一、SpringBoot集成Swagger2
1.1、导入两个springfox的jar包
- Springfox-Swagger2
- Swagger-Springmvcs
二、使用Swagger
要求:jdk 1.8 + 否则Swagger2无法运行
步骤:
2.1、新建一个SpringBoot-web项目
2.2、添加Maven依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.springfox/springfox-swagger2 --><dependency><groupId>io.springfox</groupId><artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId><version>2.9.2</version></dependency><!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.springfox/springfox-swagger-ui --><dependency><groupId>io.springfox</groupId><artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId><version>2.9.2</version></dependency>
2.3、编写HelloController,测试确保运行成功!
2.4、要使用Swagger,我们需要编写一个配置类SwaggerConfig来配置 Swagger
@Configuration //配置类
@EnableSwagger2// 开启Swagger2的自动配置
public class SwaggerConfig {
}
2.5、访问测试 :http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html ,可以看到swagger的界面;
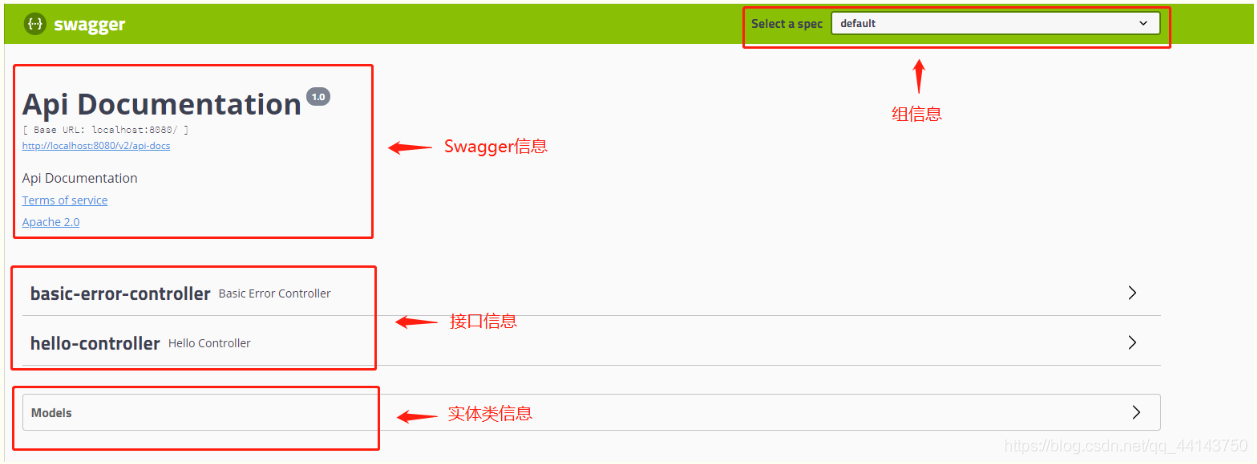
三、配置Swagger
3.1、Swagger实例Bean是Docket,所以通过配置Docket实例来配置Swaggger。
@Configuration //定义Java配置类
@EnableSwagger2 //开启Swagger2
public class SwaggerConfig {
@Bean //配置docket以配置Swagger具体参数
public Docket docket() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2);
}
}
3.2、可以通过apiInfo()属性配置文档信息
//配置Swagger的apiInfo信息
@Bean
public ApiInfo apiInfo(){
//作者信息
Contact CONTACT = new Contact("未进化的程序猿", "https://www.cnblogs.com/the-undeveloped-procedural-ape/", "486566947@qq.com");
return new ApiInfo("未进化的程序猿的Swagger日志", //Swagger文档标题
"Api Documentation",//Swagger文档描述
"v1.0",//Swagger文档版本号
"https://www.cnblogs.com/the-undeveloped-procedural-ape/",//博客地址
CONTACT,//作者信息
"Apache 2.0",
"http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0",
new ArrayList());
}
3.3、Docket 实例关联上 apiInfo()
@Bean
public Docket docket() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).apiInfo(apiInfo());
}
3.4、重启项目,访问测试 http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html;
四、配置扫描接口
4.1、构建Docket时通过select()方法配置怎么扫描接口。
//往容器中注入一个Docket
//配置了Swagger的Docket的Bean实例
@Bean
public Docket docket(Environment environment){
//设置要显示的Swagger环境
Profiles profiles = Profiles.of("dev","test");
//获取项目的环境
