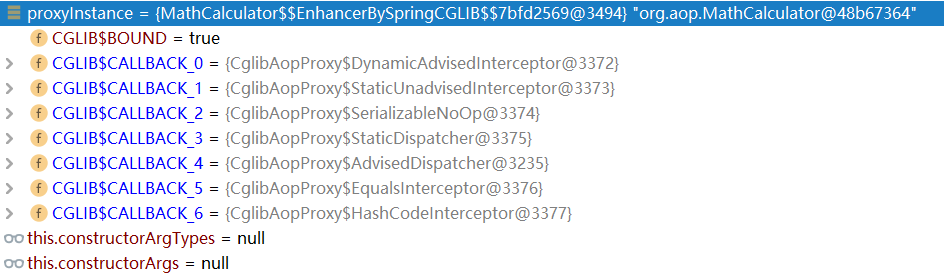
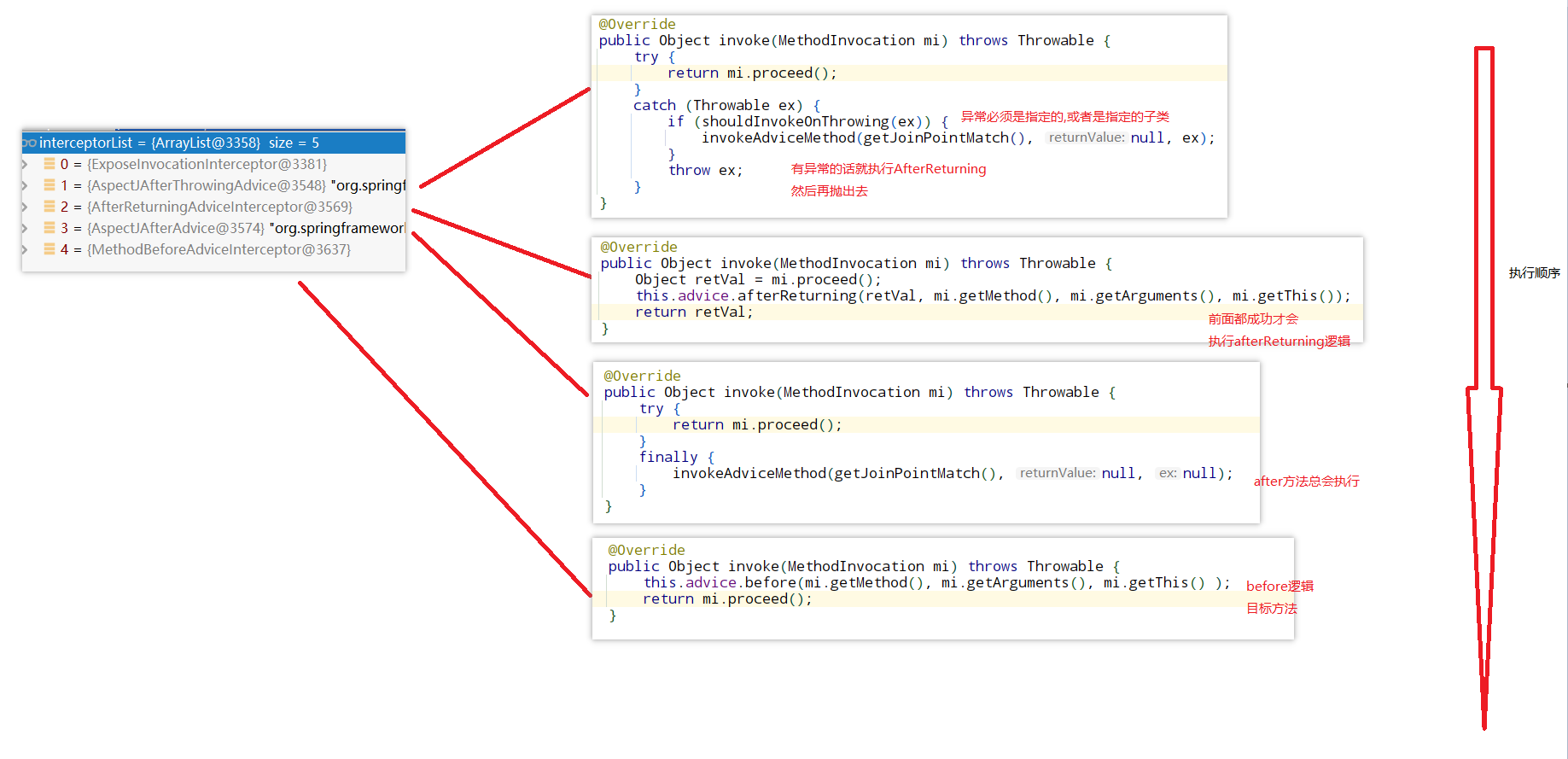
环境搭建
pom文件
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId><version>4.3.12.RELEASE</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-context</artifactId><version>4.3.12.RELEASE</version></dependency>
1.被代理对象
public class MathCalculator {public int div(int i, int j) {System.out.println("MathCalculator...div...");return i / j;}}
2.切面类
@Aspectpublic class LogAspects {@Pointcut("execution(public int org.aop.MathCalculator.*(..))")public void pointCut() {}// @Before:在目标方法(即div方法)运行之前切入,public int com.meimeixia.aop.MathCalculator.div(int, int)这一串就是切入点表达式,指定在哪个方法切入@Before("pointCut()")public void logStart(JoinPoint joinPoint) {Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs(); // 拿到参数列表,即目标方法运行需要的参数列表System.out.println(joinPoint.getSignature().getName() + "运行......@Before,参数列表是:{" + Arrays.asList(args) + "}");}// 在目标方法(即div方法)结束时被调用@After("pointCut()")public void logEnd(JoinPoint joinPoint) {System.out.println(joinPoint.getSignature().getName() + "结束......@After");}// 在目标方法(即div方法)正常返回了,有返回值,被调用@AfterReturning(value="pointCut()", returning="result")public void logReturn(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result) {System.out.println("除法正常返回......@AfterReturning,运行结果是:{}"+result);}// 在目标方法(即div方法)出现异常,被调用@AfterThrowing(value = "pointCut()",throwing = "ex")public void logException(Throwable ex) {System.out.println("除法出现异常......异常信息:{}"+ex.getMessage());}}
用到了注解
@Aspect
@Pointcut(“execution(public int org.aop.MathCalculator.*(..))”)
