注解
##元注解
@Target
注解传入
ElementType作为参数public enum ElementType {/**标明该注解可以用于类、接口(包括注解类型)或enum声明*/TYPE,/** 标明该注解可以用于字段(域)声明,包括enum实例 */FIELD,/** 标明该注解可以用于方法声明 */METHOD,/** 标明该注解可以用于参数声明 */PARAMETER,/** 标明注解可以用于构造函数声明 */CONSTRUCTOR,/** 标明注解可以用于局部变量声明 */LOCAL_VARIABLE,/** 标明注解可以用于注解声明(应用于另一个注解上)*/ANNOTATION_TYPE,/** 标明注解可以用于包声明 */PACKAGE,/*** 标明注解可以用于类型参数声明(1.8新加入)* @since 1.8*/TYPE_PARAMETER,/*** 类型使用声明(1.8新加入)* @since 1.8*/TYPE_USE}
@Retention:标识了注解的声明周期
- 使用
RetentionPolicy作为参数
SOURCE:注解将被编译器丢弃(该类型的注解信息只会保留在源码里,源码经过编译后,注解信息会被丢弃,不会保留在编译好的class文件里)CLASS:注解在class文件中可用,但会被VM丢弃(该类型的注解信息会保留在源码里和class文件里,在执行的时候,不会加载到虚拟机中),请注意,当注解未定义Retention值时,默认值是CLASS,如Java内置注解,@Override、@Deprecated、@SuppressWarnning等RUNTIME:注解信息将在运行期(JVM)也保留,因此可以通过反射机制读取注解的信息(源码、class文件和执行的时候都有注解的信息),如SpringMvc中的@Controller、@Autowired、@RequestMapping等。public enum RetentionPolicy {/*** Annotations are to be discarded by the compiler.*/SOURCE,/*** Annotations are to be recorded in the class file by the compiler* but need not be retained by the VM at run time. This is the default* behavior.*/CLASS,/*** Annotations are to be recorded in the class file by the compiler and* retained by the VM at run time, so they may be read reflectively.** @see java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedElement*/RUNTIME}
@Inherited
- 当该注解标注在父类上的时候,其子类也会有该注解 ```java @Inherited @Documented @Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface DocumentA { }
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface DocumentB { }
@DocumentA class A{ }
class B extends A{ }
@DocumentB class C{ }
class D extends C{ }
//测试 public class DocumentDemo {
public static void main(String... args){A instanceA=new B();System.out.println("已使用的@Inherited注解:"+Arrays.toString(instanceA.getClass().getAnnotations()));C instanceC = new D();System.out.println("没有使用的@Inherited注解:"+Arrays.toString(instanceC.getClass().getAnnotations()));}/*** 运行结果:已使用的@Inherited注解:[@com.zejian.annotationdemo.DocumentA()]没有使用的@Inherited注解:[]*/
}
4. @Documented1. 被修饰的注解会生成到javadoc中5. @Repeatable1. 元注解@Repeatable是JDK1.8新加入的,它**表示在同一个位置重复相同的注解**。1. 在没有该注解前,一般是无法在同一个类型上使用相同的注解的1. 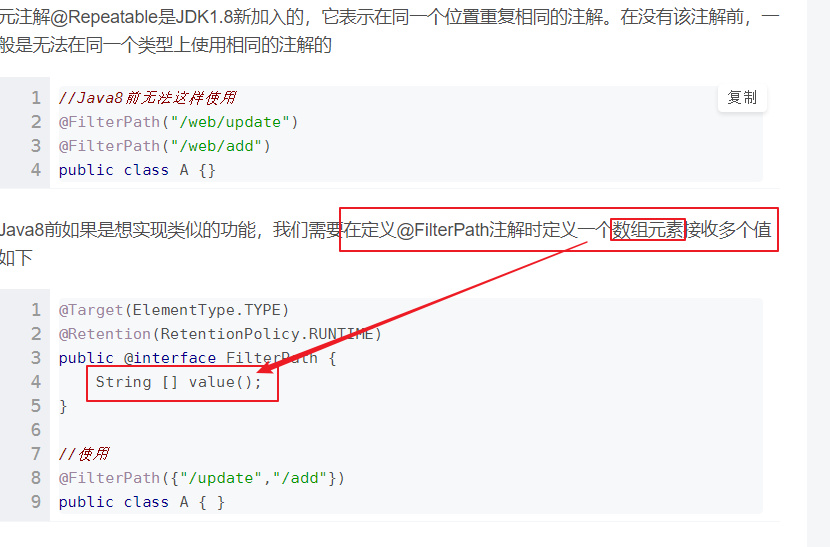<br />在Java8新增了@Repeatable注解后就可以采用如下的方式定义并使用了```javapackage com.zejian.annotationdemo;import java.lang.annotation.*;/*** Created by zejian on 2017/5/20.* Blog : http://blog.csdn.net/javazejian [原文地址,请尊重原创]*///使用Java8新增@Repeatable原注解@Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.FIELD,ElementType.METHOD})@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Repeatable(FilterPaths.class)//参数指明接收的注解classpublic @interface FilterPath {String value();}// 有一个注解数组作为其内部对象@Target(ElementType.TYPE)@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@interface FilterPaths {FilterPath[] value();}//使用案例@FilterPath("/web/update")@FilterPath("/web/add")@FilterPath("/web/delete")class AA{ }
