- 算法很有趣
- 算法很重要
- 算法有点难
- 刷题网址https://www.nowcoder.com/activity/oj?tab=1
源码地址:https://github.com/daijunyi/structure-learn-one.git
1、数据结构与算法概述
1、数据结构与算法的关系
1、数据data结构(structure)是一门研究组织数据方式的学科,有了编程语言也就有了数据结构,学号数据结构可以编写出更加漂亮,更加高效的代码
- 2、学习好数据结构就要多多考虑如何将生活中遇到的问题,用程序去实现解决
- 3、程序=数据结构+算法
4、数据结构是算法的基础,换言之,想要学习好算法,需要把数据结构学到位
2、实际编程中遇到的问题
1、字符串替换问题

-
2、五子棋程序
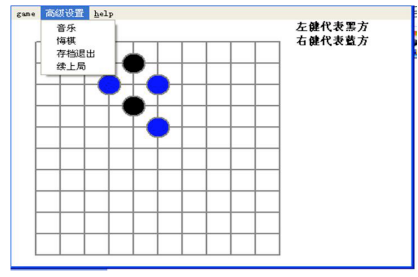
如何判断游戏的输赢,并可以完成存盘退出和继续上局的功能 1) 棋盘 二维数组=>(稀疏数组)-> 写入文件【存档功能】
2) 读取文件-》稀疏数组-》二维数组 -》 棋盘 【接上局】
3、约瑟夫(Josephu)问题(丢手帕问题)
1、Josephu 问题为:设编号为1,2,… n的n个人围坐一圈,约定编号为k(1<=k<=n)的人从1开始报数,数到 m 的那个人出列,它的下一位又从1 开始报数,数到 m 的那个人又出列,依次类推,直到所有人出列为止,由此产生一个出队编号的序列。
- 2、提示:用一个不带头结点的循环链表来处理Josephu 问题:先构成一个有 n 个结点的单循环链表(单向环形链表),然后由 k 结点起从 1 开始计数,计到 m 时,对应结点从链表中删除,然后再从被删除结点的下一个结点又从1开始计数,直到最后一个结点从链表中删除算法结束。
- 3、小结:完成约瑟夫问题,需要使用到单向环形链表,这个数据结构
4、其他问题

- 修路问题=> 最小生成树(加权值)【数据结构】+ 普利姆算法
- 最短路径问题=> 图+弗洛伊德算法
- 汉诺塔塔=>分支算法
-
3、线性结构和非线性结构
1、线性结构
线性结构作为最常用的数据结构,其特点是数据元素之间存在一对一的线性关系
- 线性结构有两种不同的存储结构,即顺序存储结构(数组)和链式存储结构(链表)。顺序存储的线性表称为顺序表,顺序表中的存储元素是连续的
- 链式存储的线性表称为链表,链表中的存储元素不一定是连续的,元素节点中存放数据元素以及相邻元素的地址信息,可以使用内存中的非连续地址
- 线性结构常见的有:数组、队列、链表和栈,后面我们会详细讲解
2、非线性结构
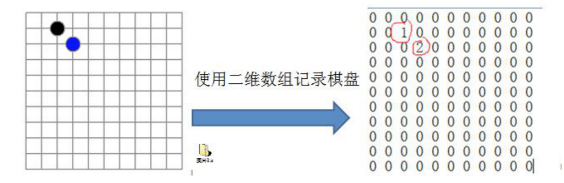
分析问题:因为该二维数组的很多值是默认值0,因此记录了很多没有意义的数据.->稀疏数组。
2、基本介绍
稀疏数组本质是改造了数据的记录方式,改造成了一个多行3列的二维数组。
- 第一行记录 二维数组 是几行几列 并且有多少个是有有值的
- 第二行开始 就是记录具体的第几行第几列的值是多少
- 当一个数组中大部分元素为0,或者为同一个值的数组时,可以使用稀疏数组来保存该数组。
- 稀疏数组的处理方法是:
- 记录数组一共有几行几列,有多少个不同的值
- 把具有不同值的元素的行列及值记录在一个小规模的数组中,从而缩小程序的规模
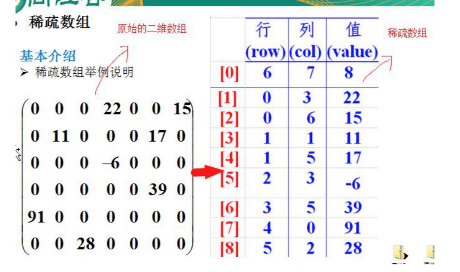
- 从原来的67=42变成了93=27,数据变小了不少
3、实现思路
1、二维数组转稀疏数组的思路
- 遍历原始的二维数组,得到有效数据的个数sum
- 根据sum就可以创建稀疏数组sparseArr int[sum+1][3]
-
2、稀疏数组转原始的二维数组
先读取稀疏数组的第一行,根据第一行的数据,创建原始的二维数组,比如上面的chessArr=int[11][11]
- 在读取稀疏数组后几行的数据,并赋给原始的二维数组即可
4、代码实现
- 普通二维数组转稀疏数组
- 稀疏数组存硬盘
- 从硬盘读取转稀疏数组
- 稀疏数组转普通二维数组 ```java package com.daijunyi.structure.sparse;
import java.io.*;
/**
- @author djy
- @createTime 2021/12/19 上午7:20
- @description */
public class SparseArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {int[][] ints = new int[11][11];ints[1][2] = 1;ints[2][3] = 2;String filePath = "/Users/djy/Desktop/array.txt";try {int[][] spareArray = SparseArray.transitionSpareArray(ints);SparseArray.writeSpareArrayToFile(spareArray, filePath);int[][] readSpareArray = SparseArray.readSpareArrayFromFile(filePath);SparseArray.spareToNormalArray(readSpareArray);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}/*** 