@Before等
3.配置类
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy@Configurationpublic class MainConfigOfAOP {// 将业务逻辑类(目标方法所在类)加入到容器中@Beanpublic MathCalculator calculator() {return new MathCalculator();}// 将切面类加入到容器中@Beanpublic LogAspects logAspects() {return new LogAspects();}}
4.测试方法
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfigOfAOP.class);// 我们要使用Spring容器中的组件MathCalculator mathCalculator = applicationContext.getBean(MathCalculator.class);mathCalculator.div(1, 0);
入口分析@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
作用就是:@Import(AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar.class)
向容器注册bean
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy源码
class AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {/*** Register, escalate, and configure the AspectJ auto proxy creator based on the value* of the @{@link EnableAspectJAutoProxy#proxyTargetClass()} attribute on the importing* {@code @Configuration} class.核心:注册AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator*/@Overridepublic void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {//方法1:注册名为internalAutoProxyCreator的AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator类AopConfigUtils.registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry);//方法2:提取注解的属性,正常都是空,如果有属性,则调用下面AopConfigUtils的方法,对aop处理进行设置AnnotationAttributes enableAspectJAutoProxy =AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(importingClassMetadata, EnableAspectJAutoProxy.class);if (enableAspectJAutoProxy.getBoolean("proxyTargetClass")) {AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToUseClassProxying(registry);}if (enableAspectJAutoProxy.getBoolean("exposeProxy")) {AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToExposeProxy(registry);}}}
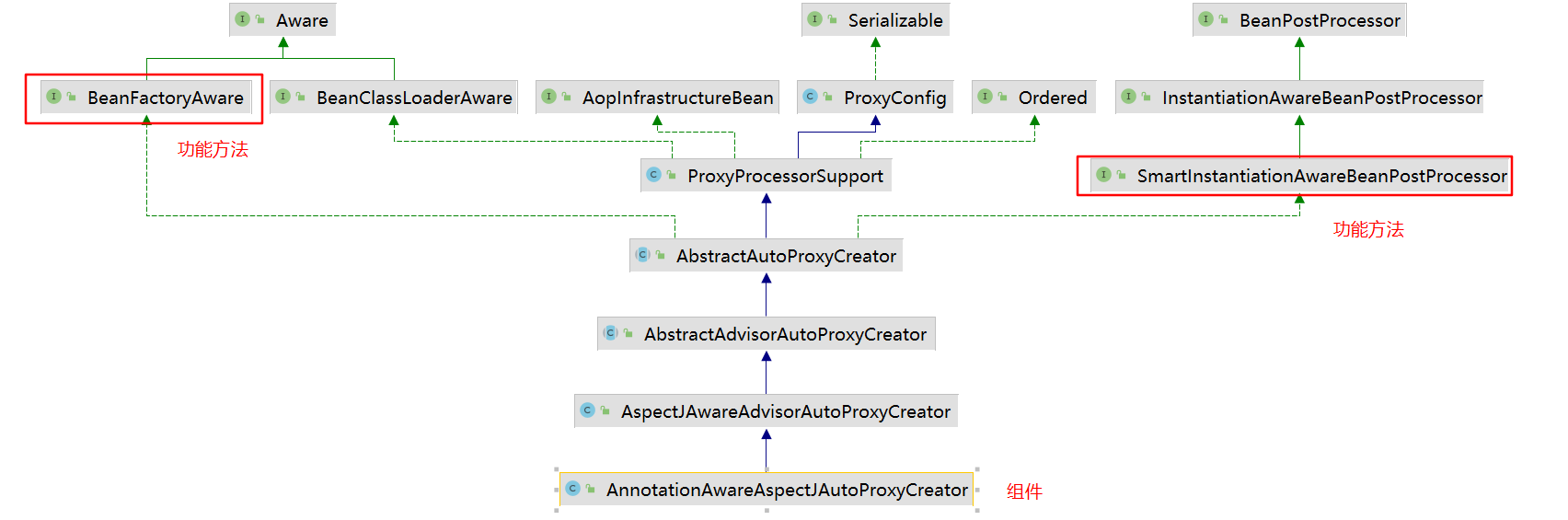
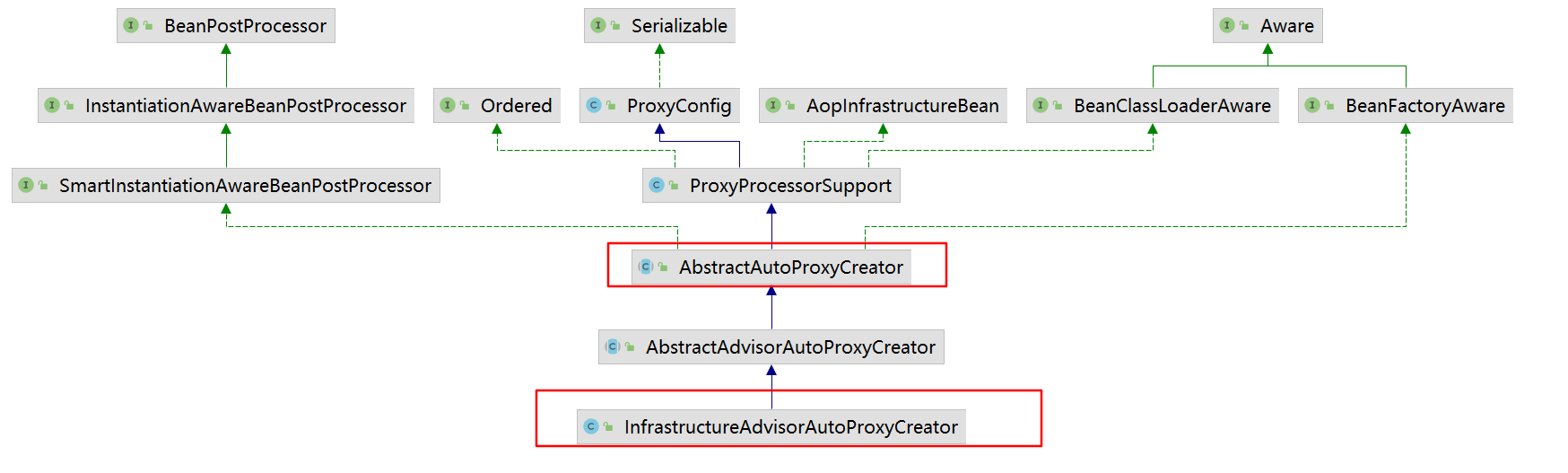
