- 1. 两数之和">1. 两数之和
- 2. 两数相加">2. 两数相加
- 42. 接雨水">42. 接雨水
- 3. 无重复字符的最长子串">3. 无重复字符的最长子串
- 206. 反转链表">206. 反转链表
- 5. 最长回文子串">5. 最长回文子串
- 11. 盛最多水的容器">11. 盛最多水的容器
- 53. 最大子序和">53. 最大子序和
- 15. 三数之和">15. 三数之和
- 33. 搜索旋转排序数组">33. 搜索旋转排序数组
- 46. 全排列">46. 全排列
- 47. 全排列 II">47. 全排列 II
- 21. 合并两个有序链表">21. 合并两个有序链表
- 146. LRU 缓存机制">146. LRU 缓存机制
- 7. 整数反转">7. 整数反转
- 215. 数组中的第K个最大元素">215. 数组中的第K个最大元素
1. 两数之和
难度简单10472
思路:使用hash记录已经遍历过的值,然后判断 目标值减去当前值 的差在不在map之中
class Solution {public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {if(nums.length==0)return new int[]{};Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap(); // key为num[i],value为ifor(int i = 0 ; i < nums.length;i++) {if(map.containsKey(target-nums[i])) { // 判断在不在map里面return new int[]{i,map.get(target-nums[i])};}map.put(nums[i],i); //放入当前值}return null;}}
2. 两数相加
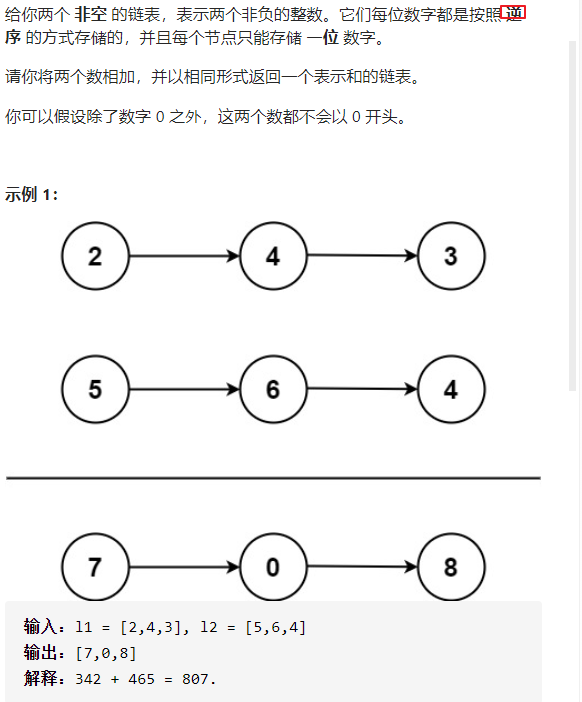
思路:
- 使用一个进位标识来判断是不是产生进位
遍历完两个数组以后判断一下标志位是不是为1,为1需要+1
class Solution {public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);ListNode pre = dummy;int ten = 0;// 两者长度的公共部分while(l1!=null && l2!=null) {int now = l1.val + l2.val + ten;ten = 0; // 清除之前的进位信息if(now>=10)ten = 1;now = now%10; // now值为0-9pre.next = new ListNode(now);pre = pre.next;l1 = l1.next; // 不要忘了往下走l2 = l2.next;}// 其中一个长度比较长,这个时候只需要计算长的和进位标记就行了while(l1!=null) {int now = l1.val+ten;ten = 0;if(now>=10)ten = 1;now = now%10;pre.next = new ListNode(now);pre = pre.next;l1 = l1.next;}while(l2!=null) {int now = l2.val+ten;ten = 0;if(now>=10)ten = 1;now = now%10;pre.next = new ListNode(now);pre = pre.next;l2 = l2.next;}// 两个链表可能会在最后产生进位if(ten!=0) {pre.next = new ListNode(1);}return dummy.next;}}