@Repeatable
后,将使用@FilterPaths注解作为接收同一个类型上重复注解的容器,而每个@FilterPath则负责保存指定的路径串。
- 为了处理上述的新增注解,Java8还在AnnotatedElement接口新增了getDeclaredAnnotationsByType() 和 getAnnotationsByType()两个方法并在接口给出了默认实现,在指定@Repeatable的注解时,可以通过这两个方法获取到注解相关信息。
- 注意
getDeclaredAnnotationsByType方法获取到的注解不包括父类 - 其实当 getAnnotationsByType()方法调用时,其内部先执行了getDeclaredAnnotationsByType方法,只有当前类不存在指定注解时,getAnnotationsByType()才会继续从其父类寻找,
- 注意如果@FilterPath和@FilterPaths没有使用了@Inherited的话,仍然无法获取。
- 注意
- 旧版API中的getDeclaredAnnotation()和 getAnnotation()是不对@Repeatable注解的处理的(除非该注解没有在同一个声明上重复出现)。 ```java @FilterPath(“/web/list”) class CC { }
//使用案例 @FilterPath(“/web/update”) @FilterPath(“/web/add”) @FilterPath(“/web/delete”) class AA extends CC{ public static void main(String[] args) {
Class<?> clazz = AA.class;//通过getAnnotationsByType方法获取所有重复注解FilterPath[] annotationsByType = clazz.getAnnotationsByType(FilterPath.class);FilterPath[] annotationsByType2 = clazz.getDeclaredAnnotationsByType(FilterPath.class);if (annotationsByType != null) {for (FilterPath filter : annotationsByType) {System.out.println("1:"+filter.value());}}System.out.println("-----------------");if (annotationsByType2 != null) {for (FilterPath filter : annotationsByType2) {System.out.println("2:"+filter.value());}}//getAnnotation 无法处理@RepeatableSystem.out.println("使用getAnnotation的结果:"+clazz.getAnnotation(FilterPath.class));/*** 执行结果(当前类拥有该注解FilterPath,则不会从CC父类寻找)1:/web/update1:/web/add1:/web/delete-----------------2:/web/update2:/web/add2:/web/delete使用getAnnotation的结果:null*/}
}
如果子类没有实现注解,那么```java/*** Created by zejian on 2017/5/20.* Blog : http://blog.csdn.net/javazejian [原文地址,请尊重原创]*///使用Java8新增@Repeatable原注解@Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.FIELD,ElementType.METHOD})@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Inherited //添加可继承元注解@Repeatable(FilterPaths.class)public @interface FilterPath {String value();}@Target(ElementType.TYPE)@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Inherited //添加可继承元注解@interface FilterPaths {FilterPath[] value();}@FilterPath("/web/list")@FilterPath("/web/getList")class CC { }//AA上不使用@FilterPath注解,getAnnotationsByType将会从父类查询class AA extends CC{public static void main(String[] args) {Class<?> clazz = AA.class;//通过getAnnotationsByType方法获取所有重复注解FilterPath[] annotationsByType = clazz.getAnnotationsByType(FilterPath.class);FilterPath[] annotationsByType2 = clazz.getDeclaredAnnotationsByType(FilterPath.class);if (annotationsByType != null) {for (FilterPath filter : annotationsByType) {System.out.println("1:"+filter.value());}}System.out.println("-----------------");if (annotationsByType2 != null) {for (FilterPath filter : annotationsByType2) {System.out.println("2:"+filter.value());}}System.out.println("使用getAnnotation的结果:"+clazz.getAnnotation(FilterPath.class));/*** 执行结果(当前类没有@FilterPath,getAnnotationsByType方法从CC父类寻找)1:/web/list1:/web/getList-----------------使用getAnnotation的结果:null*/}}