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator继承图
类分析和打断点
主要方法在接口里面,在BeanFactoryAware的setBeanFactory和InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInstantiation以及BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization
具体的实现在这四个类的方法里面,可以打上断点看看看
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator组件
流程:如何创建这个组件
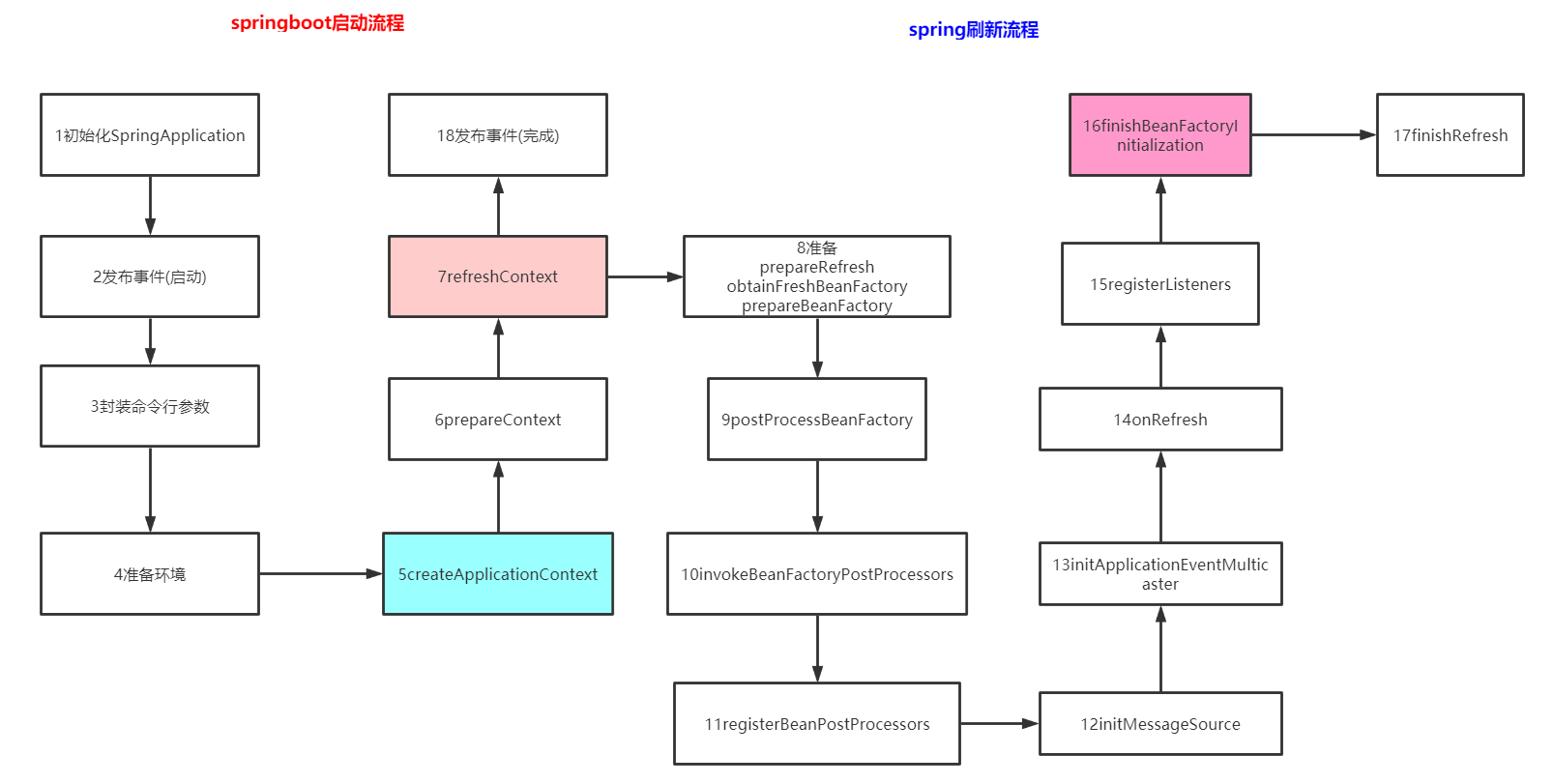
- 为什么从这里开始,因为AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator实现了BeanPostProcessor
- 所有的BeanPostProcessor分为三个等级PriorityOrdered/Ordered/regular
- 这里属于Ordered
- 进入到beanFactory.getBean的创建Bean流程
- getBean在ioc章节已经有流程图了https://www.processon.com/diagraming/607ada88f346fb647a594af3,继续温习一遍
下面是通用的流程
类beanFactory{方法getBean{}方法createBean{//Give BeanPostProcessors a chance to return a proxy instead of the target bean instance//我们自定义的类在这里就会被组件拿去增强//具体就是遍历后置处理器,对方法进行增强,如果得到了,就return,如果得不到代理对象才会进入doCreateBean来创建resolveBeforeInstantiation();doCreateBean();}....最终进入下面这个方法方法doCreateBean{//1创建对象instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);//2.1初始化实例-1详见IOC流程图populateBean();//2.2初始化实例-2initializeBean();}方法initializeBean{//2.2.1回调BeanNameAware/BeanClassLoaderAware/BeanFactoryAware set对应的值invokeAwareMethods();//2.2.2遍历后置处理器增强applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization();//2.2.3invokeInitMethods();//2.2.4遍历后置处理器增强applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization();}方法resolveBeforeInstantiation{//组件在这里就发挥作用了bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(targetType, beanName);if (bean != null) {bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(bean, beanName);}}}
流程:这个组件的使用(其他地方用它)
- 故事从16finishBeanFactoryInitialization开始
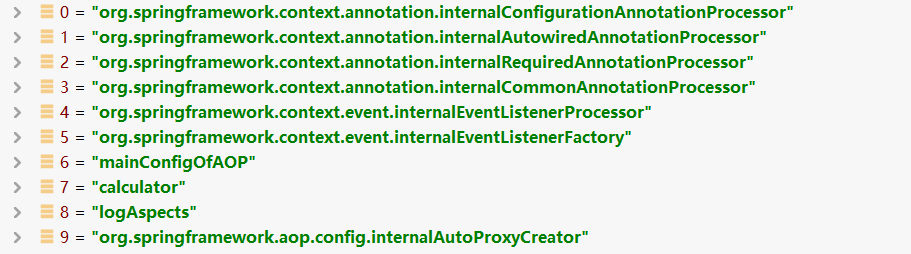
- 这里就是初始化一些spring自定义的普通组件和我们的配置类,组件了.让我们看看有谁进来了?进入到组件的postProcessAfterInitialization方法里面呢?