正常数组转稀疏数组* @param source 原始数组* @return 返回稀疏数组*/public static int[][] transitionSpareArray(int[][] source) {int sum = 0;for (int[] row : source) {for (int data : row) {System.out.printf("%d\t", data);if (data != 0) {sum++;}}System.out.println();}if (sum == 0) {return null;}System.out.println("稀疏数组打印:");//初始化稀疏数组int[][] spare = new int[sum + 1][3];spare[0][0] = source.length;spare[0][1] = source[0].length;spare[0][2] = sum;System.out.printf("%d\t%d\t%d\t", source.length, source[0].length, sum);System.out.println();//遍历赋值int count = 0;for (int row = 0; row < source.length; row++) {int[] rows = source[row];for (int col = 0; col < rows.length; col++) {int data = rows[col];if (data != 0) {count++;spare[count][0] = row;spare[count][1] = col;spare[count][2] = data;System.out.printf("%d\t%d\t%d\t", row, col, data);System.out.println();}}}return spare;}/*** 稀疏数组转正常数组* @param spareArray 稀疏数组* @return 正则数组*/public static int[][] spareToNormalArray(int[][] spareArray) {if (spareArray == null || spareArray.length < 1) {return null;}int[][] normalArray = new int[spareArray[0][0]][spareArray[0][1]];for (int row = 1; row < spareArray.length; row++) {int[] rows = spareArray[row];normalArray[rows[0]][rows[1]] = rows[2];}System.out.println("打印转回来的数组");for (int[] row : normalArray) {for (int data : row) {System.out.printf("%d\t", data);}System.out.println();}return normalArray;}/*** 从硬盘读取稀疏数组* @param path* @return* @throws IOException*/public static int[][] readSpareArrayFromFile(String path) throws IOException {File file = new File(path);BufferedReader bufferedReader = null;try {bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));String value = null;int[][] spareArray = null;int index = 0;while ((value = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {if (index == 0){spareArray = new int[Integer.valueOf(value)][3];}else{String[] split = value.split(",");if (split.length != 3){throw new IOException("文件格式异常");}spareArray[index-1][0] = Integer.valueOf(split[0]);spareArray[index-1][1] = Integer.valueOf(split[1]);spareArray[index-1][2] = Integer.valueOf(split[2]);}index++;}return spareArray;} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();throw e;} finally {if (bufferedReader != null){bufferedReader.close();}}}/*** 把数据写如硬盘* @param array* @param path* @throws IOException*/public static