注意定义@FilterPath和@FilterPath时必须指明@Inherited,getAnnotationsByType方法否则依旧无法从父类获取@FilterPath注解,这是为什么呢,不妨看看getAnnotationsByType方法的实现源码:
//接口默认实现方法default <T extends Annotation> T[] getAnnotationsByType(Class<T> annotationClass) {//先调用getDeclaredAnnotationsByType方法T[] result = getDeclaredAnnotationsByType(annotationClass);//判断当前类获取到的注解数组是否为0if (result.length == 0 && this instanceof Class &&//判断定义注解上是否使用了@Inherited元注解AnnotationType.getInstance(annotationClass).isInherited()) { // Inheritable//从父类获取Class<?> superClass = ((Class<?>) this).getSuperclass();if (superClass != null) {result = superClass.getAnnotationsByType(annotationClass);}}return result;}
声明注解
//声明Test注解@Target(ElementType.METHOD)@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)public @interface Test {String name() default "";}
使用了@interface声明了Test注解,并使用@Target注解传入ElementType.METHOD参数来标明@Test只能用于方法上,@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)则用来表示该注解生存期是运行时,从代码上看注解的定义很像接口的定义,确实如此,毕竟在编译后也会生成Test.class文件。
关于注解支持的元素数据类型除了上述的String name() default "";还支持如下数据类型
- 所有基本类型(int,float,boolean,byte,double,char,long,short)
- String
- Class
- enum
- Annotation
- 上述类型的数组
- 倘若使用了其他数据类型,编译器将会丢出一个编译错误
- 声明注解元素时可以使用基本类型但不允许使用任何包装类型
- 注解也可以作为元素的类型,也就是嵌套注解 ```java package com.zejian.annotationdemo;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
- Created by wuzejian on 2017/5/19.
- 数据类型使用Demo */
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @interface Reference{ boolean next() default false; }
public @interface AnnotationElementDemo { //枚举类型 enum Status {FIXED,NORMAL};
//声明枚举Status status() default Status.FIXED;//布尔类型boolean showSupport() default false;//String类型String name()default "";//class类型Class<?> testCase() default Void.class;//注解嵌套Reference reference() default @Reference(next=true);//数组类型long[] value();
}
1. 元素不能有不确定的值。也就是说,元素必须要么具有**默认值**,要么在使用注解时**初始化**元素的值。1. 对于非基本类型的元素,无论是在源代码中声明,还是在注解接口中定义默认值,都不能以null作为值<a name="xddax"></a>#### 不能继承注解注解是不支持继承的,因此不能使用关键字extends来继承某个@interface,但注解在编译后,编译器会自动继承java.lang.annotation.Annotation接口.```java/*** Created by wuzejian on 2017/5/18.* 对应数据表注解*/@Target(ElementType.TYPE)//只能应用于类上@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//保存到运行时public @interface DBTable {String name() default "";}
虽然反编译后发现DBTable注解继承了Annotation接口,请记住,即使Java的接口可以实现多继承,但定义注解时依然无法使用extends关键字继承@interface。
package com.zejian.annotationdemo;import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;//反编译后的代码public interface DBTable extends Annotation{public abstract String name();}
注解元素赋值
如果被赋值的元素只有一个并且名为value,那么不需要使用key进行标识
否则需要使用kv进行标识