- EventListenerMethodProcessor
- DefaultEventListenerFactory
- 自定义的MainConfigOfAOP
- 自定义的MathCalculator
- 自定义的LogAspects
细节分析-组件
看一下大致流程
组件MathCalculator的调用顺序来看大致流程
16finishBeanFactoryInitialization
BeanFactory#createBean
resolveBeforeInstantiation生成代理对象(遍历所有后置处理器)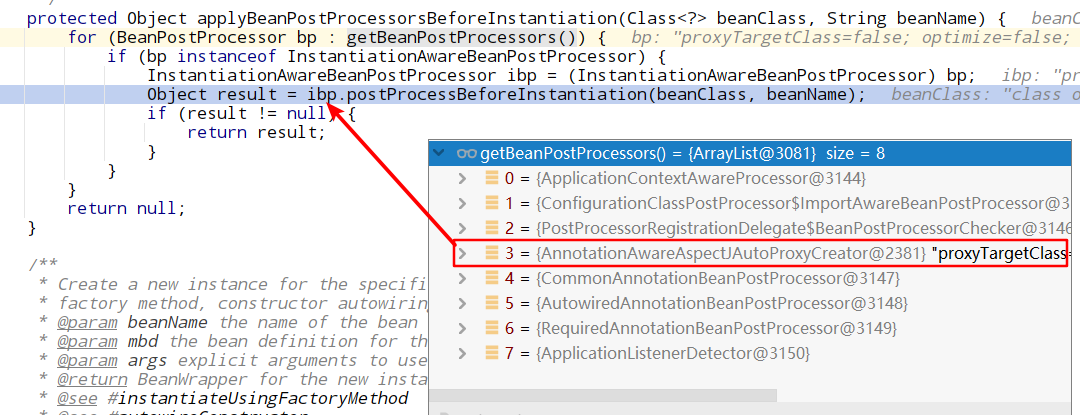
第一次进入postProcessBeforeInstantiation
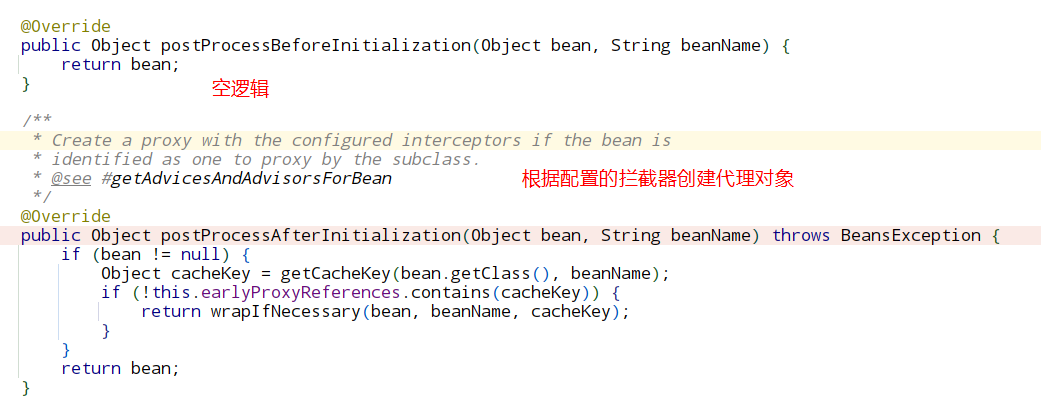
@Overridepublic Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(beanClass, beanName);if (beanName == null || !this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {if (this.advisedBeans.containsKey(cacheKey)) {return null;}//shouldSkip就会去找潜在的adivce增强器if (isInfrastructureClass(beanClass) || shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName)) {this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);return null;}}// Create proxy here if we have a custom TargetSource.// Suppresses unnecessary default instantiation of the target bean:// The TargetSource will handle target instances in a custom fashion.if (beanName != null) {TargetSource targetSource = getCustomTargetSource(beanClass, beanName);if (targetSource != null) {this.targetSourcedBeans.add(beanName);Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(beanClass, beanName, targetSource);Object proxy = createProxy(beanClass, beanName, specificInterceptors, targetSource);this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());return proxy;}}return null;}
返回null,然后就要进入正常的doCreateBean流程创建Bean
然后进入applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(遍历BeanPostProcessor)
接着组件的postProcessAfterInitialization
流程比较多先进入wrapIfNecessary
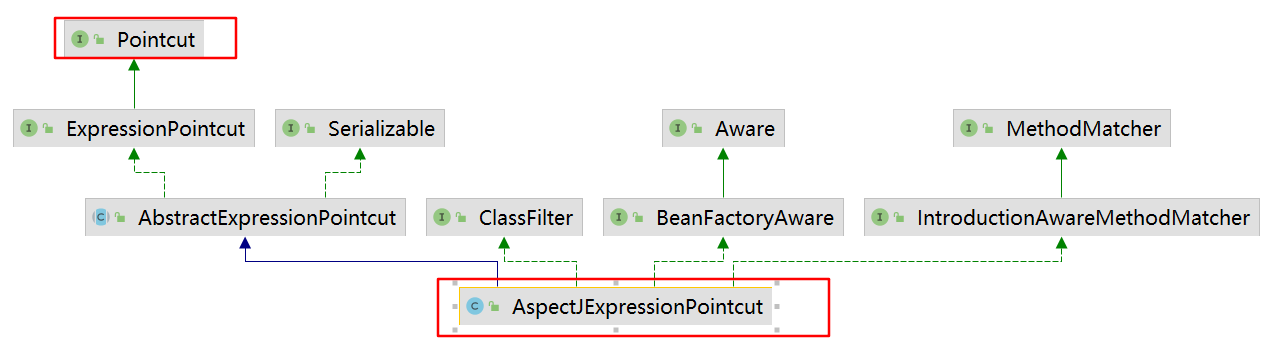
//核心逻辑都在2,会返回代理对象protected Object wrapIfNecessary{//1这个详细看看Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);//2这个比较复杂!Object proxy = createProxy(bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));return proxy;//最终这里返回了cglib代理对象}getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean就是调用findEligibleAdvisors//1.1找到所有需要增强的切面方法,包装成List<Advisor>//找到所有的切面方法,然后去匹配,最终得到当前方法适配的protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {//找到所有List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();//匹配List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName);//AspectJ的话list开头加一个ExposeInvocationInterceptorextendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);//排序eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);return eligibleAdvisors;}//1.1.1protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors() {// Add all the Spring advisors found according to superclass rules.List<Advisor> advisors = super.findCandidateAdvisors();空// Build Advisors for all AspectJ aspects in the bean factory.advisors.addAll(this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors());//真正逻辑return advisors;}//1.1.1.1遍历所有的Aspect,把每个Aspect的InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl放在list里面public List<Advisor> buildAspectJAdvisors() {List<Advisor> advisors = new LinkedList<Advisor>();//这数据类型有点意思for (String aspectName : aspectNames) {List<Advisor> cachedAdvisors = this.advisorsCache.get(aspectName);//进来的时候缓存就有,直接取出来if (cachedAdvisors != null) {advisors.addAll(cachedAdvisors);}else {MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory = this.aspectFactoryCache.get(aspectName);advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));}}return advisors;}//1.1.2protected List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {ProxyCreationContext.setCurrentProxiedBeanName(beanName);try {return AopUtils.findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass);真正逻辑}finally {ProxyCreationContext.setCurrentProxiedBeanName(null);}}public static List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> clazz) {List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = new LinkedList<Advisor>();boolean hasIntroductions = !eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty();for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {if (canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions)) {eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);}}return eligibleAdvisors;}//第一个参数就是InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImplpublic static boolean canApply(Advisor advisor, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {else if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) {PointcutAdvisor pca = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;return canApply(pca.getPointcut(), targetClass, hasIntroductions);}}//第一个参数是InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl的AspectJExpressionPointcut//真正逻辑在introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matchespublic static boolean canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {MethodMatcher methodMatcher = pc.getMethodMatcher();//就是本身IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher introductionAwareMethodMatcher = null;if (methodMatcher instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) {introductionAwareMethodMatcher = (IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) methodMatcher;}Set<Class<?