构建速度
1. 优化 babel-loader
{test: /\.js$/,use: ['babel-loader?cacheDirectory'], // 开启缓存,未改变部分不重新编译include: path.resolve(__dirname, 'src') // 明确范围/*排除范围,include和exclude两者选一个即可exclude: path.resolve(__dirname, 'node_modules')*/}
2. webpack.IgnorePlugin 避免引入无用模块
例如 import moment from ‘moment’,默认会引入所有语言版本的js代码,代码过大
先是不使用IgnorePlugin
// 引入moment,默认会引入全部语言包import moment from 'moment'moment.locale('zh-cn')console.log('local', moment.locale())console.log('date',moment().format('ll'))
打包查看index.[contentHash:8].js的尺寸,这个我关闭了代码分割功能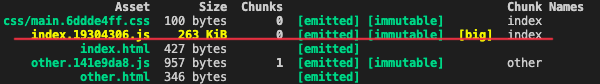
263kb,并且高亮警告⚠️了
我们在webpack.prod.js中配置一个新的plugin
// webpack.pro.jsplugins: [// 忽略 moment 下的 /locale 目录new webpack.IgnorePlugin(/\.\/locale/, /moment/),]// 但是这么一忽略,moment的中文语言包也没了,于是需要修改index.js
// index.js// 引入moment,举例IgnorePluginimport moment from 'moment'// 手动引入中文语言包import 'moment/locale/zh-cn'moment.locale('zh-cn')console.log('local', moment.locale())console.log('date',moment().format('ll'))
再次打包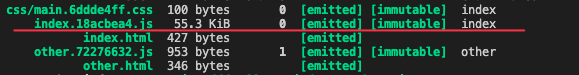
3. noParse避免重复打包
像 react.min.js vue.min.js都是打包好的,文件就没有采用模块化
module.exports = {module: {// 独立完整的 `vue.min.js` 文件就没有采用模块化// 忽略对 `react.min.js` 文件的递归解析处理noParse: [/vue\.min\.js$/]}}
IgnorePlugin 和 noParse 的区别
- IgnorePlugin 直接不引入,代码中没有
-
4. happyPack 多进程打包
JS单线程,开启多进程打包
- 提高构建速度(特别是多核CPU) ```javascript // webpack.js // 这里babel-loader就不能放在common.js中了
const HappyPack = require(‘happypack’)
module.exports = { / …… / module: { rules: [ { test: /.js$/, // 把对 .js 文件的处理权交给 id 为 babel 的 HappyPack 实例 use: [‘happypack/loader?id=babel’], include: srcPath } ], / …… / plugins: [ / …… / new HappyPack({ // 用唯一标识 id 来代表当前的 HappyPack 是用来处理一类特定的文件 id: ‘babel’, // 如何处理 .js 文件,用法和 loader 配置一样 loaders: [‘babel-loader?cacheDirectory’] }) ] } }
<a name="JejLT"></a>## 5. ParallelUglifyPlugin多进程压缩JS- webpack内置Uglify工具压缩JS- JS单线程,开启多进程压缩更快- 和happyPack同理```javascript// webpack.prod.jsconst ParallelUglifyPlugin = require('webpack-parallel-uglify-plugin')module.exports = {/* ...... */plugins: [new ParallelUglifyPlugin({uglifyJS: {output: {beautify: false, // 不美化输出,最紧凑的输出comment: false // 不保留注释,删除所有注释},compress: {// 删除所有consolelog语句drop_console: true,// 内嵌定义了但是只用到一次的变量collapse_vars: true,// 提取出出现多次但是还没有定义成变量去引用的静态值reduce_vars: true}}})]}
关于开启多进程
- 项目较大,打包较慢,开启多进程能提高速度
- 项目较小,打包很快,开启多进程会降低速度(进程开销)
- 按需使用
6. 自动刷新
一般不用自己配置,devServer会带上这个功能
module.exports = {watch: true, // 开启监听,默认为false// 配置监听watchOptions: {ignored: /node_modules/, // 忽略哪些// 监听到变化后会等300ms再去执行动作,防止文件更新太快导致重新编译频率太高aggregateTimeout: 300, // 默认为 300mspoll: 1000 // 默认每隔1000毫秒询问一次}}
7. 热更新
自动刷新需要刷新整个网页,速度较慢,且状态会丢失。
热更新:新代码生效,网页不刷新,状态不丢失
// webpack.dev.jsconst HotModuleReplacementPlugin = require('webpack/lib/HotModuleReplacementPlugin');moduel.exports = {mode: 'development',entry: {// 配置热更新需要更改的地方// index: path.join(srcPath, 'index.js')index: ['webpack-dev-server/client?http://localhost:8080/','webpack/hot/dev-server',path.join(srcPath, 'index.js')],other: path.join(srcPath, 'other.js')},/* ...... */plugins: [new HotModuleReplacementPlugin()],devServer: {/* ...... */hot: true //开启热更新}}
