算数运算
Constant numbers 常数
整数类型95 // decimal 10进制0137// octal 8进制0x5F // hexadecimal 16进制95 // int95u // unsigned int95l // long95ul // unsigned long95lu // unsigned long
浮点数类型3.14159 // 3.141596.02e23 // 6.02 x 10^231.6e-19 // 1.6 x 10^-193.0 // 3.06.02e23L // long double6.02e23f // float6.02e23 // double
const type qualifier:const类型限定符
const float PI = 3.1415926f;PI += 1; //error!
- If a variable/object is const-qualified, it cannot be modified. 变量被const修饰后,其值不可更改
- It must be initialized when you define it. const变量定义时就要初始化,可以替代宏定义
auto (since C++11)
- auto is placeholder type specifier.
- The type of the variable will be deduced from its initializer. 数据类型由变量初始化的时候自动识别
Question: ```cpp auto a = 2; // type of a is intauto a = 2; // type of a is intauto bc = 2.3; // type of b is doubleauto c ; //valid in C, error in C++auto d = a * 1.2; // double
// will a be converted to a double type variable? a = 2.3; // No! 2.3 will be converted to a int 2, then assigned to a
变量的类型一旦在初始化的阶段确定之后,就不会在变Arithmetic operators:算数操作符<br />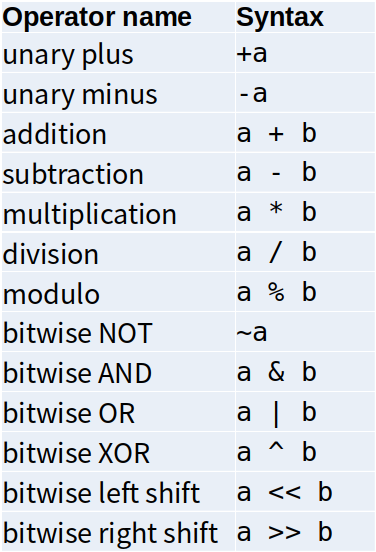Operator Precedence 运算符优先级<br />If you cannot remember the precedence, use parentheses(括号)!1. a++1. ++a1. * /1. + -1. << >>Assignment Operators 赋值操作| a = b | a += b | a -= b | a *= b | a /= b | a %= b || --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- || a &= b | a |= b | a ^= b | a <<= b | a >>= b | |Increment/decrement| a++ | ++a | a-- | --a || --- | --- | --- | --- |```cppint a = 3;int b = a++; // What's the value of b? -> b = 3, a = 4,先取值在自增int c = ++a; // What's the value of c? -> c = 5, 先自增,再取值
Data type conversions
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int num_int1 = 9; // assigning an int value to num_int1
int num_int2 = 'C'; // 'C' is a char, implicit conversion to int type
int num_int3 = (int)'C'; // explicit conversion, C-style
int num_int4 = int('C'); // explicit conversion, function style
int num_int5 = 2.8; //implicit conversion
float num_float = 2.3; // implicit conversion from double to float, may loss precision
short num_short = 650000;
cout << "num_short = " << num_short << endl;
return 0;
}
DANGER:
- The source code can be compiled successfully (even with warning messages) when the data types do not match.
- Please use explicit conversion if possible
Data loss
上图中从上到下,数据存储范围从长到短,如果从上面类型转换到下面类型,数据会损失精度。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int num_int1 = 0x7ABCDEF0;
float num_int_float = num_int1;
int num_int2 = (int)(num_int_float);
cout << "num_int1 = " << num_int1 << endl;
cout << "num_int_float = " << num_int_float << endl;
cout << "num_int2 = " << num_int2 << endl;
return 0;
}
Will num_int2 be the same with num_int1? Nope
num_int1 = 2059198192
num_int_float = 2.0592e+09
num_int2 = 2059198208
Operator Associativity 结合率
- Left-to-right associativity or a right-to-left associativity
The following two lines are equivalent.
int i = 17 / 5 * 5; int i = (17 / 5) * 5;Divisions
Both operands are integers
- Perform integer division 整数除法
- Any fractional part of the answer is discarded to make the result an integer
float f = 17 / 5; // f will be 3.f, not 3.4f.
One or both operands are floating-point numbers
- Perform floating-point division
float f = 17 / 5.f; // f will be 3.4f.
- Perform floating-point division
Distinct Operations for Different Types
int,long,float,double: four kinds of operationsIf the operands are not the four types, automatic convert their types
unsigned char a = 255; unsigned char b = 1; int c = a + b; // c = 256如果两个unsigned char类型的变量相加,只能转换成int类型相加。
The operands will be converted to one of the four types without losing data: int, long, float, double
C/C++ Supposes
- You (the programmer) are smart enough!
- You know what exactly the source code means!
C++ 非常灵活,很容易出bug,所以一定要谨慎,明晰语句作用和原理,对每个操作、符号的原理进行深刻理解

