1、什么是事物
(1)事务是数据库操作最基本单元,逻辑上一组操作,要么都成功,如果有一个失败所有操作都失败
(2)典型场景:银行转账
2、事务四个特性(ACID)
(1)原子性(要么都成功,要么都失败)
(2)一致性(操作之前和操作之后,总量不变。)
(3)隔离性(在多事务操作的时候,相互之间不会产生影响)
(4)持久性(操作完之后数据真正存储在表中,永久保存)
3、事务操作(搭建事务操作环境)
(1)创建数据库表并添加记录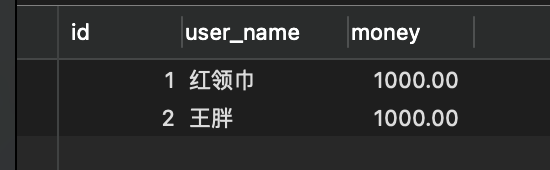
(2)创建Dao类和实现类
package com.daijunyi.dao;public interface AccountDao {public void changeMoneyById(Integer userId,Double money);}
package com.daijunyi.dao;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;@Repositorypublic class AccountDaoImp implements AccountDao {@Autowiredprivate JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;@Overridepublic void changeMoneyById(Integer userId, Double money) {String sql = "update t_account set money=money+? where id=?";Object[] args = {money,userId};int update = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, args);System.out.println("操作结果:"+update);}}
(3)创建service类
package com.daijunyi.service;import com.daijunyi.dao.AccountDao;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;@Servicepublic class AccountService {@Autowiredprivate AccountDao accountDao;public void changeMoney(Integer fromUserId,Integer toUserId,Double changeMoney){accountDao.changeMoneyById(fromUserId,-changeMoney);accountDao.changeMoneyById(toUserId,changeMoney);}}
(4)配置数据库properties文件
druid.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driverdruid.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/learndruid.username=rootdruid.password=qwerasdf123
(5)创建bean.xml并且配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"><!--开启主键扫描--><context:component-scan base-package="com.daijunyi"/><!--引入外部属性文件--><context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"/><!--配置datasource 数据库连接池--><bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"><property name="driverClassName" value="${druid.driver}"/><property name="url" value="${druid.url}"/><property name="username" value="${druid.username}"/><property name="password" value="${druid.password}"/></bean><!--配置jdbcTemplate对象--><bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"><property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/></bean></beans>
(6)测试
@Test
public void testChangeMoney(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
AccountService accountService = (AccountService) context.getBean("accountService");
accountService.changeMoney(1,2,100.0);
}
结果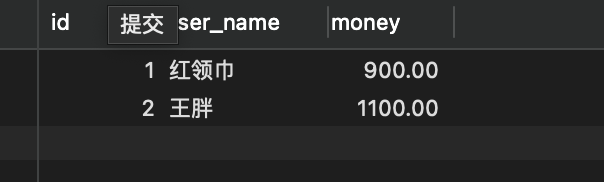
这是正常请求,如果中间发生了错误,比如我们在service类中
@Service
public class AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao;
public void changeMoney(Integer fromUserId,Integer toUserId,Double changeMoney){
accountDao.changeMoneyById(fromUserId,-changeMoney);
int i=1/0;
accountDao.changeMoneyById(toUserId,changeMoney);
}
}
这样做 我们在恢复到每个人都1000块钱的时候,再次执行就会产生错误
结果为: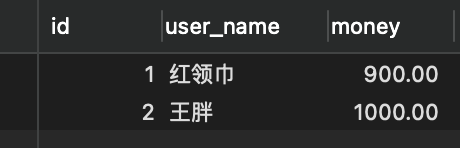
就少了100了,接下去我们就来用事物解决这个问题