void writeSpareArrayToFile(int[][] array, String path) throws IOException {if (path == null || path.length() == 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("数组为空");}File file = new File(path);if (!file.getParentFile().exists()) {file.getParentFile().mkdirs();}if (!file.exists()) {try {file.createNewFile();} catch (IOException e) {System.out.println("文件创建失败");throw e;}}FileWriter fileWriter = null;try {fileWriter = new FileWriter(file);fileWriter.write(array.length+"");fileWriter.write("\n");for (int[] rows : array) {String value = rows[0] + "," + rows[1] + "," + rows[2];fileWriter.write(value + "\n");}fileWriter.flush();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();throw e;} finally {if (fileWriter != null) {fileWriter.close();}}}
}
<a name="bAEAN"></a>
## 2、队列
<a name="Sj5UJ"></a>
### 1、什么是队列
- 队列是一个有序列表,可以用数组或是链表来实现
- 遵循先入先出的原则。即:先存入队列的数据,要先取出。后存入的要后取出
<a name="B8bZj"></a>
### 2、数组模拟队列思路
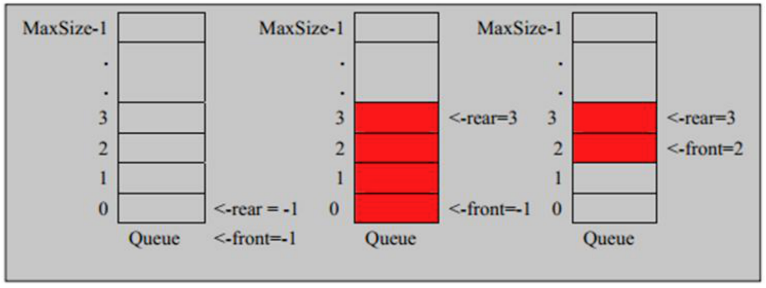
- 队列本身是有序列表,若使用数组的结构来存储队列的数据,则队列数组的声明如下图,其中maxSize是该队列的最大容量。
- 因为队列的输出、输入是分别从前后端来处理,因此需要两个变量 front 及 rear 分别记录队列前后端的下标,front 会随着数据输出而改变,而 rear则是随着数据输入而改变,如图所示:
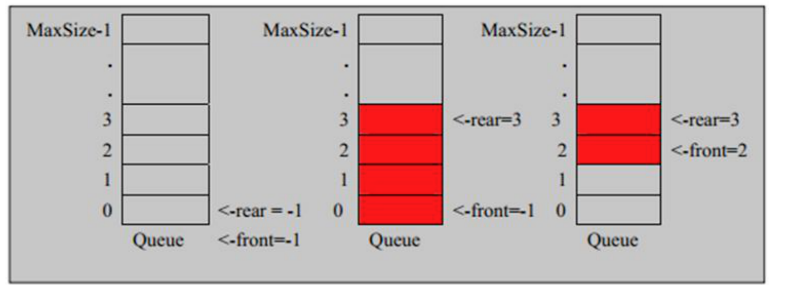
- 当我们将数据存入队列时称为”addQueue”,addQueue 的处理需要有两个步骤:思路分析
1. 将尾指针往后移:rear+1,当 front == rear【空】
1. 若尾指针 rear 小于队列的最大下标 maxSize-1,则将数据存入 rear所指的数组元素中,否则无法存入数据。rear== maxSize - 1[队列满]
<a name="MyNxV"></a>
### 3、代码实现
```java
package com.daijunyi.structure.queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @author djy
* @createTime 2021/12/20 下午5:16
* @description
*/
class ArrayQueueMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayQueue arrayQueue = new ArrayQueue(5);
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean loop = true;
char key;
while (loop) {
System.out.println("s(show):显示队列");
System.out.println("e(exit):退出程序");
System.out.println("a(add):添加数据到队列");
System.out.println("g(get):从队列取出数据");
System.out.println("h(head):查看队列头的数据");
key = scanner.next().charAt(0);
switch (key) {
case 's':
arrayQueue.showQueue();
break;
case 'e':
loop = false;
scanner.close();
break;
case 'a':
System.out.println("请输入一个数字");
arrayQueue.addQueue(scanner.nextInt());
break;
case 'g':
int queue = arrayQueue.getQueue();
System.out.printf("值:%d\t",queue);
System.out.println();
break;
case 'h':
arrayQueue.headQueue();
break;
default:
}
}
System.out.println("程序退出");