>> classes = new LinkedHashSet<Class<?>>(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetClass));classes.add(targetClass);for (Class<?> clazz : classes) {Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getAllDeclaredMethods(clazz);//只要有一个方法匹配就是truefor (Method method : methods) {if ((introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null &&introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions)) ||methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)) {return true;}}}return false;}@Overridepublic boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass, boolean beanHasIntroductions) {Method targetMethod = AopUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, targetClass);ShadowMatch shadowMatch = getShadowMatch(targetMethod, method);// Special handling for this, target, @this, @target, @annotation// in Spring - we can optimize since we know we have exactly this class,// and there will never be matching subclass at runtime.if (shadowMatch.alwaysMatches()) {return true;}}
具体是这样的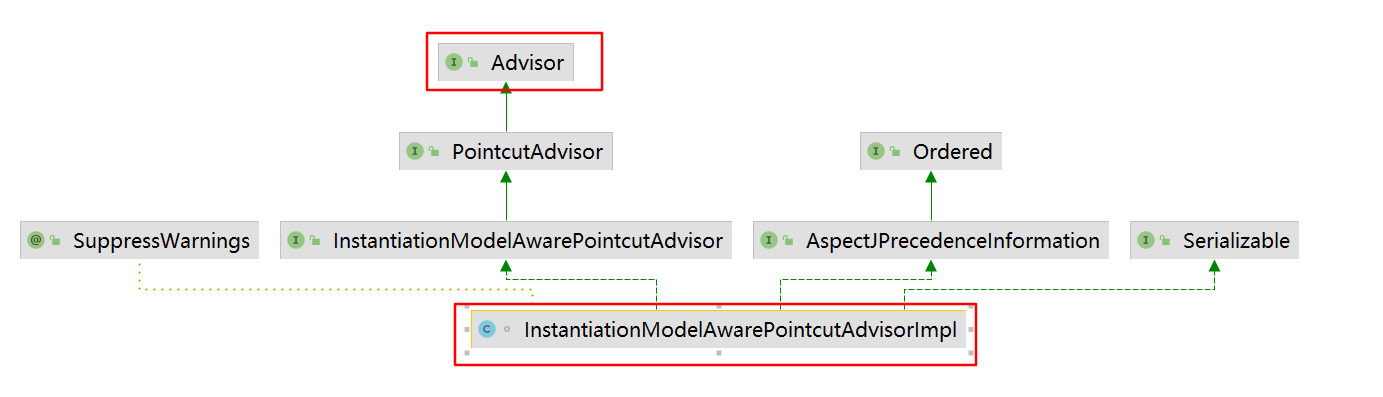
继续分析之前没看到的
Object proxy = createProxy(beanClass, beanName, specificInterceptors, targetSource);
具体
//Create an AOP proxy for the given bean.protected Object createProxy(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);//切面类proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);//需要增强的类customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);//空的,等子类实现return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());//逻辑在这里}public Object getProxy(ClassLoader classLoader) {return createAopProxy().getProxy(classLoader);}protected final synchronized AopProxy createAopProxy() {if (!this.active) {activate();}return getAopProxyFactory().createAopProxy(this);}//Create an {@link AopProxy} for the given AOP configuration.工厂模式,根据代理的情况(配置),创建不同的代理对象public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass();if (targetClass == null) {throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");}if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);}return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);}else {return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);}}
针对工厂的注释
现在就看看cglib怎么生成代理对象吧
@Overridepublic Object getProxy(ClassLoader classLoader) {try {Class<?> proxySuperClass = rootClass;if (ClassUtils.isCglibProxyClass(rootClass)) {proxySuperClass = rootClass.getSuperclass();Class<?>[] additionalInterfaces = rootClass.getInterfaces();for (Class<?> additionalInterface : additionalInterfaces) {this.advised.addInterface(additionalInterface);}}// Validate the class, writing log messages as necessary.validateClassIfNecessary(proxySuperClass, classLoader);// Configure CGLIB Enhancer...Enhancer enhancer = createEnhancer();if (classLoader != null) {enhancer.setClassLoader(classLoader);if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader &&((SmartClassLoader) classLoader).isClassReloadable(proxySuperClass)) {enhancer.setUseCache(false);}}enhancer.setSuperclass(proxySuperClass);enhancer.setInterfaces(AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised));enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE);enhancer.setStrategy(new ClassLoaderAwareUndeclaredThrowableStrategy(classLoader));//这里貌似是核心逻辑先记录一下Callback[] callbacks = getCallbacks(rootClass);Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[callbacks.length];for (int x = 0; x < types.length; x++) {types[x] = callbacks[x].getClass();}// fixedInterceptorMap only populated at this point, after getCallbacks call aboveenhancer.setCallbackFilter(new ProxyCallbackFilter(this.advised.getConfigurationOnlyCopy(), this.fixedInterceptorMap, this.fixedInterceptorOffset));enhancer.setCallbackTypes(types);// Generate the proxy class and create a proxy instance.return createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks);}catch (CodeGenerationException ex) {throw new AopConfigException("Could not generate CGLIB subclass of class [" +this.advised.getTargetClass() + "]: " +"Common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class",ex);}catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {throw new AopConfigException("Could not generate CGLIB subclass of class [" +this.advised.getTargetClass() + "]: " +"Common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class",ex);}catch (Throwable ex) {// TargetSource.getTarget() failedthrow new AopConfigException("Unexpected AOP exception", ex);}}private Callback[] getCallbacks(Class<?