在本案例中,我们将展示如何用AWEL创建一个RAG(Retrieval Augmented Generation) 程序。
首先创建一个名称为first_rag_with_awel.py的python文件。
本案例提供的教程中,我们通过URL来获取知识,并存储到向量数据库当当中。
首先,需要创建环境并安装对应的依赖。 这里需要注意,dbgpt 包SDK的安装,不要安装在当前运行dbgpt服务的虚拟环境下。最好起个新的虚拟环境,如dbgpt_use
conda create -n dbgpt_use python=3.10conda activate dbgpt_usepip install dbgpt
准备Embedding模型
将知识处理为向量,我们需要用到向量模型。 DB-GPT支持许多的向量模型,比如代理模型OpenAI Embedding,本地模型text2vec,当然也支持集群模式部署好之后,通过API的方式来使用。下面是几种方式的使用案例。
三种不同的向量模型使用方式
OpenAI Embedding API
from dbgpt.rag.embedding import DefaultEmbeddingFactoryembeddings = DefaultEmbeddingFactory.openai()
本地向量模型
from dbgpt.rag.embedding import DefaultEmbeddingFactoryembeddings = DefaultEmbeddingFactory.default("/data/models/text2vec-large-chinese")
集群部署下API调用
from dbgpt.rag.embedding import DefaultEmbeddingFactoryembeddings = DefaultEmbeddingFactory.remote(api_url="http://localhost:8100/api/v1/embeddings",api_key="{your_api_key}",model_name="text2vec")
在本案例中,我们使用本地向量模型来完成相关的操作。
获取知识并存储在向量数据库中
如下的DAG程序可以通过URL获取数据,并将其存储在向量数据库中。
from dbgpt.rag.embedding import DefaultEmbeddingFactoryembeddings = DefaultEmbeddingFactory.default("DB-GPT/models/text2vec-large-chinese")import asyncioimport shutilfrom dbgpt.core.awel import DAGfrom dbgpt.rag import ChunkParametersfrom dbgpt.rag.knowledge import KnowledgeTypefrom dbgpt.rag.operators import EmbeddingAssemblerOperator, KnowledgeOperatorfrom dbgpt.storage.vector_store.chroma_store import ChromaVectorConfigfrom dbgpt.storage.vector_store.connector import VectorStoreConnector# Delete old vector store directory(/tmp/awel_rag_test_vector_store)shutil.rmtree("/tmp/awel_rag_test_vector_store", ignore_errors=True)# 2.init vector_connectorvector_connector = VectorStoreConnector.from_default("Chroma",vector_store_config=ChromaVectorConfig(name="test_vstore",persist_path="/tmp/awel_rag_test_vector_store",),embedding_fn=embeddings)# 3. write awel assembler_taskwith DAG("load_knowledge_dag") as knowledge_dag:# Load knowledge from URLknowledge_task = KnowledgeOperator(knowledge_type=KnowledgeType.URL.name)assembler_task = EmbeddingAssemblerOperator(vector_store_connector=vector_connector,chunk_parameters=ChunkParameters(chunk_strategy="CHUNK_BY_SIZE"))knowledge_task >> assembler_taskchunks = asyncio.run(assembler_task.call("https://docs.dbgpt.site/docs/latest/awel/"))print(f"Chunk length: {chunks}")
从向量库中检索知识
你可以检索相关的知识,从向量数据库中。
from dbgpt.core.awel import MapOperatorfrom dbgpt.rag.operators import EmbeddingRetrieverOperatorwith DAG("retriever_dag") as retriever_dag:retriever_task = EmbeddingRetrieverOperator(top_k=3,vector_store_connector=vector_connector,)content_task = MapOperator(lambda cks: "\n".join(c.content for c in cks))retriever_task >> content_taskchunks = asyncio.run(content_task.call("What is the AWEL?"))print(chunks)
准备LLM
可以有几种方式来调用LLM归纳总结,这里我们使用OpenAI的API
pip install openaiexport OPENAI_API_KEY=sk-xxexport OPENAI_API_BASE=https://xx:80/v1
使用代理模型Client来连接到OpenAI API
from dbgpt.model.proxy import OpenAILLMClientllm_client = OpenAILLMClient()
创建RAG程序
最后我们创建一个rag程序,来进行智能问答。
from dbgpt.core.awel import InputOperator, JoinOperator, InputSourcefrom dbgpt.core.operators import PromptBuilderOperator, RequestBuilderOperatorfrom dbgpt.model.operators import LLMOperatorprompt = """Based on the known information below, provide users with professional and concise answers to their questions.If the answer cannot be obtained from the provided content, please say:"The information provided in the knowledge base is not sufficient to answer this question.".It is forbidden to make up information randomly. When answering, it is best to summarize according to points 1.2.3.known information:{context}question:{question}"""with DAG("llm_rag_dag") as rag_dag:input_task = InputOperator(input_source=InputSource.from_callable())retriever_task = EmbeddingRetrieverOperator(top_k=3,vector_store_connector=vector_connector,)content_task = MapOperator(lambda cks: "\n".join(c.content for c in cks))merge_task = JoinOperator(lambda context, question: {"context": context, "question": question})prompt_task = PromptBuilderOperator(prompt)# The model is gpt-3.5-turbo, you can replace it with other models.req_build_task = RequestBuilderOperator(model="gpt-3.5-turbo")llm_task = LLMOperator(llm_client=llm_client)result_task = MapOperator(lambda r: r.text)input_task >> retriever_task >> content_task >> merge_taskinput_task >> merge_taskmerge_task >> prompt_task >> req_build_task >> llm_task >> result_taskprint(asyncio.run(result_task.call("What is the AWEL?")))