42. 接雨水
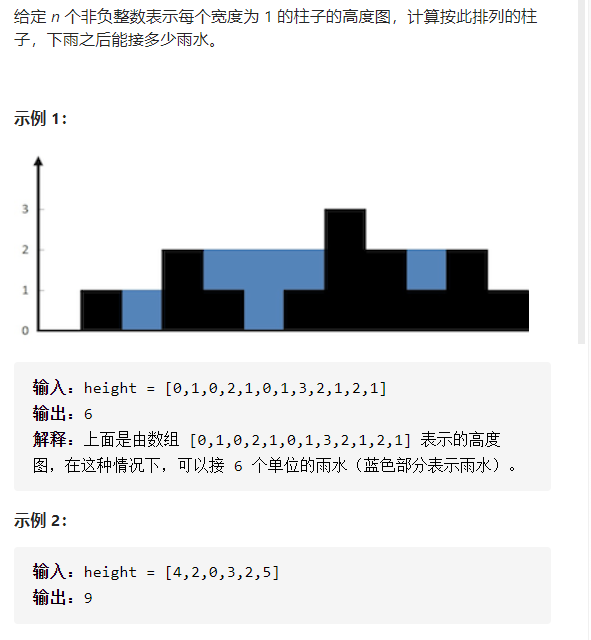
思路:定义一个左指针,一个右指针
如果h[left] < h[right] 则说明左边的比右边的低,那么h[left]一定是被左边走过的最大值leftMax所约束,因为只有左边比右边低的时候,左边才往前走,所以这个时候左边最大值一定是小于等于右边最大值的。
class Solution {public int trap(int[] height) {int res = 0;int left = 0;int right = height.length-1;int leftMax = 0;int rightMax = 0;while(left<right) {if(height[left] < height[right]) {// 这个时候可以确定当前的left指向的位置一定是被leftMax所限定的,// 因为现在leftMax一定小于rightMax// 如果这个时候leftMax 大于 rightMax ,是不可能的,因为right--只有在右边低的时候才进行,一直前进到rightMax > leftMaxleftMax = Math.max(leftMax,height[left]);res += (leftMax - height[left]);left++;} else {rightMax = Math.max(rightMax,height[right]);res += (rightMax - height[right]);right--;}}return res;}}
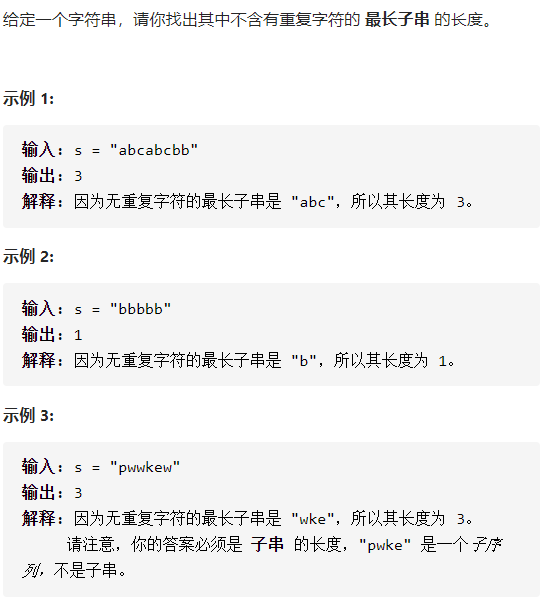
3. 无重复字符的最长子串
206. 反转链表
难度简单1561

迭代
class Solution {public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);ListNode pre = dummy;ListNode now = head;while(now!=null) {ListNode next = now.next;now.next = dummy.next;dummy.next = now;now = next;}return dummy.next;}}
递归
- 对于A->B->C->D;
- 如果CD混产科反转,则A->B->C<-D;
- 现在对于B来说,需要让C.next = B;则可以B.next.next = B;B.next = null;现在:
- A->B<-C<-D
class Solution {public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {if(head==null || head.next==null)return head;ListNode newNode = reverseList(head.next);head.next.next = head;head.next = null;return newNode;}}