}
}
public class ArrayQueue {
/**
* 表示数组最大的容量
*/
private int maxSize;
/**
* 队列头
*/
private int front;
/**
* 队列尾
*/
private int rear;
/**
* 存储数据
*/
private int[] arr;
public ArrayQueue(int maxSize) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
arr = new int[maxSize];
//指向队列头部,分析出front是指向队列头的前一个位置
front = -1;
//指向队列尾,指向队列尾的数据(即就是队列最后一个数据)
rear = -1;
}
/**
* 队列是否满了
* @return
*/
public boolean isFull() {
return rear >= maxSize - 1;
}
/**
* 队列是否空
* @return
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return front == rear;
}
/**
* 添加值
* @param value
* @return
*/
public boolean addQueue(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("队列满了");
return false;
}
arr[++rear] = value;
return true;
}
/**
* 获取队列
* @return
*/
public int getQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("队列为空,没有更多数据了");
throw new RuntimeException("队列空了");
}
return arr[++front];
}
/**
* 显示头部数据
* @return
*/
public int headQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列空了,没有数据了");
}
return arr[front + 1];
}
public void showQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("队列是空的");
return;
}
for (int i = front; i < rear; i++) {
System.out.printf("%d\t", arr[i + 1]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
4、问题
-
3、环形队列
-
1、分析
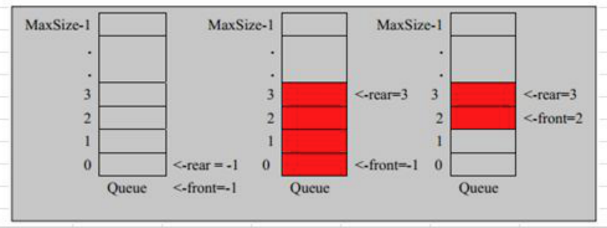
front变量:指向队列的第一个元素,也就是说arr[front]就是队列的第一个元素,front初始值0
- rear变量:指向队列的最后一个元素的后一个位置,空出一个空间作为约定,好计算,rear的初始值=0
- 队列满:条件(rear+1)%maxSize = front【满】
- 队列空:rear==front【空】
- 队列中值个数:(rear+maxSzie-front)%maxSize
2、代码实现
```java package com.daijunyi.structure.queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
class ArrayAnnularQueueMain{ public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayAnnularQueue arrayQueue = new ArrayAnnularQueue(5); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); boolean loop = true; char key; while (loop) { System.out.println(); System.out.println(); System.out.println(); System.out.println(“s(show):显示队列”); System.out.println(“e(exit):退出程序”); System.out.println(“a(add):添加数据到队列”); System.out.println(“g(get):从队列取出数据”); System.out.println(“h(head):查看队列头的数据”); System.out.println(“l(length):查看队列个数”); key = scanner.next().charAt(0); switch (key) { case ‘s’: arrayQueue.showQueue(); break; case ‘e’: loop = false; scanner.close(); break; case ‘a’: System.out.println(“请输入一个数字”);
try {
