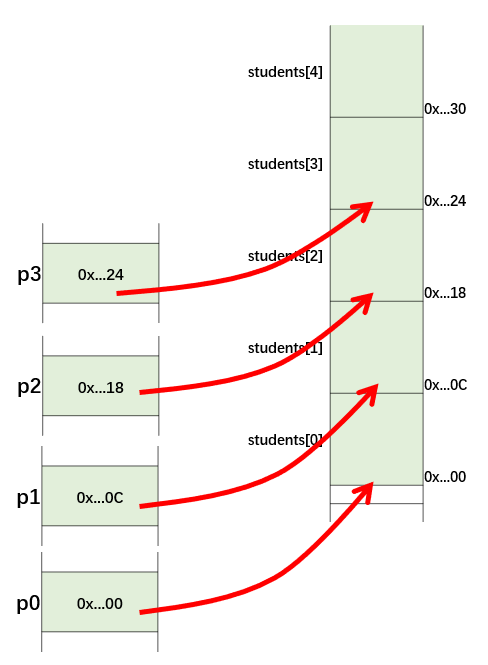
The addresses of array elements
Use & operator to get the addresses of elements
数组中每个元素都放在内存中
|  | ```cpp
| ```cpp
include
using namespace std;
struct Student { char name[4]; int born; bool male; };
int main() { // Part One Student students[128]; Student p0 = &students[0]; Student p1 = &students[1]; Student p2 = &students[2]; Student p3 = &students[3];
printf("p0 = %p\n", p0);printf("p1 = %p\n", p1);printf("p2 = %p\n", p2);printf("p3 = %p\n", p3);//the same behaviorstudents[1].born = 2000;p1->born = 2000;// Part Two// You can consider an array name as a pointerprintf("&students = %p\n", &students);printf("students = %p\n", students);printf("&students[0] = %p\n", &students[0]);Student *p = students;p[0].born = 2000;p[1].born = 2001;p[2].born = 2002;printf("students[0].born = %d\n", students[0].born);printf("students[1].born = %d\n", students[1].born);printf("students[2].born = %d\n", students[2].born);return 0;
}
// results // p0 = 0x7ffd3e5b2f10 // p1 = 0x7ffd3e5b2f1c // p2 = 0x7ffd3e5b2f28 // p3 = 0x7ffd3e5b2f34 // &students = 0x7ffd3e5b2f10 // students = 0x7ffd3e5b2f10 // &students[0] = 0x7ffd3e5b2f10 // students[0].born = 2000 // students[1].born = 2001 // students[2].born = 2002
|
| --- | --- |
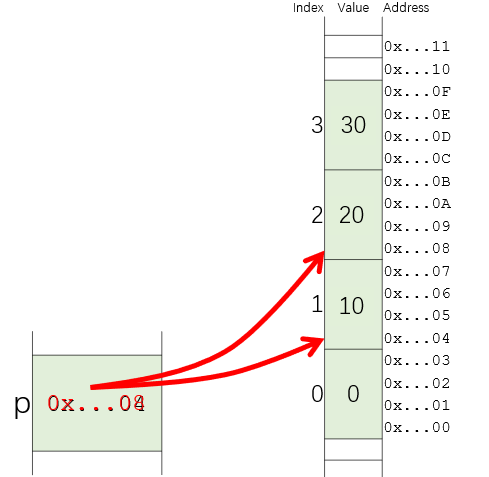
Pointer arithmetic 指针的代数操作
- `p + num` or `num + p` points to the **num-th element **of the array p.
- 对指针p的地址进行偏移,**偏移量为num个元素**,不是加一个字节
- `p - num` points to the -num-th element.
|  | ```cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define PRINT_ARRAY(array, n) \
for (int idx = 0; idx < (n); idx++) \
cout << "array[" << idx << "] = " << (array)[idx] << endl;
int main()
{
int numbers[4] = {0, 1, 2, 3};
PRINT_ARRAY(numbers, 4)
int *p = numbers + 1; // point to the element with value 1
p++; // point to the element with value 2
cout << "numbers = " << numbers << endl;
cout << "p = " << p << endl;
cout << "p0 = " << p[0] << endl;
*p = 20; //change 2 to 20
*(p - 1) = 10; //change 1 to 10
p[1] = 30; //change 3 to 30 ???
PRINT_ARRAY(numbers, 4)
return 0;
}
// array[0] = 0
// array[1] = 1
// array[2] = 2
// array[3] = 3
// numbers = 0x7fff47f36170
// p = 0x7fff47f36178
// p0 = 2
// array[0] = 0
// array[1] = 10
// array[2] = 20
// array[3] = 30
| | —- | —- |
指针的代数运算也很容易发生越界,一定注意。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a;
int num = 0;
int *p = #
p[-1] = 2; //out of bound
p[0] = 3; //okay
*(p + 1) = 4; //out of bound
cout << "num = " << num << endl;
return 0;
}
Differences between a pointer and an array
- Array is a constant pointer.
- The total size of all elements in an array can be got by operator sizeof
- sizeof operator to a pointer will return the size of the address (4 or 8) ```cpp int numbers[4] = {0, 1, 2, 3}; int p = numbers; cout << sizeof(numbers) << endl; //4sizeof(int) cout << sizeof(p) << endl; // 4 or 8 cout << sizeof(double *) << endl; // 4 or 8
```