- A->B<-C<-D
5. 最长回文子串

遍历每一个位置
- 把这个位置作为中点找两边
把这个位置作为右边一端的开始
class Solution {int max = 1;int left = 0;public String longestPalindrome(String s) {for(int i = 0 ; i < s.length();i++) {find(s,i);}return s.substring(left,max+left);}void find(String s,int m) {// 作为中点for(int l = m-1,r = m+1;l>=0 && r < s.length();l--,r++) {if(s.charAt(l)==s.charAt(r)) {if(max < r-l+1) {max = r-l+1;left = l;}} else {break;}}// 作为右边第一个for(int l = m-1,r = m;l>=0 && r <s.length();l--,r++) {if(s.charAt(l)==s.charAt(r)) {if(max < r-l+1) {max = r-l+1;left = l;}} else {break;}}}}
11. 盛最多水的容器
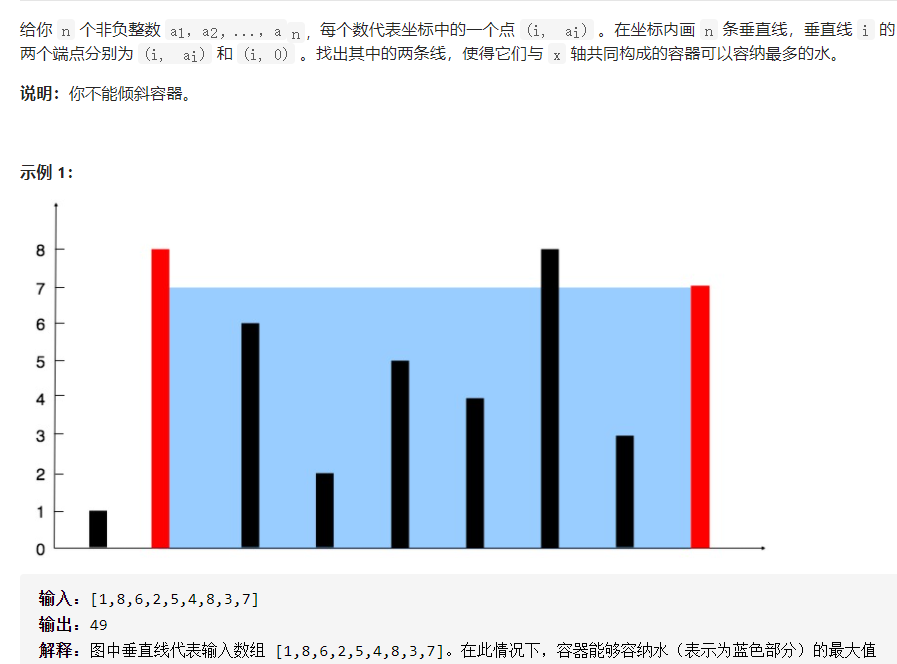
使用左右指针
- res = 长度 * 左右高度的最小值
- 如果左边低,l++
- 否则,r++
- 分析:使其中低的一个边进行移动,那么新边如果比这个边长,则res变大;如果新边比这个短,res会变小;如果移动长的一边,则res一定变小
- 所以移动段的一边更合适
class Solution {public int maxArea(int[] height) {int l = 0,r = height.length-1;int res = 0;while(l<r) {if(height[l]<height[r]) {// 按照短的一边进行计算高度res = Math.max(res,(r-l)*height[l]);l++; // 移动短的一边的}else {res = Math.max(res,(r-l)*height[r]);r--;}}return res;}}
53. 最大子序和
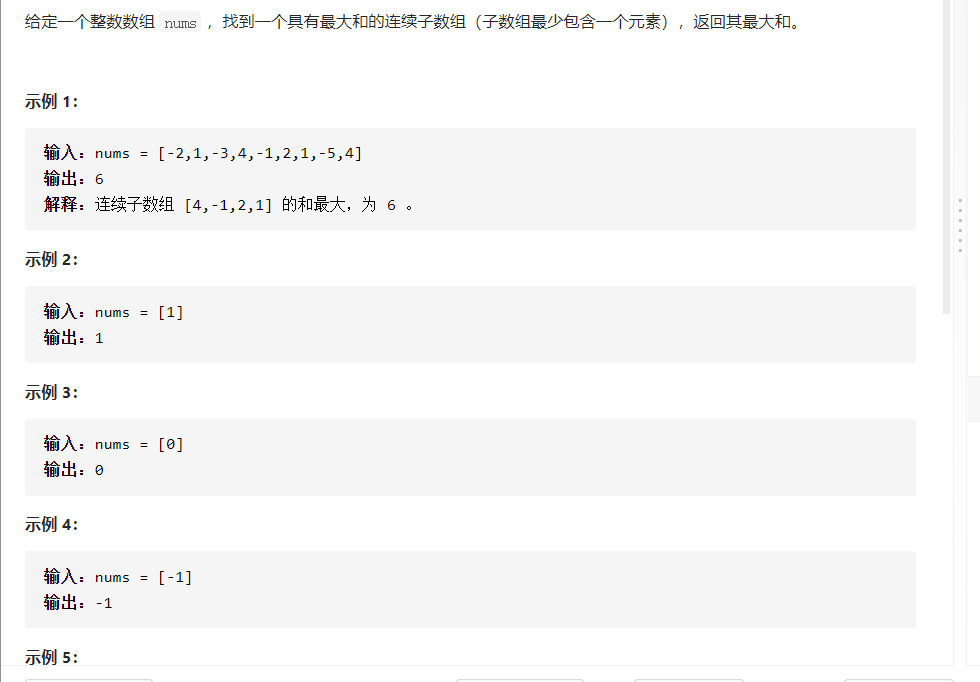
使用res记录当前区间的总和,如果res<0,那么丢弃之前的区间;如果res>0,将其放入res的区间中
class Solution {public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {if(nums.length==0)return 0;int res = nums[0];// 默认第一个数是第一个区间int max = nums[0];for(int i = 1 ; i < nums.length;i++) {if(res < 0) { // 之前的区间为负值,没有意义,丢弃max = Math.max(nums[i],max);res = nums[i];} else { // 加上之前区间的值max = Math.max(res+nums[i],max);res += nums[i];}}return max;}}