//通过environment.acceptsProfiles(profiles): 判断是否是自己设定的环境处于自己设定的环境当中
boolean acceptsProfiles = environment.acceptsProfiles(profiles);
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo()) //Swagger的基本信息
.groupName("未进化的程序猿") //分组的名称
.enable(acceptsProfiles) //配置是否启用Swagger,如果是false,在浏览器将无法访问
.select() //配置Swagger扫描接口
//RequestHandlerSelectors配置Swagger扫描接口的方式
//basePackage("扫描的包路径")
//any(): 扫描全部
//none(): 都不扫描
//withClassAnnotation(Controller.class): 扫描类上的注解
//withMethodAnnotation(GetMapper.class): 扫描方法上的注解
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.example.springbootswagger.controller"))
//paths(): 过滤什么路径
//PathSelectors.ant("/"): 过滤要求
//.paths(PathSelectors.ant("/"))
.build();
}
4.2、重启项目测试,由于我们配置根据包的路径扫描接口,所以我们只能看到一个类
4.3、除了通过包路径配置扫描接口外,还可以通过配置其他方式扫描接口,这里注释一下所有的配置方式:
any() // 扫描所有,项目中的所有接口都会被扫描到
none() // 不扫描接口
// 通过方法上的注解扫描,如withMethodAnnotation(GetMapping.class)只扫描get请求
withMethodAnnotation(final Class<? extends Annotation> annotation)
// 通过类上的注解扫描,如.withClassAnnotation(Controller.class)只扫描有controller注解的类中的接口
withClassAnnotation(final Class<? extends Annotation> annotation)
basePackage(final String basePackage) // 根据包路径扫描接口
4.4、除此之外,我们还可以配置接口扫描过滤:
@Bean
public Docket docket() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()// 通过.select()方法,去配置扫描接口,RequestHandlerSelectors配置如何扫描接口
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.kuang.swagger.controller"))
// 配置如何通过path过滤,即这里只扫描请求以/kuang开头的接口
.paths(PathSelectors.ant("/kuang/**"))
.build();
}
4.5、这里的可选值还有
any() // 任何请求都扫描
none() // 任何请求都不扫描
regex(final String pathRegex) // 通过正则表达式控制
ant(final String antPattern) // 通过ant()控制
五、配置Swagger开关
5.1、通过enable()方法配置是否启用swagger,如果是false,swagger将不能在浏览器中访问了
@Bean
public Docket docket() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.enable(false) //配置是否启用Swagger,如果是false,在浏览器将无法访问
.select()// 通过.select()方法,去配置扫描接口,RequestHandlerSelectors配置如何扫描接口
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.kuang.swagger.controller"))
// 配置如何通过path过滤,即这里只扫描请求以/kuang开头的接口
.paths(PathSelectors.ant("/kuang/**"))
.build();
}
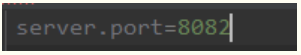
5.2、如何动态配置当项目处于test、dev环境时显示swagger,处于prod时不显示?