输出如下:
AWEL stands for Agentic Workflow Expression Language. It is a set of intelligent agent workflow expression language specially designed for large model application development. AWEL provides functionality and flexibility for development of business logic for LLMs applications without the need to focus on cumbersome model and environment details. It adopts a layered API design, consisting of the operator layer, AgentFrame layer, and DSL layer. The operator layer includes basic operation atoms in the LLM application development process such as retrieval, vectorization, model interaction, and prompt processing.
恭喜你,到这里你已经完整的运行完了通过dbgpt sdk来开发一个RAG程序的所有过程。
完整代码
整个程序完整代码如下:
import asyncioimport shutilfrom dbgpt.core.awel import DAG, MapOperator, InputOperator, JoinOperator, InputSourcefrom dbgpt.core.operators import PromptBuilderOperator, RequestBuilderOperatorfrom dbgpt.rag import ChunkParametersfrom dbgpt.rag.knowledge import KnowledgeTypefrom dbgpt.rag.operators import EmbeddingAssemblerOperator, KnowledgeOperator, EmbeddingRetrieverOperatorfrom dbgpt.rag.embedding import DefaultEmbeddingFactoryfrom dbgpt.storage.vector_store.chroma_store import ChromaVectorConfigfrom dbgpt.storage.vector_store.connector import VectorStoreConnectorfrom dbgpt.model.operators import LLMOperatorfrom dbgpt.model.proxy import OpenAILLMClient# Here we use the openai embedding model, if you want to use other models, you can# replace it according to the previous example.embeddings = DefaultEmbeddingFactory.openai()# Here we use the openai LLM model, if you want to use other models, you can replace# it according to the previous example.llm_client = OpenAILLMClient()# Delete old vector store directory(/tmp/awel_rag_test_vector_store)shutil.rmtree("/tmp/awel_rag_test_vector_store", ignore_errors=True)vector_connector = VectorStoreConnector.from_default("Chroma",vector_store_config=ChromaVectorConfig(name="test_vstore",persist_path="/tmp/awel_rag_test_vector_store",),embedding_fn=embeddings)with DAG("load_knowledge_dag") as knowledge_dag:# Load knowledge from URLknowledge_task = KnowledgeOperator(knowledge_type=KnowledgeType.URL.name)assembler_task = EmbeddingAssemblerOperator(vector_store_connector=vector_connector,chunk_parameters=ChunkParameters(chunk_strategy="CHUNK_BY_SIZE"))knowledge_task >> assembler_taskchunks = asyncio.run(assembler_task.call("https://docs.dbgpt.site/docs/latest/awel/"))print(f"Chunk length: {len(chunks)}\n")prompt = """Based on the known information below, provide users with professional and concise answers to their questions.If the answer cannot be obtained from the provided content, please say:"The information provided in the knowledge base is not sufficient to answer this question.".It is forbidden to make up information randomly. When answering, it is best to summarize according to points 1.2.3.known information:{context}question:{question}"""with DAG("llm_rag_dag") as rag_dag:input_task = InputOperator(input_source=InputSource.from_callable())retriever_task = EmbeddingRetrieverOperator(top_k=3,vector_store_connector=vector_connector,)content_task = MapOperator(lambda cks: "\n".join(c.content for c in cks))merge_task = JoinOperator(lambda context, question: {"context": context, "question": question})prompt_task = PromptBuilderOperator(prompt)# The model is gpt-3.5-turbo, you can replace it with other models.req_build_task = RequestBuilderOperator(model="gpt-3.5-turbo")llm_task = LLMOperator(llm_client=llm_client)result_task = MapOperator(lambda r: r.text)input_task >> retriever_task >> content_task >> merge_taskinput_task >> merge_taskmerge_task >> prompt_task >> req_build_task >> llm_task >> result_taskprint(asyncio.run(result_task.call("What is the AWEL?")))