> rootClass) throws Exception {// Parameters used for optimization choices...boolean exposeProxy = this.advised.isExposeProxy();boolean isFrozen = this.advised.isFrozen();boolean isStatic = this.advised.getTargetSource().isStatic();// Choose an "aop" interceptor (used for AOP calls).Callback aopInterceptor = new DynamicAdvisedInterceptor(this.advised);// Choose a "straight to target" interceptor. (used for calls that are// unadvised but can return this). May be required to expose the proxy.Callback targetInterceptor;if (exposeProxy) {targetInterceptor = isStatic ?new StaticUnadvisedExposedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) :new DynamicUnadvisedExposedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource());}else {targetInterceptor = isStatic ?new StaticUnadvisedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) :new DynamicUnadvisedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource());}// Choose a "direct to target" dispatcher (used for// unadvised calls to static targets that cannot return this).Callback targetDispatcher = isStatic ?new StaticDispatcher(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) : new SerializableNoOp();Callback[] mainCallbacks = new Callback[] {aopInterceptor, // for normal advicetargetInterceptor, // invoke target without considering advice, if optimizednew SerializableNoOp(), // no override for methods mapped to thistargetDispatcher, this.advisedDispatcher,new EqualsInterceptor(this.advised),new HashCodeInterceptor(this.advised)};Callback[] callbacks;// If the target is a static one and the advice chain is frozen,// then we can make some optimizations by sending the AOP calls// direct to the target using the fixed chain for that method.if (isStatic && isFrozen) {Method[] methods = rootClass.getMethods();Callback[] fixedCallbacks = new Callback[methods.length];this.fixedInterceptorMap = new HashMap<String, Integer>(methods.length);// TODO: small memory optimization here (can skip creation for methods with no advice)for (int x = 0; x < methods.length; x++) {List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(methods[x], rootClass);fixedCallbacks[x] = new FixedChainStaticTargetInterceptor(chain, this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget(), this.advised.getTargetClass());this.fixedInterceptorMap.put(methods[x].toString(), x);}// Now copy both the callbacks from mainCallbacks// and fixedCallbacks into the callbacks array.callbacks = new Callback[mainCallbacks.length + fixedCallbacks.length];System.arraycopy(mainCallbacks, 0, callbacks, 0, mainCallbacks.length);System.arraycopy(fixedCallbacks, 0, callbacks, mainCallbacks.length, fixedCallbacks.length);this.fixedInterceptorOffset = mainCallbacks.length;}else {callbacks = mainCallbacks;}return callbacks;}
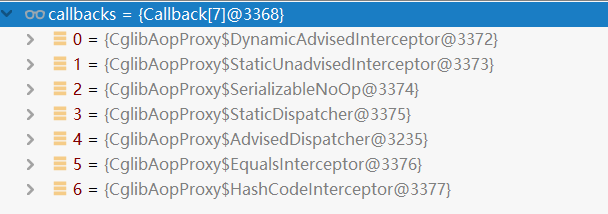 得到这些
得到这些
最终来生成
protected Object createProxyClassAndInstance(Enhancer enhancer, Callback[] callbacks) {Class<?> proxyClass = enhancer.createClass();Object proxyInstance = null;if (objenesis.isWorthTrying()) {try {proxyInstance = objenesis.newInstance(proxyClass, enhancer.getUseCache());}catch (Throwable ex) {logger.debug("Unable to instantiate proxy using Objenesis, " +"falling back to regular proxy construction", ex);}}if (proxyInstance == null) {// Regular instantiation via default constructor...try {proxyInstance = (this.constructorArgs != null ?proxyClass.getConstructor(this.constructorArgTypes).newInstance(this.constructorArgs) :proxyClass.newInstance());}catch (Throwable ex) {throw new AopConfigException("Unable to instantiate proxy using Objenesis, " +"and regular proxy instantiation via default constructor fails as well", ex);}}((Factory) proxyInstance).setCallbacks(callbacks);return proxyInstance;}
流程:真正运作
主要就是把
转换成
可以看看转换的逻辑
public MethodInterceptor[] getInterceptors(Advisor advisor) throws UnknownAdviceTypeException {List<MethodInterceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<MethodInterceptor>(3);Advice advice = advisor.getAdvice();//这个还不一样if (advice instanceof MethodInterceptor) {interceptors.add((MethodInterceptor) advice);}for (AdvisorAdapter adapter : this.adapters) {if (adapter.supportsAdvice(advice)) {interceptors.add(adapter.getInterceptor(advisor));}}if (interceptors.isEmpty()) {throw new UnknownAdviceTypeException(advisor.getAdvice());}return interceptors.toArray(new MethodInterceptor[interceptors.size()]);}
实际运作
