指针的声明一般要加*,在类型名之后加*,来声明指针变量,指针变量存储的是地址。
- A pointer is declared like a variable, but with * after the type.
- What stored in a pointer variable is an address.
- Operator
&can take the address of an object or a variable of fundamental types.&: 取地址符号
- Operator can *take the content that the pointer points to
*: 对该指针取内容 ```cpp int num = 10; int p1 = NULL, p2 = NULL; // declaration two pointers, initialized to 0, NULL == 0 p1 = # // take the address of num, assign to p1 p2 = # // take the address of num, assign to p2
p1 = 20; // assign 20 to num p2 = 30; // assign 20 to num
How pointers work?| 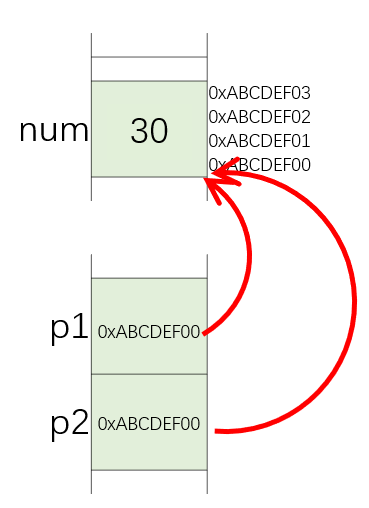 | ```cpp#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main(){int num = 10;int * p1 = NULL, * p2 = NULL; // declaration, initialize to 0p1 = # // take the address of num, assign to p1p2 = # // take the address of num, assign to p2cout << "num = " << num << endl;*p1 = 20; // assign to numcout << "num = " << num << endl;*p2 = 30; // assign to numcout << "num = " << num << endl;cout << "p1 = " << *p1 << endl; // p1's value has been modifiedreturn 0;}// results// num = 10// num = 20// num = 30// p1 = 30
| | —- | —- |
num是个整数,要占用四个字节,
Structure member accessing ,结构体成员读取
取成员的两种方法,等价:
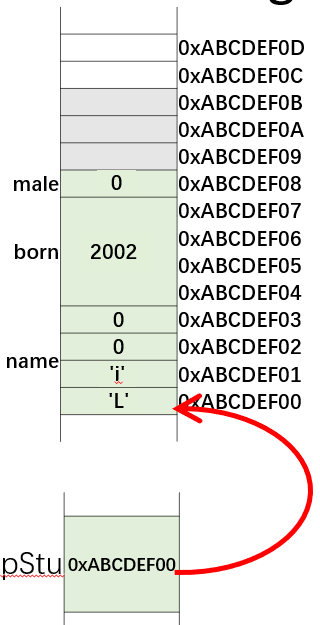
struct Student { char name[4]; int born; bool male; };
int main() { Student stu = {“Yu”, 2000, true}; Student *pStu = &stu;
cout << stu.name << " was born in " << stu.born
<< ". Gender: " << (stu.male ? "male" : "female") << endl;
strncpy(pStu->name, "Li", 4);
pStu->born = 2001;
(*pStu).born = 2002;
pStu->male = false;
cout << stu.name << " was born in " << stu.born
<< ". Gender: " << (stu.male ? "male" : "female") << endl;
printf("Address of stu: %p\n", pStu); //C style
cout << "Address of stu: " << pStu << endl; //C++ style
cout << "Address of stu: " << &stu << endl;
cout << "Address of member name: " << &(pStu->name) << endl;
cout << "Address of member born: " << &(pStu->born) << endl;
cout << "Address of member male: " << &(pStu->male) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(pStu) = " << sizeof(pStu) << endl;
return 0;
}
// results // Yu was born in 2000. Gender: male // Li was born in 2002. Gender: female // Address of stu: 0x7ffda985df3c // Address of stu: 0x7ffda985df3c // Address of stu: 0x7ffda985df3c // Address of member name: 0x7ffda985df3c // Address of member born: 0x7ffda985df40 // Address of member male: 0x7ffda985df44 // sizeof(pStu) = 8
|
| --- | --- |
Print out the addresses
- Since the value of a pointer is an address, we can print it out
- The address should be an unsigned 32-bit or 64-bit integer.
```cpp
cout << "sizeof(pStu) = " << sizeof(pStu) << endl; // 取决于系统是32位(4),还是64位(8)
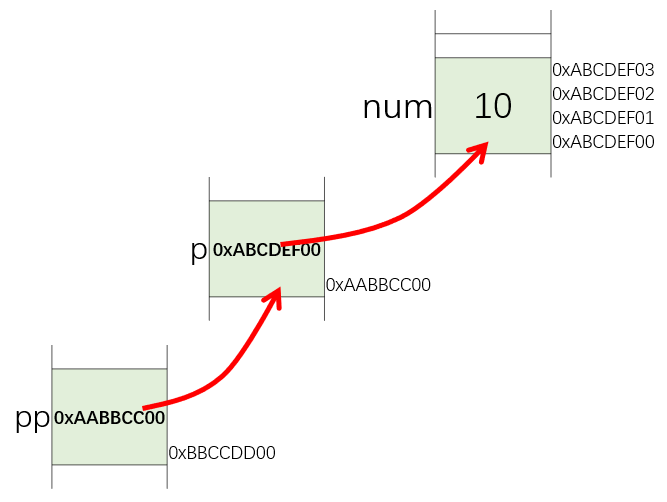
指针就是存储地址的特殊变量。
Pointers are variables, they also have addresses。
指针是一个变量,所以指针也有地址
|  | ```cpp
| ```cpp
include
using namespace std;
int main() { int num = 10; int p = # int **pp = &p; // 指针的指针 (*pp) = 20;
cout << "num = " << num << endl;
return 0;
} // results // num = 20
|
| --- | --- |
Constant pointers 常数指针
```cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int foo(const char *p)
{
// the value that p points to cannot be changed
// play a trick?
char *p2 = p; //syntax error;const指针赋值给普通指针是不允许的
//...
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int num = 1;
int another = 2;
// You cannot change the value that p1 points to through p1
// 指针指向的内容不可通过该指针去修改
const int *p1 = #
*p1 = 3; //error
num = 3; //okay
// You cannot change value of p2 (address)
// 可以修改指针指向的内容,但是不可以修改指针指向的地址
int *const p2 = #
*p2 = 3; //okay
p2 = &another; //error,始终指向num的地址,不可修改地址
//You can change neither
const int *const p3 = #
*p3 = 3; //error
p3 = &another; // error
return 0;
}
 | ```cpp
| ```cpp