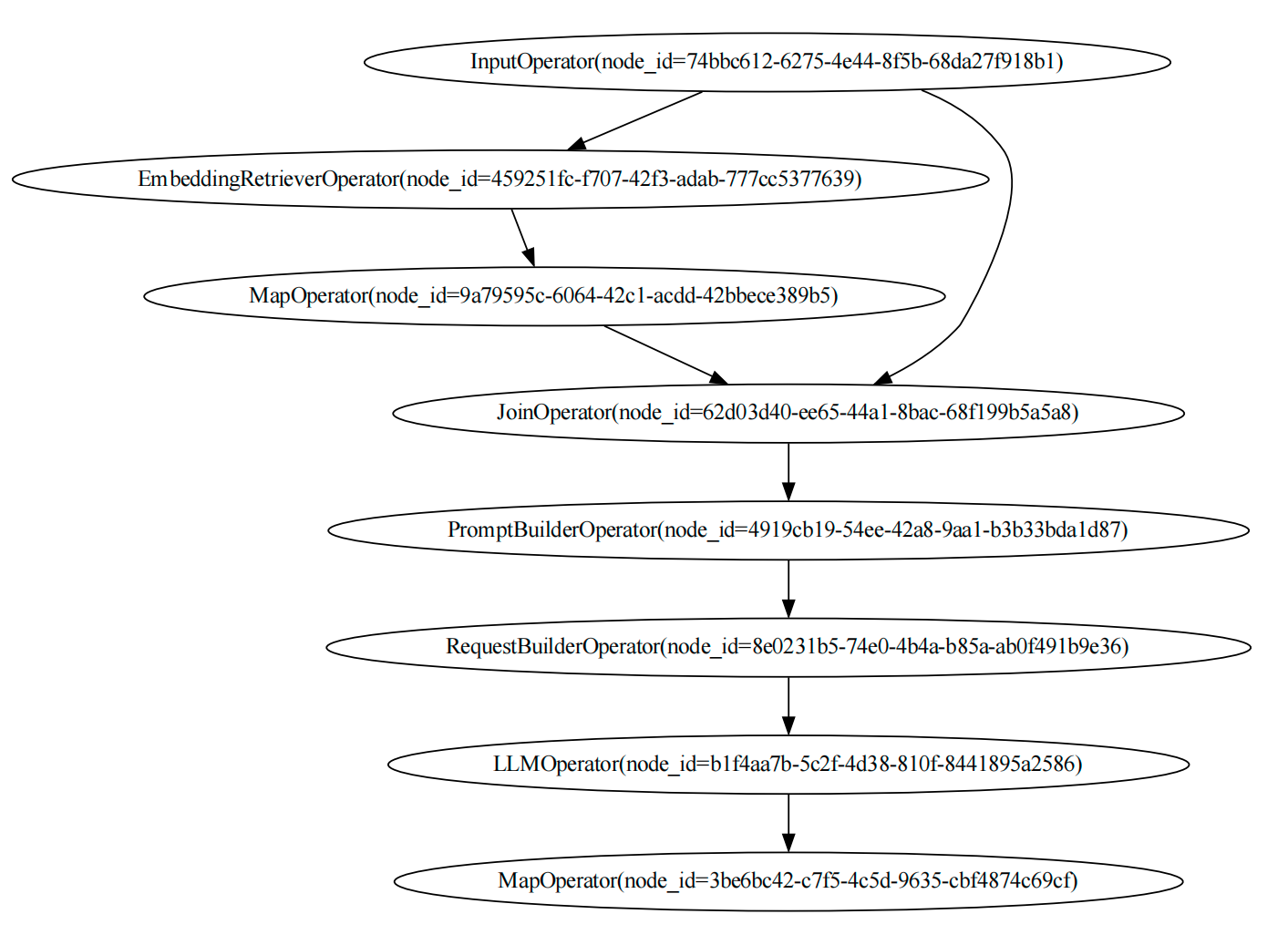
可视化DAGs
可以通过如下代码进行DAG可视化
knowledge_dag.visualize_dag()rag_dag.visualize_dag()
如果在 Jupyter Notebook 中执行代码,可以在笔记本中看到 DAG。
display(knowledge_dag.show())display(rag_dag.show())
Knowledge_dag可视化图如下:

rag_dag可视化图如下