15. 三数之和
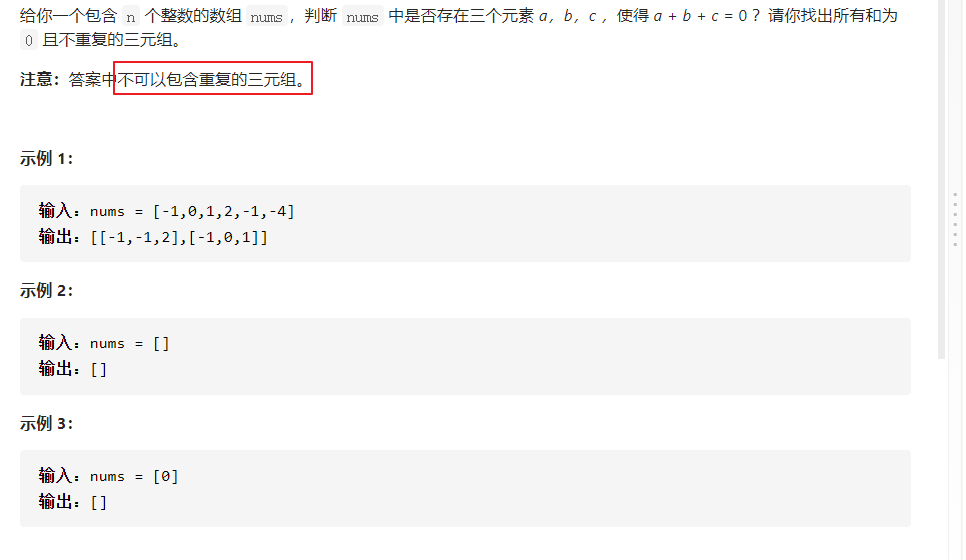
排序
- 按顺序选出第一个元素
- 第一个元素不能已经出现过
- 根据第一个元素选出第二个元素
- 第二个元素在第一个元素已经确定的那么循环中不能已经出现过
根据1,2选第三个数
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList();Arrays.sort(nums);for(int i = 0 ; i < nums.length-2;i++) {// 开始的头一个元素不能跟之前的元素是一样// 例如 [-1,-1,0,1,1],第二次遍历时候,-1与之前的-1相等,// 那么之前的在第二个-1之后如果有两个数使满足条件,// 那么在第一个-1的时候,这两个数一定已经被发现了if(i!=0 && nums[i]==nums[i-1])continue;int r = nums.length-1;for(int l = i+1;l < nums.length-1;l++) {// 对于三个数来说,这个时候第一个数已经确定了,如果第二个数之前已经被添加到了结果集合中// 那么第二个数会重复,因为三个数已经确定了第一个数和第二个数,那么第三个数一定也是确定的值// 所以第二个数在第一个数确定的时候不能重复if(l!=i+1 && nums[l]==nums[l-1]) {continue;}while(l<r && nums[i]+nums[l]+nums[r]>0) {r--;}// 后面两个数不能是同一个数if(l==r) {break;}if(l < r && nums[i]+nums[l]+nums[r]==0){List<Integer> list = new ArrayList();list.add(nums[i]);list.add(nums[l]);list.add(nums[r]);res.add(list);}}}return res;}}
33. 搜索旋转排序数组
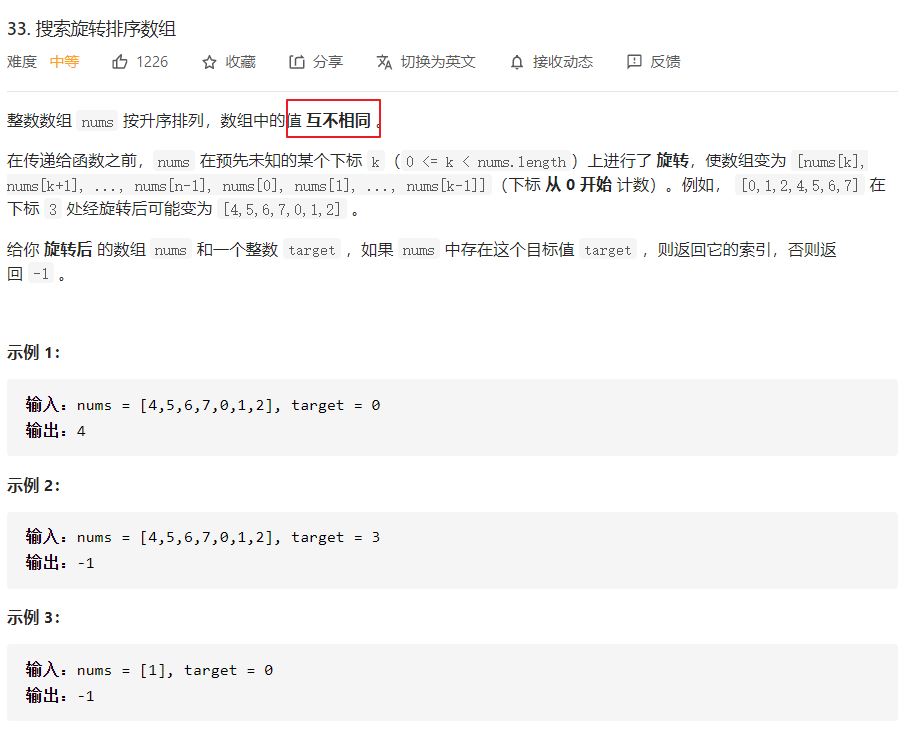
二分查找旋转点
二分查找目标值
class Solution {public int search(int[] nums, int target) {int len = nums.length;if(len==0)return -1;int point = findReversePoint(nums);if(point==0){return find(nums,0,len-1,target);} else {// 跟最右边的数比较,如果小于等于就查找右半边if(nums[len-1]>=target) {return find(nums,point,len-1,target);} else { // 查找左半边return find(nums,0,point-1,target);}}}// 找到旋转点int findReversePoint(int[] nums) {int l = 0;int r = nums.length-1;while(l<r) {int m = (l+r)>>1;// 中点跟左右两边进行对比if(nums[m] > nums[r]) {l = m+1;} else {r = m;}}return l;}// 二分查找int find(int[] nums,int l,int r,int target) {while(l<r) {int m = l+r>>1;if(nums[m]<target) {l = m+1;} else {r = m;}}if(nums[l] == target)return l;return -1;}}
46. 全排列
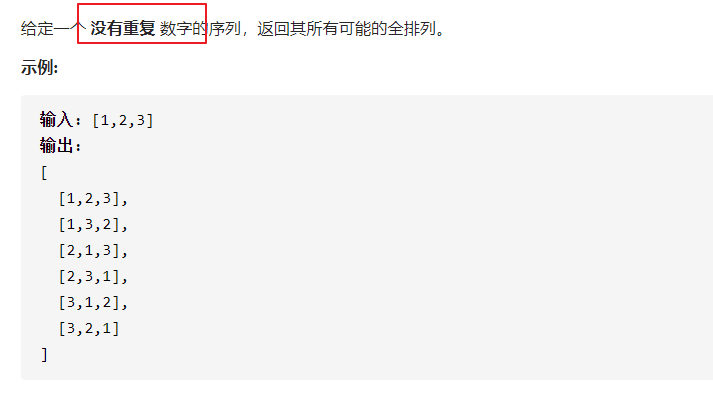
使用一个标记数组判断是不是已经访问过
终止条件:已经收集了长度为数组长度的list内容
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList();List<Integer> list = new ArrayList();int len = nums.length;if(len==0)return res;boolean[] flag = new boolean[nums.length];find(res,list,0,nums,flag);return res;}void find(List<List<Integer>> res,List<Integer> list,int len,int[] nums,boolean[] flag) {if(len==nums.length){res.add(new ArrayList(list));return;}for(int i = 0 ; i < nums.length;i++) {if(!flag[i]) {flag[i] = !flag[i];list.add(nums[i]);find(res,list,len+1,nums,flag);list.remove(len);flag[i] = !flag[i];}}}}
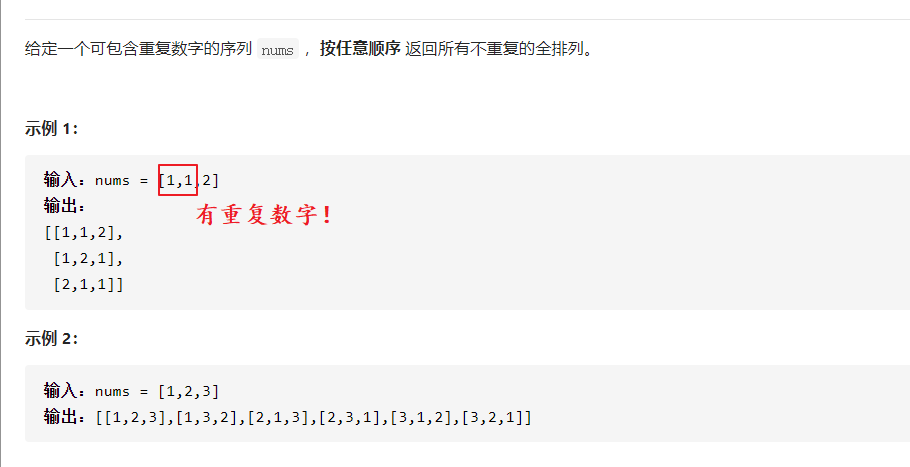
47. 全排列 II
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {int len = nums.length;List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList();List<Integer> list = new ArrayList();if(len==0)return res;Arrays.sort(nums);boolean[] flag = new boolean[nums.length];find(res,list,0,nums,flag);return res;}void find(List<List<Integer>> res,List<Integer> list,int len,int[] nums,boolean[] flag) {if(len==nums.length) {res.add(new ArrayList(list));return;}for(int i = 0 ; i < nums.length ; i++) {// 如果当前元素之前的元素和自己是一个值,// 并且之前的元素还没有加入list,则当前元素不能被加入listif(i!=0 && !flag[i-1] && nums[i]==nums[i-1])continue;if(!flag[i]) {flag[i] = !flag[i];list.add(nums[i]);find(res,list,len+1,nums,flag);list.remove(len);flag[i] = !flag[i];}}}}