String next = scanner.next();
int number = Integer.parseInt(next);
arrayQueue.addQueue(number);
} catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("请输入有效的数字,请重新选择您的操作");
}
break;
case 'g':
int queue = 0;
try {
queue = arrayQueue.getQueue();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.printf("值:%d\t",queue);
System.out.println();
break;
case 'h':
arrayQueue.headQueue();
break;
case 'l':
int length = arrayQueue.length();
System.out.printf("队列个数%d\t",length);
System.out.println();
break;
default:
}
}
System.out.println("程序退出");
}
}
/**
- 数组环形队列
- ● front变量:指向队列的第一个元素,也就是说arr[front]就是队列的第一个元素,front初始值0
- ● rear变量:指向队列的最后一个元素的后一个位置,空出一个空间作为约定,好计算,rear的初始值=0
- ● 队列满:条件(rear+1)%maxSize = front【满】
- ● 队列空:rear==front【空】
- ● 队列中值个数:(rear+maxSzie-front)%maxSize
- @author djy
- @createTime 2021/12/20 下午7:36
@description / public class ArrayAnnularQueue { /*
表示数组最大的容量 */ private int maxSize;
/**
队列头 */ private int front;
/**
队列尾 */ private int rear;
/**
- 存储数据 */ private int[] arr;
public ArrayAnnularQueue(int maxSize) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
arr = new int[maxSize];
//指向队列头部,分析出front是指向队列头的第一个位置
front = 0;
//指向队列尾,指向队列尾的数据的后一个位置
rear = 0;
}
/**
* 队列是否满了
* @return
*/
public boolean isFull() {
return (rear+1)%maxSize == front;
}
/**
* 队列是否空
* @return
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return front == rear;
}
/**
* 添加值
* @param value
* @return
*/
public boolean addQueue(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("队列满了");
return false;
}
arr[rear] = value;
rear = (rear+1)%maxSize;
return true;
}
/**
* 获取队列
* @return
*/
public int getQueue() throws Exception {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("队列为空,没有更多数据了");
throw new Exception("队列空了");
}
int result = arr[front];
arr[front] = 0;
front = (front+1)%maxSize;
return result;
}
/**
* 显示头部数据
* @return
*/
public int headQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列空了,没有数据了");
}
return arr[front];
}
public int length(){
return (rear+maxSize-front)%maxSize;
}
public void showQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("队列是空的");
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < maxSize; i++) {
System.out.printf("%d\t", arr[i]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
<a name="qK7ux"></a>
# 3、链表
<a name="AgSuy"></a>