配置热更新还需要主动配置运行热更新的模块
// index.jsimport { sum } from './math'// 例如我们运行 math.js 文件支持热更新// 增加开启热更新之后的代码逻辑if(module.hot) {module.hot.accept(['./math'], () => {// 这里写模块热更新后的回调逻辑const sumRes = sum(10, 80)console.log('sumRes in hot', sumRes)})}
8. DllPlugin 动态链接库插件
- 前端框架如 vue react,体积大,构建慢
- 较稳定,不常升级版本
同一个版本只构建一次即可,不用每次都重新构建
webpack已内置DllPlugin支持
- DllPlugin 打包出dll文件
- DllReferencePlugin 使用dll文件
第一步
配置打包dll文件的配置文件
// webpack.dll.jsconst path = require('path')const DllPlugin = require('webpack/lib/DllPlugin')const { srcPath, distPath } = require('./paths')module.exports = {mode: 'development',// JS 执行入口文件entry: {// 把 React 相关模块的放到一个单独的动态链接库react: ['react', 'react-dom']},output: {// 输出的动态链接库的文件名称,[name] 代表当前动态链接库的名称,// 也就是 entry 中配置的 react 和 polyfillfilename: '[name].dll.js',// 输出的文件都放到 dist 目录下path: distPath,// 存放动态链接库的全局变量名称,例如对应 react 来说就是 _dll_react// 之所以在前面加上 _dll_ 是为了防止全局变量冲突library: '_dll_[name]',},plugins: [// 接入 DllPluginnew DllPlugin({// 动态链接库的全局变量名称,需要和 output.library 中保持一致// 该字段的值也就是输出的 manifest.json 文件 中 name 字段的值// 例如 react.manifest.json 中就有 "name": "_dll_react"name: '_dll_[name]',// 描述动态链接库的 manifest.json 文件输出时的文件名称path: path.join(distPath, '[name].manifest.json'),}),],}
第二步,运行打包
npx webpack --config webpack.dll.js
我们会在dist目录下看到,react.dll.js 和 react.manifest.json 文件
第三步,使用
首先模板文件需要修改
<!-- index.html --><!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"><title>Document</title></head><body><div id="root"></div>需要配置引入这个js文件<script src="./react.dll.js"></script></body></html>
在webpack.dev.js中
const path = require('path')const webpack = require('webpack')const { smart } = require('webpack-merge')const webpackCommonConf = require('./webpack.common.js')const { srcPath, distPath } = require('./paths')// 第一,引入 DllReferencePluginconst DllReferencePlugin = require('webpack/lib/DllReferencePlugin');module.exports = smart(webpackCommonConf, {mode: 'development',module: {rules: [{test: /\.js$/,loader: ['babel-loader'],include: srcPath,exclude: /node_modules/ // 第二,不要再转换 node_modules 的代码},]},plugins: [new webpack.DefinePlugin({// window.ENV = 'production'ENV: JSON.stringify('development')}),// 第三,告诉 Webpack 使用了哪些动态链接库new DllReferencePlugin({// 描述 react 动态链接库的文件内容manifest: require(path.join(distPath, 'react.manifest.json')),}),],devServer: {port: 8080,progress: true, // 显示打包的进度条contentBase: distPath, // 根目录open: true, // 自动打开浏览器compress: true, // 启动 gzip 压缩// 设置代理proxy: {// 将本地 /api/xxx 代理到 localhost:3000/api/xxx'/api': 'http://localhost:3000',// 将本地 /api2/xxx 代理到 localhost:3000/xxx'/api2': {target: 'http://localhost:3000',pathRewrite: {'/api2': ''}}}}})

