函数重载
Why to overload?
// C99<math.h>double round (double x);float roundf (float x);long double roundl (long double x);
// C++11<cmath>double round (double x);float round (float x);long double round (long double x);
- Which function to choose?
using namespace std;
int sum(int x, int y) { cout << “sum(int, int) is called” << endl; return x + y; } float sum(float x, float y) { cout << “sum(float, float) is called” << endl; return x + y; } double sum(double x, double y) { cout << “sum(double, double) is called” << endl; return x + y; }
// //Is the following definition correct? // double sum(int x, int y) // { // cout << “sum(int, int) is called” << endl; // return x + y; // }
int main() {
cout << "sum = " << sum(1, 2) << endl;cout << "sum = " << sum(1.1f, 2.2f) << endl;cout << "sum = " << sum(1.1, 2.2) << endl;//which function will be called?// cout << "sum = " << sum(1, 2.2) << endl;return 0;
}
// sum = sum(int, int) is called
// 3
// sum = sum(float, float) is called
// 3.3
// sum = sum(double, double) is called
// 3.3
``
上面例子中,三个函数虽然名字相同sum`,但是参数列表不同,所以,这三个函数不是相同的函数。
如果有两个函数,名字和参数列表完全相同,但是返回类型不同,这时候编译会出错,编译器会觉得这是相同的函数,但是返回类型不同,有两种不同的实现,相当于函数重定义,所以不被允许。
对比上述代码中的第五行和第22行的sum函数,函数名和参数列表都是相同的,但是返回类型不同,一个是int,一个是double,这是不能够编译的。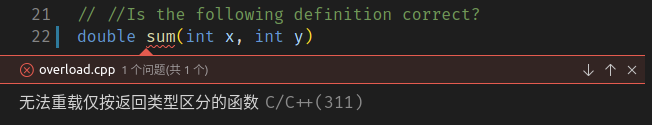
将36行打开,编译也会报错,会发生歧义。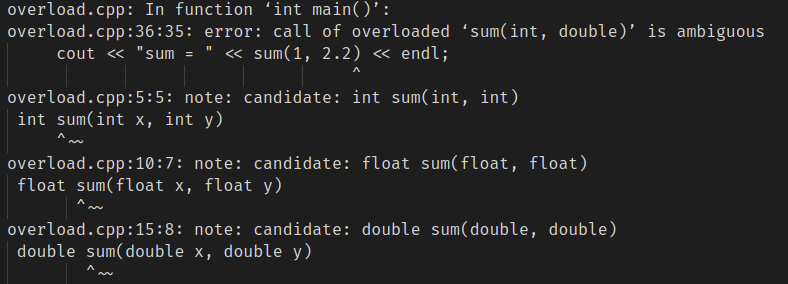
如果只保留第一个sum函数,运行36行代码,编译会有警告的通过,警告:隐式的类型转化 double -> int
:::info 函数调用不应该有歧义 :::

