。 使用mapState需要引入该方法。
computed: {...mapState(['currentDeptNode', 'currUserInfo']),name() {return this.$store.state.name;}}
getter
相当于计算属性,过滤出来一些值
getters: {//vuex中的计算属性,用于筛选数据getMessage(state) { // 获取修饰后的name,第一个参数state为必要参数,必须写在形参上return `hello${state.name}`;}//挂载<h2>{{$store.getters.getMessage}}</h2>
mapGetters
mapGetters 辅助函数仅仅是将 store 中的 getter 映射到局部计算属性,当我们想在组件里面引入多个getter时,可以使用mapGetter:
computed: {...mapGetters(['getMessage']),// 也可以取别名...mapGetters({msg: 'getMessage'})}
const store = new Vuex.Store({state: {name: '张三',number: 0,},mutations: {setNumber(state) {state.number = 5;},setNumberIsWhat(state, payload) {// 增加一个带参数的mutations方法,并且官方建议payload为一个对象state.number = payload.number;}}})
// 调用this.$store.commit('setNumberIsWhat', { number: 666 });
官方建议:使用mapMutations以代替this.$store.commit(‘XXX’)
mapMutations
Mutations里面的函数必须是同步操作
methods: {...mapMutations(['setNumberIsWhat']),//别名...mapMutations({ setNumberIsAlias: 'setNumberIsWhat' }),},
const store = new Vuex.Store({state: {name: '张三',number: 0,},mutations: {setNumberIsWhat(state, payload) {state.number = payload.number;},},actions: { // 增加actions属性setNum(content, payload) { // 增加payload参数return new Promise(resolve => {setTimeout(() => {content.commit('setNumberIsWhat', { number: payload.number });resolve();}, 1000);});}});// commit方法可以直接解构出来
async mounted() {console.log(`旧值:${this.$store.state.number}`);await this.$store.dispatch('setNum', { number: 611 });console.log(`新值:${this.$store.state.number}`);},
mapActions
methods: {...mapActions(['setNum']), // 就像这样,解构到methods中// 别名...mapActions({ setNumAlias: 'setNum' }),},async mounted() {await this.setNum({ number: 123 }); // 直接这样调用即可},
模块化
const moduleA = {state: () => ({ ... }),mutations: { ... },actions: { ... },getters: { ... }}const moduleB = {state: () => ({ ... }),mutations: { ... },actions: { ... }}const store = new Vuex.Store({modules: {a: moduleA,b: moduleB}})store.state.a // -> moduleA 的状态store.state.b // -> moduleB 的状态
默认情况下,模块内部的 action、mutation 和 getter 是注册在全局命名空间的——这样使得多个模块能够对同一 mutation 或 action 作出响应。
如果希望你的模块具有更高的封装度和复用性,你可以通过添加 namespaced: true 的方式使其成为带命名空间的模块。当模块被注册后,它的所有 getter、action 及 mutation 都会自动根据模块注册的路径调整命名。
const store = new Vuex.Store({modules: {account: {namespaced: true,// 模块内容(module assets)state: () => ({ ... }), // 模块内的状态已经是嵌套的了,使用 `namespaced` 属性不会对其产生影响getters: {isAdmin () { ... } // -> getters['account/isAdmin']},actions: {login () { ... } // -> dispatch('account/login')},mutations: {login () { ... } // -> commit('account/login')}}}})