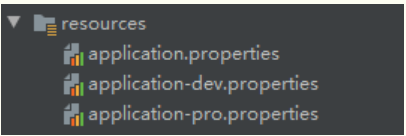
application.properties
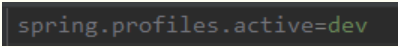
application-dev.properties
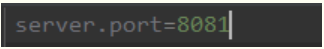
application-pro.properties
//往容器中注入一个Docket
//配置了Swagger的Docket的Bean实例
@Bean
public Docket docket(Environment environment){
//设置要显示的Swagger环境
Profiles profiles = Profiles.of("dev","test");
//获取项目的环境
//通过environment.acceptsProfiles(profiles): 判断是否是自己设定的环境处于自己设定的环境当中
boolean acceptsProfiles = environment.acceptsProfiles(profiles);
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo()) //Swagger的基本信息
.groupName("未进化的程序猿") //分组的名称
.enable(acceptsProfiles) //配置是否启用Swagger,如果是false,在浏览器将无法访问
.select() //配置Swagger扫描接口
//RequestHandlerSelectors配置Swagger扫描接口的方式
//basePackage("扫描的包路径")
//any(): 扫描全部
//none(): 都不扫描
//withClassAnnotation(Controller.class): 扫描类上的注解
//withMethodAnnotation(GetMapper.class): 扫描方法上的注解
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.example.springbootswagger.controller"))
//paths(): 过滤什么路径
//PathSelectors.ant("/"): 过滤要求
//.paths(PathSelectors.ant("/"))
.build();
}
5.3、可以在项目中增加一个dev的配置文件查看效果!
六、配置API分组

6.1、如果没有配置分组,默认是default。通过groupName()方法即可配置分组:
@Bean
public Docket docket(Environment environment) {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).apiInfo(apiInfo())
.groupName("hello") // 配置分组
// 省略配置....
}
6.2、重启项目查看分组 6.3、如何配置多个分组?配置多个分组只需要配置多个docket即可:
@Bean
public Docket docket1(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("group1");
}
@Bean
public Docket docket2(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("group2");
}
@Bean
public Docket docket3(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("group3");
}
6.4、重启项目查看即可
七、实体配置
7.1、新建一个实体类
@ApiModel("用户实体")
public class User {
@ApiModelProperty("用户名")
public String username;
@ApiModelProperty("密码")
public String password;
}
7.2、只要这个实体在请求接口的返回值上(即使是泛型),都能映射到实体项中:
@RequestMapping("/getUser")
public User getUser(){
return new User();
}
7.3、重启查看测试
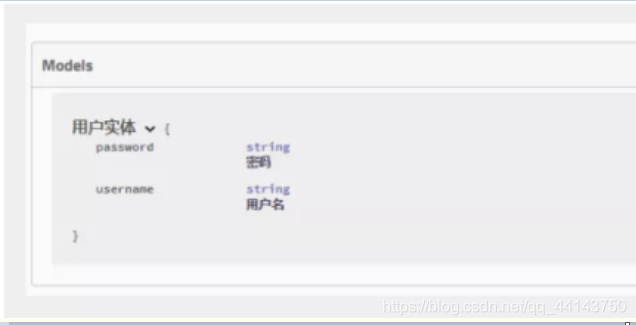
注意:并不是因为@ApiModel这个注解让实体显示在这里了,而是只要出现在接口方法的返回值上的实体都会显示在这里,而@ApiModel和@ApiModelProperty这两个注解只是为实体添加注释的。
@ApiModel为类添加注释 @ApiModelProperty为类属性添加注释
八、常用注解
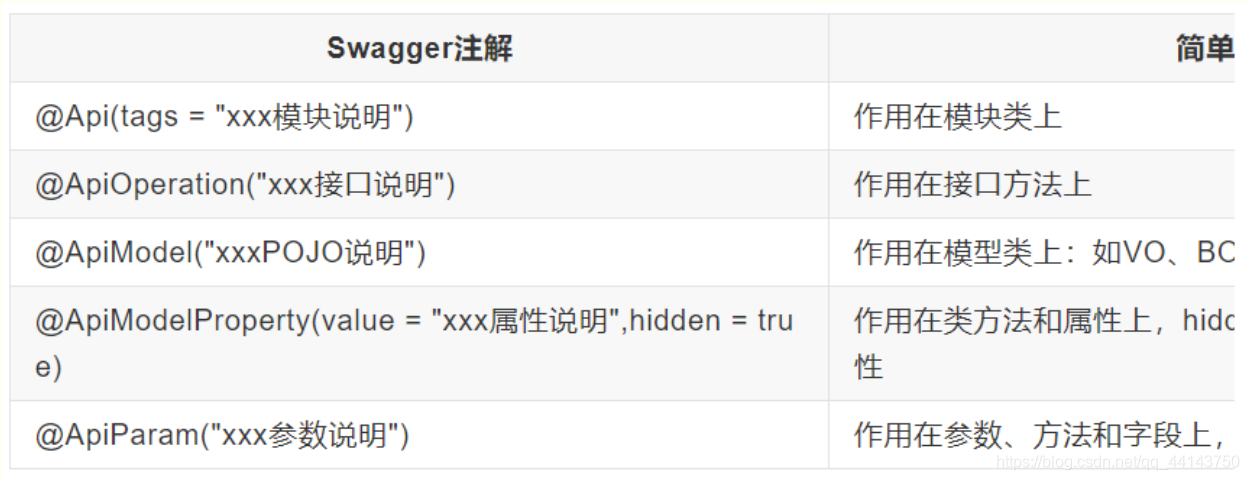
Swagger的所有注解定义在io.swagger.annotations包下 下面列一些经常用到的,未列举出来的可以另行查阅说明:
我们也可以给请求的接口配置一些注释
@ApiOperation("未进化的程序猿的接口")
@PostMapping("/kuang")
@ResponseBody