## 1、什么是链表
链表是一种物理存储单元上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的
<a name="AEIeX"></a>
### 1、链表的物理表示
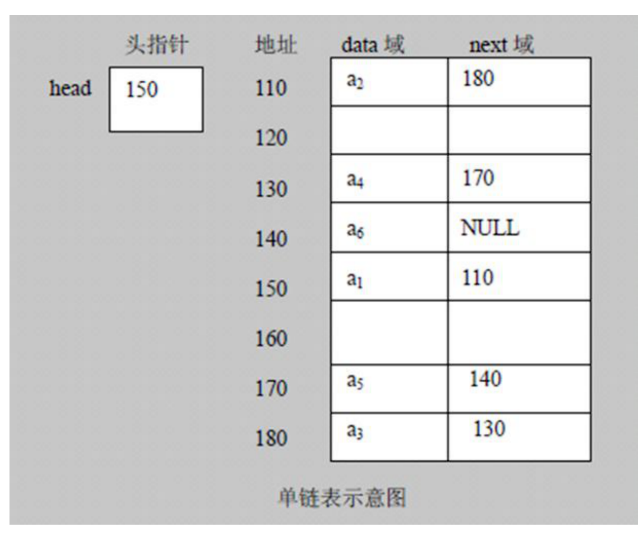<br />1)链表是以节点的方式来存储,是链式存储<br />2)每个节点包含 data 域,next 域:指向下一个节点.<br />3) 如图:发现链表的各个节点不一定是连续存储.<br />4) 链表分带头节点的链表和没有头节点的链表,根据实际的需求来确定
<a name="BhoKj"></a>
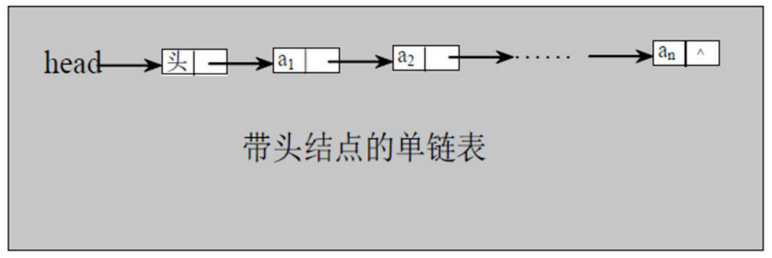
### 2、单链表(带头结点) 逻辑结构示意图如下
<a name="fIzQE"></a>
## 2、单链表应用
<a name="L5yy0"></a>
### 1、分析
- 使用带head头的单向链表实现,水浒英雄排行榜管理完成对英雄人物的增删改查操作
1. 第一种方法在添加英雄时,直接添加到链表的尾部
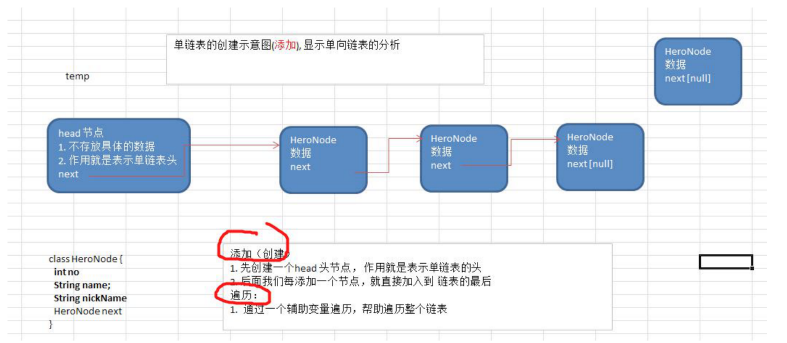
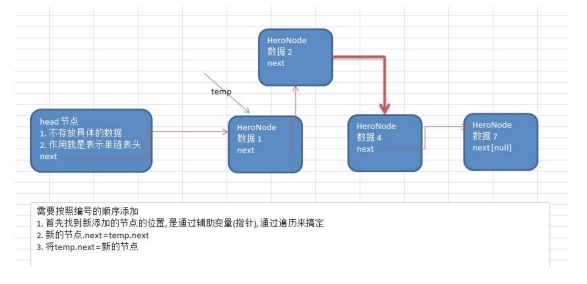
2. 根据排名将英雄插入到指定位置(如果有这个排名,添加失败,并给出提示)
- 修改节点
```java
public boolean update(HeroNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return false;
}
HeroNode tmp = headNode.next;
while (tmp != null) {
if (tmp.id == node.id) {
tmp.name = node.name;
tmp.nickName = node.nickName;
return true;
}
tmp = tmp.next;
}
return false;
}
删除节点
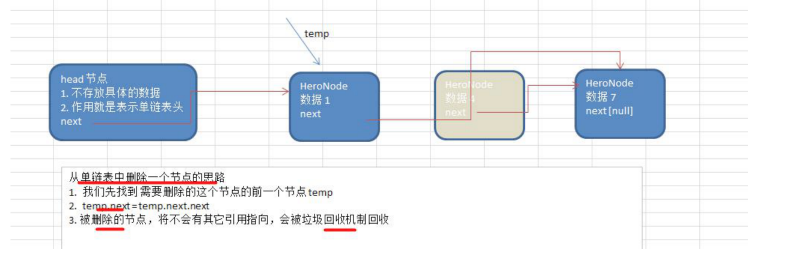
/** * 删除 * @param node * @return */ public boolean delete(HeroNode node){ if (node == null){ return false; } HeroNode tmp = headNode; while (tmp.next != null){ if (tmp.next.id == node.id){ //删除 tmp.next = tmp.next.next; return true; } tmp = tmp.next; } return false; }2、代码实现
1、HeroNode
```java /**
- @author djy
- @createTime 2021/12/21 下午2:13
- @description */ public class HeroNode { public int id; public String name; public String nickName; public HeroNode next;
public HeroNode() {
}
public HeroNode(Integer id, String name, String nickName) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.nickName = nickName; }
@Override public String toString() { return “HeroNode{“ +
"id=" + id + ", name='" + name + '\'' + ", nickName='" + nickName + '\'' + '}';} }
<a name="UXd49"></a>
#### 2、SigleLinkedList
```java
package com.daijunyi.structure.linked;
/**
* @author djy
* @createTime 2021/12/21 下午2:12
* @description
*/
public class SingleLinkedList {
private final HeroNode headNode = new HeroNode();
/**
* 添加在最后
* @param node
* @return
*/
public boolean add(HeroNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return false;
}
HeroNode tmp = headNode;
while (tmp.next != null) {
if (node.id == tmp.next.id) {
System.out.println("已经存在相同的节点不能重复添加" + node);
return false;
}
tmp = tmp.next;
}
tmp.next = node;
return true;
}
/**
* 排序添加
* @param node
* @return
*/