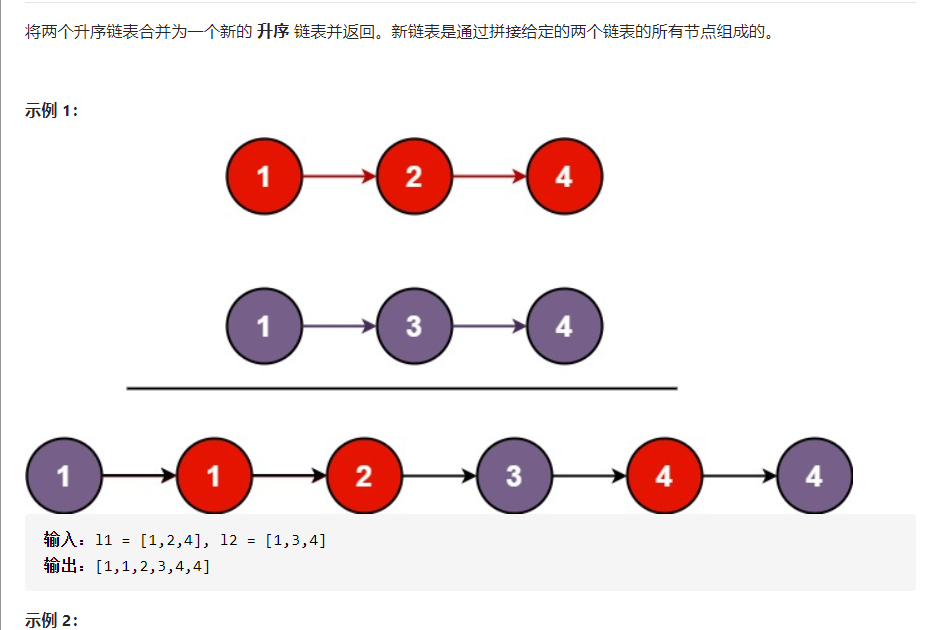
21. 合并两个有序链表
class Solution {public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);ListNode pre = dummy;while(l1!=null && l2!=null) {if(l1.val < l2.val) {pre.next = l1;l1=l1.next;} else {pre.next = l2;l2 = l2.next;}pre =pre.next;}if(l1!=null) {pre.next = l1;}if(l2!=null) {pre.next = l2;}return dummy.next;}}
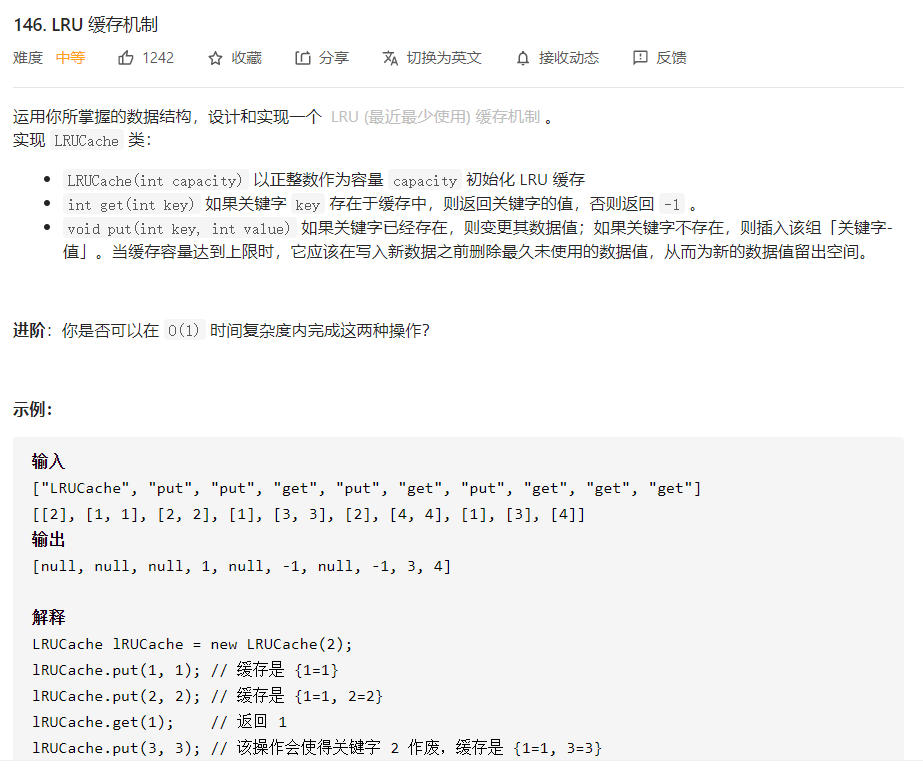
146. LRU 缓存机制
创建链表的节点
- 使用一个map记录已经存在的key
- 插入到队头
不要忘记更新操作 ```java class LRUCache {
class Node{
int key;int value;Node pre;Node next;public Node() {}public Node(int k,int v) {key = k;value = v;}
}
Map<Integer,Node> map = new HashMap();Node head = null;Node tail = null;int capacity = 0;public LRUCache(int capacity) {head = new Node();tail = new Node();head.next = tail;tail.pre = head;this.capacity = capacity;}public int get(int key) {if(!map.containsKey(key)) {return -1;}Node now = map.get(key);int value = now.value;// 将这个Node放到队头if(now!=head.next) {// 处理now前后节点now.pre.next = now.next;now.next.pre = now.pre;// 处理head的后面节点head.next.pre = now;now.next = head.next;head.next = now;now.pre = head;}return value;}public void put(int key, int value) {if(!map.containsKey(key)) {Node now = new Node(key,value);map.put(key,now);// 