public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {Object oldProxy = null;boolean setProxyContext = false;Class<?> targetClass = null;Object target = null;try {if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {// Make invocation available if necessary.oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);setProxyContext = true;}// May be null. Get as late as possible to minimize the time we// "own" the target, in case it comes from a pool...target = getTarget();if (target != null) {targetClass = target.getClass();}//真正逻辑List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);Object retVal;// Check whether we only have one InvokerInterceptor: that is,// no real advice, but just reflective invocation of the target.if (chain.isEmpty() && Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly.// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor, so we know// it does nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot// swapping or fancy proxying.Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);retVal = methodProxy.invoke(target, argsToUse);}else {// We need to create a method invocation...//真正逻辑retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();}retVal = processReturnType(proxy, target, method, retVal);return retVal;}finally {if (target != null) {releaseTarget(target);}if (setProxyContext) {// Restore old proxy.AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);}}}
public List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {MethodCacheKey cacheKey = new MethodCacheKey(method);List<Object> cached = this.methodCache.get(cacheKey);if (cached == null) {cached = this.advisorChainFactory.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(this, method, targetClass);this.methodCache.put(cacheKey, cached);}return cached;}
@Overridepublic List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(Advised config, Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {// This is somewhat tricky... We have to process introductions first,// but we need to preserve order in the ultimate list.List<Object> interceptorList = new ArrayList<Object>(config.getAdvisors().length);Class<?> actualClass = (targetClass != null ? targetClass : method.getDeclaringClass());boolean hasIntroductions = hasMatchingIntroductions(config, actualClass);AdvisorAdapterRegistry registry = GlobalAdvisorAdapterRegistry.getInstance();for (Advisor advisor : config.getAdvisors()) {if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) {// Add it conditionally.PointcutAdvisor pointcutAdvisor = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;if (config.isPreFiltered() || pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)) {//真正逻辑MethodInterceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);MethodMatcher mm = pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getMethodMatcher();if (MethodMatchers.matches(mm, method, actualClass, hasIntroductions)) {if (mm.isRuntime()) {// Creating a new object instance in the getInterceptors() method// isn't a problem as we normally cache created chains.for (MethodInterceptor interceptor : interceptors) {interceptorList.add(new InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher(interceptor, mm));}}else {interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));}}}}else if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {IntroductionAdvisor ia = (IntroductionAdvisor) advisor;if (config.isPreFiltered() || ia.getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)) {Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));}}else {Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));}}return interceptorList;}@Overridepublic MethodInterceptor[] getInterceptors(Advisor advisor) throws UnknownAdviceTypeException {List<MethodInterceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<MethodInterceptor>(3);Advice advice = advisor.getAdvice();//取出来,进行封装if (advice instanceof MethodInterceptor) {//直接塞进去interceptors.add((MethodInterceptor) advice);}for (AdvisorAdapter adapter : this.adapters) {//适配一下塞进去if (adapter.supportsAdvice(advice)) {interceptors.add(adapter.getInterceptor(advisor));}}if (interceptors.isEmpty()) {throw new UnknownAdviceTypeException(advisor.getAdvice());}return interceptors.toArray(new MethodInterceptor[interceptors.size()]);}
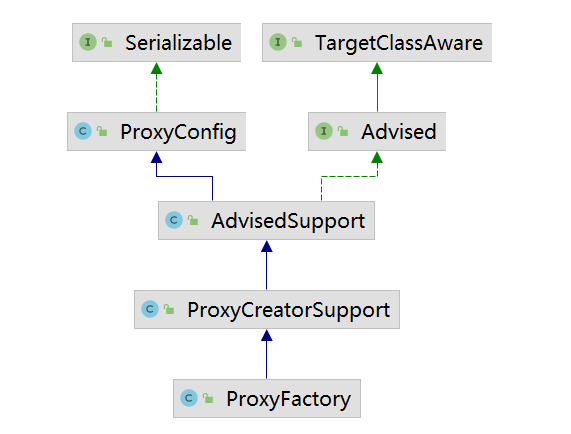 config.getAdvisors()得到
config.getAdvisors()得到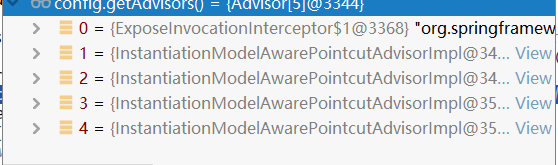 这两个就是前面生成的
这两个就是前面生成的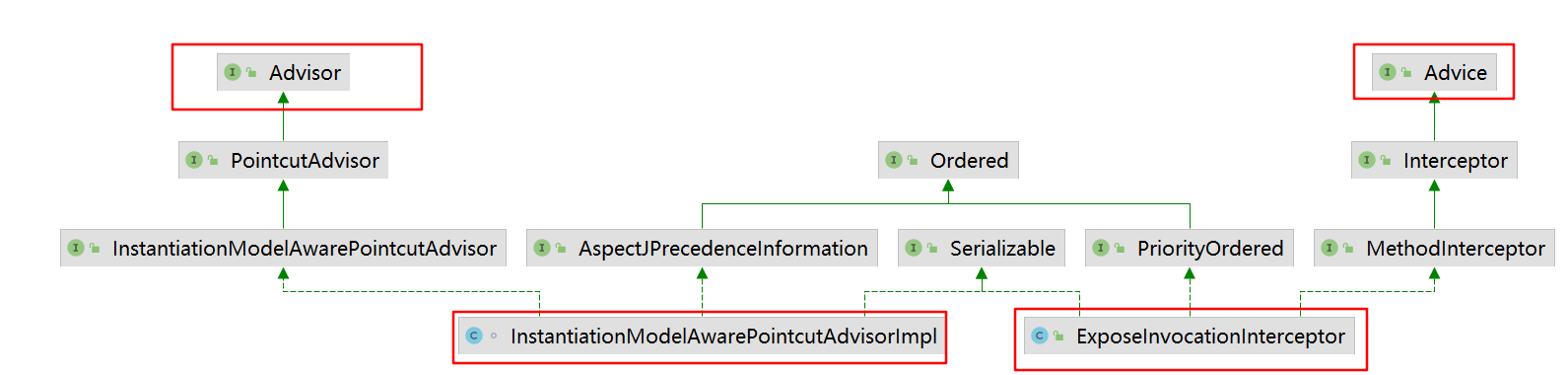
遍历这5个,利用适配器封装为MethodInterceptor[]
最终转换成的样子,主要看关键方法,以及实现的接口
public class AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice extends AbstractAspectJAdviceimplements MethodInterceptor, AfterAdvice, Serializable {@Overridepublic boolean isAfterAdvice() {return true;}@Overridepublic Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {try {return mi.proceed();}catch (Throwable ex) {if (shouldInvokeOnThrowing(ex)) {//调用业务逻辑invokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), null, ex);}throw ex;}}/*** In AspectJ semantics, after throwing advice that specifies a throwing clause* is only invoked if the thrown exception is a subtype of the given throwing type.*/private boolean shouldInvokeOnThrowing(Throwable ex) {return getDiscoveredThrowingType().isAssignableFrom(ex.getClass());}}public class AspectJAfterAdvice extends AbstractAspectJAdviceimplements MethodInterceptor, AfterAdvice, Serializable {@Overridepublic Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {try {return mi.proceed();}finally {invokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), null, null);}}@Overridepublic boolean isAfterAdvice() {return true;}}