public boolean addByOrder(HeroNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return false;
}
//1、与下一个节点的id进行比对是否是小于该节点,如果是小于的就就添加在该节点前面
HeroNode tmp = headNode;
while (tmp.next != null) {
if (node.id < tmp.next.id) {
node.next = tmp.next;
tmp.next = node;
return true;
} else if (node.id == tmp.next.id) {
System.out.println("已经存在相同的节点,无法重复添加" + node);
return false;
}
tmp = tmp.next;
}
tmp.next = node;
return true;
}
/**
* 更新
* @param node
* @return
*/
public boolean update(HeroNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return false;
}
HeroNode tmp = headNode.next;
while (tmp != null) {
if (tmp.id == node.id) {
tmp.name = node.name;
tmp.nickName = node.nickName;
return true;
}
tmp = tmp.next;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 删除
* @param id
* @return
*/
public boolean delete(int id){
HeroNode tmp = headNode;
while (tmp.next != null){
if (tmp.next.id == id){
//删除
tmp.next = tmp.next.next;
return true;
}
tmp = tmp.next;
}
return false;
}
public void printList() {
HeroNode tmp = headNode.next;
if (tmp == null) {
System.out.println("数据为空");
return;
}
do {
System.out.println(tmp);
tmp = tmp.next;
} while (tmp != null);
}
}
3、测试
package com.daijunyi.structure.linked;
/**
* @author djy
* @createTime 2021/12/21 下午2:25
* @description
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SingleLinkedList linkedList = new SingleLinkedList();
linkedList.add(new HeroNode(1, "宋江", "及时雨"));
linkedList.add(new HeroNode(2,"卢俊义","玉麒麟"));
linkedList.add(new HeroNode(3,"吴用","智多星"));
linkedList.add(new HeroNode(4,"林冲","豹子头"));
linkedList.addByOrder(new HeroNode(50, "燕顺", "锦毛虎"));
linkedList.addByOrder(new HeroNode(40,"宣赞","丑郡马"));
linkedList.addByOrder(new HeroNode(7,"秦明","霹雳火"));
linkedList.addByOrder(new HeroNode(30,"张顺","浪里白条"));
linkedList.addByOrder(new HeroNode(4,"林冲","豹子头"));
linkedList.printList();
linkedList.update(new HeroNode(4,"公孙胜","入云龙"));
System.out.println("更新后");
linkedList.printList();
linkedList.delete(30);
System.out.println("删除后");
linkedList.printList();;
}
}
4、结果打印
已经存在相同的节点,无法重复添加HeroNode{id=4, name='林冲', nickName='豹子头'}
HeroNode{id=1, name='宋江', nickName='及时雨'}
HeroNode{id=2, name='卢俊义', nickName='玉麒麟'}
HeroNode{id=3, name='吴用', nickName='智多星'}
HeroNode{id=4, name='林冲', nickName='豹子头'}
HeroNode{id=7, name='秦明', nickName='霹雳火'}
HeroNode{id=30, name='张顺', nickName='浪里白条'}
HeroNode{id=40, name='宣赞', nickName='丑郡马'}