直接插入到队头,处理head的后面节点head.next.pre = now;now.next = head.next;head.next = now;now.pre = head;if(capacity==0) {map.remove(tail.pre.key); // 从map删除节点// 删除最后一个nodetail.pre.pre.next = tail;tail.pre = tail.pre.pre;}else {capacity--;}} else {// 已经有这个key了Node now = map.get(key);now.value = value; // 第一次忘了更新这个出错if(now!=head.next) {// 处理now前后节点now.pre.next = now.next;now.next.pre = now.pre;// 处理head的后面节点head.next.pre = now;now.next = head.next;head.next = now;now.pre = head;}}}
}
<a name="ka5aW"></a>#### [31. 下一个排列](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/next-permutation/)- 我们需要将一个左边的「较小数」与一个右边的「较大数」交换,以能够让当前排列变大,从而得到下一个排列。- 同时我们要让这个「较小数」尽量靠右,而「较大数」尽可能小。当交换完成后,「较大数」右边的数需要按照升序重新排列。这样可以在保证新排列大于原来排列的情况下,使变大的幅度尽可能小。1. 首先从后向前查找第一个顺序对 (i,i+1)(i,i+1),满足 a[i] < a[i+1]a[i]<a[i+1]。这样「较小数」即为 a[i]a[i]。此时 [i+1,n)[i+1,n) 必然是下降序列。1. 如果找到了顺序对,那么在区间 [i+1,n)[i+1,n) 中从后向前查找第一个元素 jj 满足 a[i] < a[j]a[i]<a[j]。这样「较大数」即为 a[j]a[j]。1. 交换 a[i]a[i] 与 a[j]a[j],此时可以证明区间 [i+1,n)[i+1,n) 必为降序。我们可以直接使用双指针反转区间 [i+1,n)[i+1,n) 使其变为升序,而无需对该区间进行排序。```javaclass Solution {public void nextPermutation(int[] nums) {if(nums.length<=1)return;int reverseL = nums.length-2; // 被反转区间的左边界int reverseR = nums.length-1; // 被反转区间的右边界while(reverseL>=0 && nums[reverseL] >= nums[reverseL+1]) {reverseL--; // 找到第一个reverseL指向的数小于其后面一个数字的数 [1,3,5,4,2,1] 则找到数字三的位置,因为3<5}// reverseL!=-1则说明存在上面说的这样一个reverseL,否则数组就是全局逆序的if(reverseL!