public class MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable {private MethodBeforeAdvice advice;/*** Create a new MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor for the given advice.* @param advice the MethodBeforeAdvice to wrap*/public MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor(MethodBeforeAdvice advice) {Assert.notNull(advice, "Advice must not be null");this.advice = advice;}@Overridepublic Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {this.advice.before(mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis() );return mi.proceed();}}public class AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, AfterAdvice, Serializable {private final AfterReturningAdvice advice;/*** Create a new AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor for the given advice.* @param advice the AfterReturningAdvice to wrap*/public AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor(AfterReturningAdvice advice) {Assert.notNull(advice, "Advice must not be null");this.advice = advice;}@Overridepublic Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {Object retVal = mi.proceed();this.advice.afterReturning(retVal, mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis());return retVal;}}
看看CglibMethodInvocation#proceed逻辑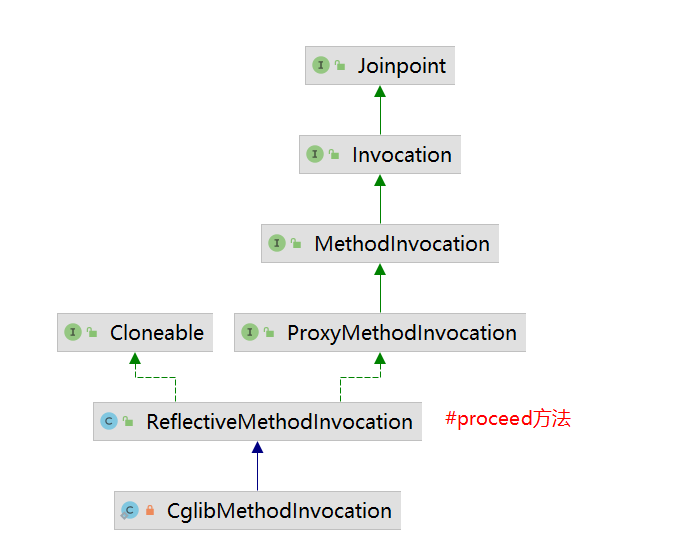
@Overridepublic Object proceed() throws Throwable {// We start with an index of -1 and increment early.if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {return invokeJoinpoint();}Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {// Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have// been evaluated and found to match.InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, this.targetClass, this.arguments)) {return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);}else {// Dynamic matching failed.// Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain.return proceed();}}else {// It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcut will have// been evaluated statically before this object was constructed.return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);}}
第一次进来ExposeInvocationInterceptor,没做什么内容就第二个了
第二个AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice,调用一下,捕捉异常,执行切面异常逻辑
第三个AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor,{1,调用下一个,执行切面afterReturning逻辑}
第四个AspectJAfterAdvice,{调用下一个,然后finally执行切面after逻辑}
第五个是MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor,{调用切面before逻辑,执行下一个}
执行完是4了,proceed就执行目标真正逻辑
执行After逻辑
正常的话执行AfterReturning逻辑,异常执行AfterThrowing逻辑
总结一下
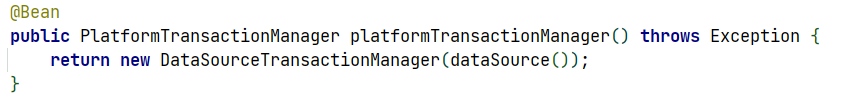
声明式事务
service->
doCreateBean
initializeBean
applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization
进入到AbstractAutoProxyCreator(InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator)#postProcessAfterInitialization
wrapIfNecessary
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);Object proxy = createProxy(bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());return proxy;}
拦截器是谁?
BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor
封装成Advisor放在ProxyFactory
创建的cglibAopProxy生成代理对象
执行的时候代理对象
用TransactionInterceptor拦截目标对象
DynamicAdvisedInterceptor#intercept
{new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();}
TransactionInterceptor#invoke
#invokeWithinTransaction
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, Class<?> targetClass, final InvocationCallback invocation)throws Throwable {// If the transaction attribute is null, the method is non-transactional.注解里面的属性之类的final TransactionAttribute txAttr = getTransactionAttributeSource().getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass);//这个就是我们自己配置的,见下图final PlatformTransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);if (txAttr == null || !(tm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);Object retVal = null;try {// This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain.// This will normally result in a target object being invoked.retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();//调用真正的方法}catch (Throwable ex) {// target invocation exceptioncompleteTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);//方法异常了就回滚throw ex;}finally {cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);}commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);//方法正常返回结束了就提交事务return retVal;}else {// It's a CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager: pass a TransactionCallback in....回滚}