public String index(@ApiParam("这个名字会被返回")String username){
return username;
}
九、SpringBoot集成Swagger 配置
package com.example.springbootswagger.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.core.env.Profiles;
import springfox.documentation.builders.PathSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo;
import springfox.documentation.service.Contact;
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
import java.util.ArrayList;
@Configuration //定义Java配置类
@EnableSwagger2 //开启Swagger2
public class SwaggerConfig {
//创建多个组实例
@Bean
public Docket docket1(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("张三");
}
@Bean
public Docket docket2(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("李四");
}
@Bean
public Docket docket3(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("王五");
}
//往容器中注入一个Docket
//配置了Swagger的Docket的Bean实例
@Bean
public Docket docket(Environment environment){
//设置要显示的Swagger环境
Profiles profiles = Profiles.of("dev","test");
//获取项目的环境
//通过environment.acceptsProfiles(profiles): 判断是否是自己设定的环境处于自己设定的环境当中
boolean acceptsProfiles = environment.acceptsProfiles(profiles);
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo()) //Swagger的基本信息
.groupName("未进化的程序猿") //分组的名称
.enable(acceptsProfiles) //配置是否启用Swagger,如果是false,在浏览器将无法访问
.select() //配置Swagger扫描接口
//RequestHandlerSelectors配置Swagger扫描接口的方式
//basePackage("扫描的包路径")
//any(): 扫描全部
//none(): 都不扫描
//withClassAnnotation(Controller.class): 扫描类上的注解
//withMethodAnnotation(GetMapper.class): 扫描方法上的注解
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.example.springbootswagger.controller"))
//paths(): 过滤什么路径
//PathSelectors.ant("/"): 过滤要求
//.paths(PathSelectors.ant("/"))
.build();
}
//配置Swagger的apiInfo信息
@Bean
public ApiInfo apiInfo(){
//作者信息
Contact DEFAULT_CONTACT = new Contact("未进化的程序猿", "https://www.cnblogs.com/the-undeveloped-procedural-ape/", "486566947@qq.com");
return new ApiInfo("未进化的程序猿的Swagger日志", //Swagger文档标题
"Api Documentation",//Swagger文档描述
"v1.0",//Swagger文档版本号
"https://www.cnblogs.com/the-undeveloped-procedural-ape/",//博客地址
DEFAULT_CONTACT,//作者信息
"Apache 2.0",
"http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0",
new ArrayList());
}
}
十、总结
1)、这样的话,可以给一些比较难理解的属性或者接口,增加一些配置信息,让人更容易阅读!
2)、相较于传统的Postman或Curl方式测试接口,使用swagger简直就是傻瓜式操作,不需要额外说明文档(写得好本身就是文档)而且更不容易出错,只需要录入数据然后点击Execute,如果再配合自动化框架,可以说基本就不需要人为操作了。