=-1) {while(reverseR>reverseL && nums[reverseR]<=nums[reverseL]){reverseR--;}int t = nums[reverseL];nums[reverseL] = nums[reverseR];nums[reverseR] = t;}// 反转逆序的数组,[1,3,5,4,2,1]此时变成了[1,4,5,3,2,1],// 5,3,2,1是逆序的,将其变为顺序即可,直接反转就行reverseL++;reverseR = nums.length-1;while(reverseL<reverseR) {int t = nums[reverseL];nums[reverseL] = nums[reverseR];nums[reverseR] = t;reverseL++;reverseR--;}}}
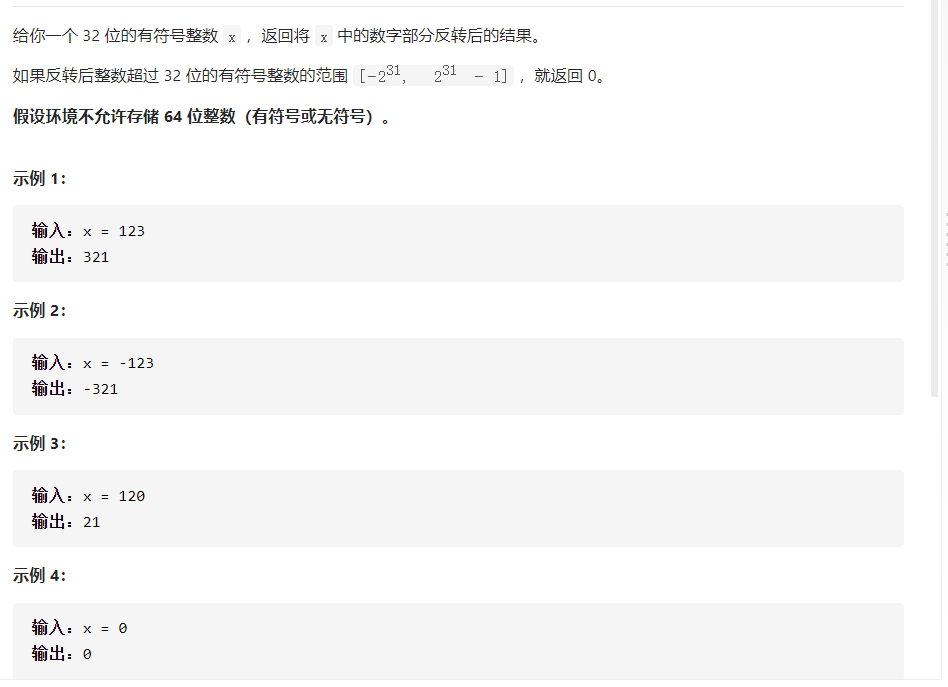
7. 整数反转

class Solution {public int reverse(int x) {int rev = 0;while (x != 0) {int pop = x % 10;x /= 10;if (rev > Integer.MAX_VALUE/10 || (rev == Integer.MAX_VALUE / 10 && pop > 7)) return 0;if (rev < Integer.MIN_VALUE/10 || (rev == Integer.MIN_VALUE / 10 && pop < -8)) return 0;rev = rev * 10 + pop;}return rev;}}
215. 数组中的第K个最大元素
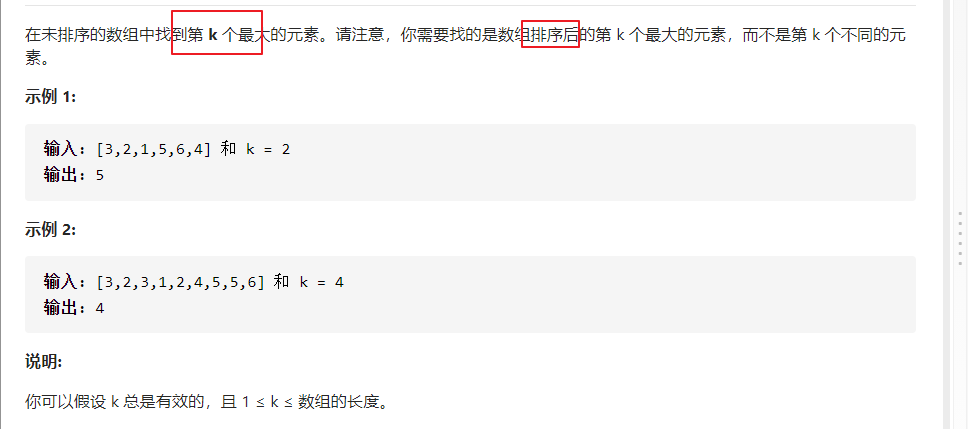
- 两种方法
- 使用优先级队列,进行堆排序 ```java import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int findKth(int[] a, int n, int K) {
// write code here
PriorityQueue
- 使用快速排序```javaimport java.util.*;public class Solution {public int findKth(int[] a, int n, int K) {return find(a,n-K,0,n-1);}// k 代表的是查找的元素在数组中的位置// [l,r]是查找区间int find(int[] nums,int k,int l,int r) {int temp = nums[l];int left = l;int right = r;while(l<r) {while(l<r && nums[r]>=temp) {r--;}while(l<r && nums[l]<=temp){l++;}if(l<r) {int t = nums[l];nums[l] = nums[r];nums[r] = t;}}nums[left] = nums[l];nums[l] = temp;if(l==k) {return nums[l];}else if(l<k){return find(nums,k,l+1,right); // 查找[l+1,r]} else {return find(nums,k,0,l-1); // 查找[0,l-1];}}}