对流操作完成之后,如果需要将流的结果保存到数组或集合中,可以收集流中的数据
1.1 目标
掌握Stream流中的结果到集合中
掌握Stream流中的结果到数组中
1.2 Stream流中的结果到集合中
Stream流提供 collect 方法,其参数需要一个 java.util.stream.Collector 接口对象来指定收集到哪 种集合中。
java.util.stream.Collectors 类提供一些方法,可以作为 Collector`接口的实例:
- public static Collector> toList() :转换为 List 集合。
- public static Collector> toSet() :转换为 Set 集合。
下面是这两个方法的基本使用代码:

// 将流中数据收集到集合中@Testpublic void testStreamToCollection() {Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("aa", "bb", "cc", "bb");// 将流中数据收集到集合中// collect收集流中的数据到集合中// List<String> list = stream.collect(Collectors.toList());// System.out.println("list = " + list);// Set<String> set = stream.collect(Collectors.toSet());// System.out.println("set = " + set);// 收集到指定的集合中ArrayList// ArrayList<String> arrayList = stream.collect(Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new));// System.out.println("arrayList = " + arrayList);HashSet<String> hashSet = stream.collect(Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new));System.out.println("hashSet = " + hashSet);}
1.3 Stream流中的结果到数组中
Stream提供 toArray 方法来将结果放到一个数组中,返回值类型是Object[]的:

其使用场景如:

// 将流中数据收集到数组中@Testpublic void testStreamToArray() {Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("aa", "bb", "cc");// 转成Object数组不方便// Object[] objects = stream.toArray();// for (Object o : objects) {// System.out.println("o = " + o);// }// String[]String[] strings = stream.toArray(String[]::new);for (String string : strings) {System.out.println("string = " + string + ", 长度: " + string.length());}}
1.4 对流中数据进行聚合计算
当我们使用Stream流处理数据后,可以像数据库的聚合函数一样对某个字段进行操作。比如获取最大值,获取最小
值,求总和,平均值,统计数量。

// 其他收集流中数据的方式(相当于数据库中的聚合函数)@Testpublic void testStreamToOther() {Stream<Student> studentStream = Stream.of(new Student("赵丽颖", 58, 95),new Student("杨颖", 56, 88),new Student("迪丽热巴", 56, 99),new Student("柳岩", 52, 77));// 获取最大值// Optional<Student> max = studentStream.collect(Collectors.maxBy((s1, s2) -> s1.getSocre() - s2.getSocre()));// System.out.println("最大值: " + max.get());// 获取最小值// Optional<Student> min = studentStream.collect(Collectors.minBy((s1, s2) -> s1.getSocre() - s2.getSocre()));// System.out.println("最小值: " + min.get());// 求总和// Integer sum = studentStream.collect(Collectors.summingInt(s -> s.getAge()));// System.out.println("总和: " + sum);// 平均值// Double avg = studentStream.collect(Collectors.averagingInt(s -> s.getSocre()));// Double avg = studentStream.collect(Collectors.averagingInt(Student::getSocre));// System.out.println("平均值: " + avg);// 统计数量Long count = studentStream.collect(Collectors.counting());System.out.println("统计数量: " + count);}
1.5 对流中数据进行分组
当我们使用Stream流处理数据后,可以根据某个属性将数据分组:


// 分组@Testpublic void testGroup() {Stream<Student> studentStream = Stream.of(new Student("赵丽颖", 52, 95),new Student("杨颖", 56, 88),new Student("迪丽热巴", 56, 55),new Student("柳岩", 52, 33));// Map<Integer, List<Student>> map = studentStream.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getAge));// 将分数大于60的分为一组,小于60分成另一组Map<String, List<Student>> map = studentStream.collect(Collectors.groupingBy((s) -> {if (s.getSocre() > 60) {return "及格";} else {return "不及格";}}));map.forEach((k, v) -> {System.out.println(k + "::" + v);});}
效果:

1.6 对流中数据进行多级分组
还可以对数据进行多级分组:

// 多级分组
@Test
public void testCustomGroup() {
Stream<Student> studentStream = Stream.of(
new Student("赵丽颖", 52, 95),
new Student("杨颖", 56, 88),
new Student("迪丽热巴", 56, 55),
new Student("柳岩", 52, 33));
// 先根据年龄分组,每组中在根据成绩分组
// groupingBy(Function<? super T, ? extends K> classifier, Collector<? super T, A, D> downstream)
Map<Integer, Map<String, List<Student>>> map = studentStream.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getAge, Collectors.groupingBy((s) -> {
if (s.getSocre() > 60) {
return "及格";
} else {
return "不及格";
}
})));
// 遍历
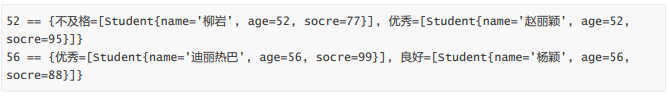
map.forEach((k, v) -> {
System.out.println(k);
// v还是一个map,再次遍历
v.forEach((k2, v2) -> {
System.out.println("\t" + k2 + " == " + v2);
});
});
}
效果:
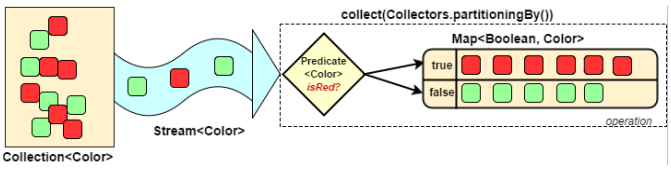
1.7 对流中数据进行分区
Collectors.partitioningBy 会根据值是否为true,把集合分割为两个列表,一个true列表,一个false列表。

// 分区
@Test
public void testPartition() {
Stream<Student> studentStream = Stream.of(
new Student("赵丽颖", 52, 95),
new Student("杨颖", 56, 88),
new Student("迪丽热巴", 56, 55),
new Student("柳岩", 52, 33));
Map<Boolean, List<Student>> map = studentStream.collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(s -> {
return s.getSocre() > 60;
}));
map.forEach((k , v) -> {
System.out.println(k + " :: " + v);
});
}
效果:

1.8 对流中数据进行拼接
Collectors.joining 会根据指定的连接符,将所有元素连接成一个字符串。

// 拼接
@Test
public void testJoining() {
Stream<Student> studentStream = Stream.of(
new Student("赵丽颖", 52, 95),
new Student("杨颖", 56, 88),
new Student("迪丽热巴", 56, 99),
new Student("柳岩", 52, 77));
// 根据一个字符串拼接: 赵丽颖__杨颖__迪丽热巴__柳岩
// String names = studentStream.map(Student::getName).collect(Collectors.joining("__"));
// 根据三个字符串拼接
String names = studentStream.map(Student::getName).collect(Collectors.joining("__", "^_^", "V_V"));
System.out.println("names = " + names);
}
效果:

1.9 小结
收集Stream流中的结果
到集合中: Collectors.toList()/Collectors.toSet()/Collectors.toCollection()
到数组中: toArray()/toArray(int[]::new)
聚合计算:
Collectors.maxBy/Collectors.minBy/Collectors.counting/Collectors.summingInt/Collectors.averagingInt
分组: Collectors.groupingBy
分区: Collectors.partitionBy
拼接: Collectors.joinging