//定义注解@Target(ElementType.FIELD)@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@interface IntegerVaule{int value() default 0;String name() default "";}//使用注解public class QuicklyWay {//当只想给value赋值时,可以使用以下快捷方式@IntegerVaule(20)public int age;//当name也需要赋值时必须采用key=value的方式赋值@IntegerVaule(value = 10000,name = "MONEY")public int money;}
内置注解
- @Override:用于标明此方法覆盖了父类的方法

- @Deprecated:用于标明已经过时的方法或类

- @SuppressWarnnings:用于有选择的关闭编译器对类、方法、成员变量、变量初始化的警告
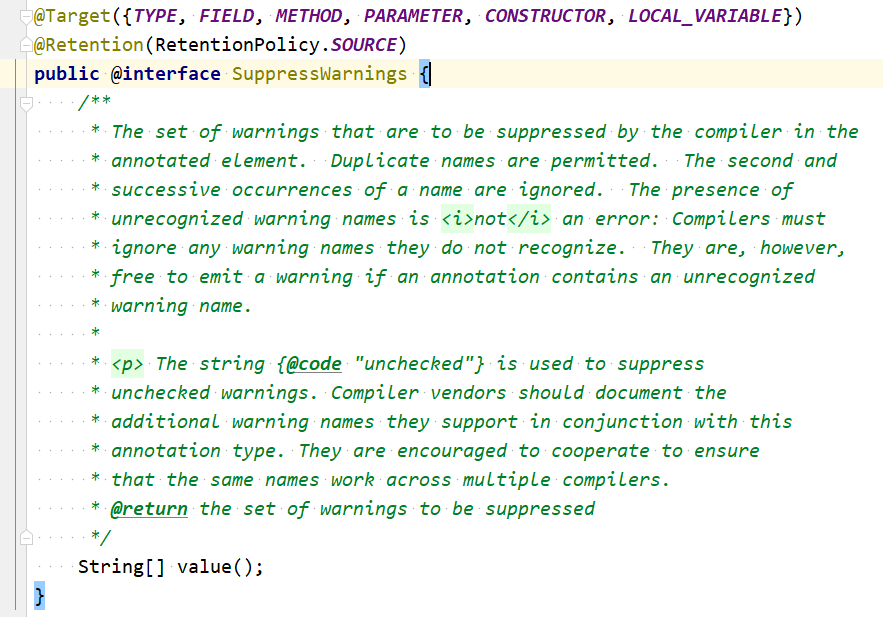
- 内部有一个String数组,主要接收值如下:
- deprecation:使用了不赞成使用的类或方法时的警告;
- unchecked:执行了未检查的转换时的警告,例如当使用集合时没有用泛型 (Generics) 来指定集合保存的类型;
- fallthrough:当 Switch 程序块直接通往下一种情况而没有 Break 时的警告;
- path:在类路径、源文件路径等中有不存在的路径时的警告;
- serial:当在可序列化的类上缺少 serialVersionUID 定义时的警告;
- finally:任何 finally 子句不能正常完成时的警告;
- all:关于以上所有情况的警告。


注解&反射
AnnotatedElement
这个接口(AnnotatedElement)的对象代表了在当前JVM中的一个“被注解元素”(可以是Class,Method,Field,Constructor,Package等)。通过该接口提供的方法可以利用反射技术地读取注解的信息,如反射包的Constructor类、Field类、Method类、Package类和Class类都实现了AnnotatedElement接口,
| 返回值 | 方法名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
<A extends Annotation> |
getAnnotation(Class<A> annotationClass) |
该元素如果存在指定类型的注解,则返回这些注解,否则返回 null。 |
Annotation[] |
getAnnotations() |
返回此元素上存在的所有注解,包括从父类继承的 |
boolean |
isAnnotationPresent(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass) |
如果指定类型的注解存在于此元素上,则返回 true,否则返回 false。 |
Annotation[] |
getDeclaredAnnotations() |
返回直接存在于此元素上的所有注解,注意,不包括父类的注解,调用者可以随意修改返回的数组;这不会对其他调用者返回的数组产生任何影响,没有则返回长度为0的数组 |
简单代码:
package com.zejian.annotationdemo;import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;import java.util.Arrays;/*** Created by zejian on 2017/5/20.* Blog : http://blog.csdn.net/javazejian [原文地址,请尊重原创]*/@DocumentAclass A{ }//继承了A类@DocumentBpublic class DocumentDemo extends A{public static void main(String... args){Class<?> clazz = DocumentDemo.class;//根据指定注解类型获取该注解DocumentA documentA=clazz.getAnnotation(DocumentA.class);System.out.println("A:"+documentA);//获取该元素上的所有注解,包含从父类继承Annotation[] an= clazz.getAnnotations();System.out.println("an:"+ Arrays.toString(an));//获取该元素上的所有注解,但不包含继承!Annotation[] an2=clazz.getDeclaredAnnotations();System.out.println("an2:"+ Arrays.toString(an2));//判断注解DocumentA是否在该元素上boolean b=clazz.isAnnotationPresent(DocumentA.class);System.out.println("b:"+b);/*** 执行结果:A:@com.zejian.annotationdemo.DocumentA()an:[@com.zejian.annotationdemo.DocumentA(), @com.zejian.annotationdemo.DocumentB()]an2:@com.zejian.annotationdemo.DocumentB()b:true*/}}
使用注解来生成数据库表
- 注解
```java
/**
- Created by wuzejian on 2017/5/18.
- 表注解 */ @Target(ElementType.TYPE)//只能应用于类上 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//保存到运行时 public @interface DBTable { String name() default “”; }
/**
- Created by wuzejian on 2017/5/18.
- 注解Integer类型的字段 */ @Target(ElementType.FIELD) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface SQLInteger { //该字段对应数据库表列名 String name() default “”; //嵌套注解 Constraints constraint() default @Constraints; }
/**
- Created by wuzejian on 2017/5/18.
注解String类型的字段 */ @Target(ElementType.FIELD) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface SQLString {
//对应数据库表的列名 String name() default “”;
//列类型分配的长度,如varchar(30)的30 int value() default 0;
Constraints constraint() default @Constraints; }
/**
- Created by wuzejian on 2017/5/18.
- 约束注解 */
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)//只能应用在字段上 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface Constraints { //判断是否作为主键约束 boolean primaryKey() default false; //判断是否允许为null boolean allowNull() default false; //判断是否唯一 boolean unique() default false; }
/**
- Created by wuzejian on 2017/5/18.
数据库表Member对应实例类bean */ @DBTable(name = “MEMBER”) public class Member { //主键ID @SQLString(name = “ID”,value = 50, constraint = @Constraints(primaryKey = true)) private String id;
@SQLString(name = “NAME” , value = 30) private String name;
@SQLInteger(name = “AGE”) private int age;
@SQLString(name = “DESCRIPTION” ,value = 150 , constraint = @Constraints(allowNull = true)) private String description;//个人描述
//省略set get….. } ```
- @DBTable(用于类上)、@Constraints(用于字段上)、 @SQLString(用于字段上)、@SQLString(用于字段上)并在Member类中使用这些注解
- 使用了嵌套注解@Constraints,该注解主要用于判断字段是否为null或者字段是否唯一。
- 注解生命周期必须为
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME),即运行时,这样才可以使用反射机制获取其信息。
- 自定义处理器的编写 ```java package com.zejian.annotationdemo; import java.lang.annotation.Annotation; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List;
/**
- Created by zejian on 2017/5/13.
- Blog : http://blog.csdn.net/javazejian [原文地址,请尊重原创]
运行时注解处理器,构造表创建语句 */ public class TableCreator {
public static String createTableSql(String className) throws ClassNotFoundException { Class<?> cl = Class.forName(className); DBTable dbTable = cl.getAnnotation(DBTable.class); //如果没有表注解,直接返回 if(dbTable == null) { System.out.println(
"No DBTable annotations in class " + className);
return null; } String tableName = dbTable.name(); // If the name is empty, use the Class name: if(tableName.length() < 1) tableName = cl.getName().toUpperCase(); List
columnDefs = new ArrayList (); //通过Class类API获取到所有成员字段 for(Field field : cl.getDeclaredFields()) { String columnName = null; //获取字段上的注解 Annotation[] anns = field.getDeclaredAnnotations(); if(anns.length < 1) continue; // Not a db table column
//判断注解类型 if(anns[0] instanceof SQLInteger) {
SQLInteger sInt = (SQLInteger) anns[0];//获取字段对应列名称,如果没有就是使用字段名称替代if(sInt.name().length() < 1)columnName = field.getName().toUpperCase();elsecolumnName = sInt.name();//构建语句columnDefs.add(columnName + " INT" +getConstraints(sInt.constraint()));
} //判断String类型 if(anns[0] instanceof SQLString) {
SQLString sString = (SQLString) anns[0];// Use field name if name not specified.if(sString.name().length() < 1)columnName = field.getName().toUpperCase();elsecolumnName = sString.name();columnDefs.add(columnName + " VARCHAR(" +sString.value() + ")" +getConstraints(sString.constraint()));
}
}//数据库表构建语句StringBuilder createCommand = new StringBuilder("CREATE TABLE " + tableName + "(");for(String columnDef : columnDefs)createCommand.append("\n " + columnDef + ",");// Remove trailing commaString tableCreate = createCommand.substring(0, createCommand.length() - 1) + ");";return tableCreate;
}
/*** 判断该字段是否有其他约束* @param con* @return*/
private static String getConstraints(Constraints con) { String constraints = “”; if(!con.allowNull()) constraints += “ NOT NULL”; if(con.primaryKey()) constraints += “ PRIMARY KEY”; if(con.unique()) constraints += “ UNIQUE”; return constraints; }
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String[] arg={“com.zejian.annotationdemo.Member”}; for(String className : arg) { System.out.println(“Table Creation SQL for “ + className + “ is :\n” + createTableSql(className)); }
/*** 输出结果:Table Creation SQL for com.zejian.annotationdemo.Member is :CREATE TABLE MEMBER(ID VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,NAME VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,AGE INT NOT NULL,DESCRIPTION VARCHAR(150));*/
}
}
``
通过传递Member的全路径后通过Class.forName()方法获取到Member的class对象,然后利用Class对象中的方法获取所有成员字段Field,最后利用field.getDeclaredAnnotations()`遍历每个Field上的注解再通过注解的类型判断来构建建表的SQL语句。