HeroNode{id=50, name='燕顺', nickName='锦毛虎'}
更新后
HeroNode{id=1, name='宋江', nickName='及时雨'}
HeroNode{id=2, name='卢俊义', nickName='玉麒麟'}
HeroNode{id=3, name='吴用', nickName='智多星'}
HeroNode{id=4, name='公孙胜', nickName='入云龙'}
HeroNode{id=7, name='秦明', nickName='霹雳火'}
HeroNode{id=30, name='张顺', nickName='浪里白条'}
HeroNode{id=40, name='宣赞', nickName='丑郡马'}
HeroNode{id=50, name='燕顺', nickName='锦毛虎'}
删除后
HeroNode{id=1, name='宋江', nickName='及时雨'}
HeroNode{id=2, name='卢俊义', nickName='玉麒麟'}
HeroNode{id=3, name='吴用', nickName='智多星'}
HeroNode{id=4, name='公孙胜', nickName='入云龙'}
HeroNode{id=7, name='秦明', nickName='霹雳火'}
HeroNode{id=40, name='宣赞', nickName='丑郡马'}
HeroNode{id=50, name='燕顺', nickName='锦毛虎'}
Process finished with exit code 0
3、增强功能
1、翻转单链表
- 步骤:
- 先保存当前节点(currentNode)的下一个节点(next)
- 然后把当前新头部节点(tmpHead)的下一个节点复制给当前节点的next(currentNode)
- 然后把当前节点赋值给临时新头部节点的next(tmpHead),完成循环赋值
- 再把当前节点currentNode = next;
简单来说就是:从头到位遍历原来的链表,每遍历一个节点,就取出,并放在新的链表的的最前端。
/** * 一次翻转 */ public void simpleReversal(){ HeroNode head = headNode; if (head.next == null || head.next.next == null){ return; } HeroNode tmpHead = new HeroNode(); HeroNode currentNode = head.next; HeroNode next = null; //从头到位遍历原来的链表,每遍历一个节点,就取出,并放在新的链表的的最前端。 while (currentNode != null){ next = currentNode.next; currentNode.next = tmpHead.next; tmpHead.next = currentNode; currentNode = next; } head.next = tmpHead.next; }2、从尾到头打印单链表
实现方式,可以使用Stack栈(先进后出),遍历单链表,装入栈,然后从栈中取出来,进行打印
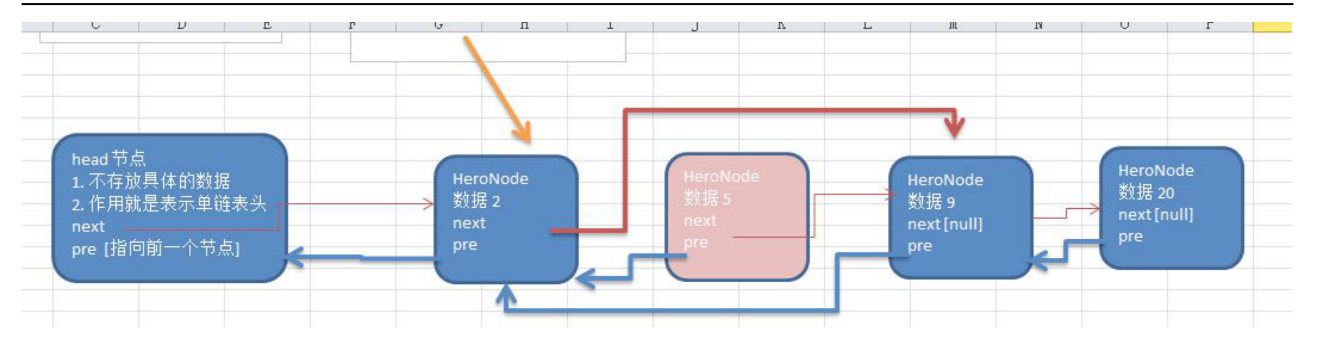
3、双向链表
1、单向链表和双向链表对比
使用带head头的双向链表实现
单向链表的缺点分析:
遍历 方和 单链表一样,,只是可以向前,也可以向后查找
- 添加 (默认添加到双向链表的最后)
- (1) 先找到双向链表的最后这个节点
- (2)temp.next=newHeroNode
- (3) newHeroNode.pre = temp;
- 修改 思路和 原来的单向链表一样.
- 删除
/**
- @author djy
- @createTime 2021/12/22 下午1:57
@description */ public class HeroDoubleNode {
public int id; public String name; public String nickName; /**
- 下一个节点 / public HeroDoubleNode next; /*
上一个节点 */ public HeroDoubleNode pre;
public HeroDoubleNode() {
}
public HeroDoubleNode(Integer id, String name, String nickName) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.nickName = nickName; }
@Override public String toString() { return “HeroNode{“ +
"id=" + id + ", name='" + name + '\'' + ", nickName='" + nickName + '\'' + '}';} }
<a name="CUsVE"></a>
#### 2、创建DoubleLinkedList
```java
package com.daijunyi.structure.linked;
import com.daijunyi.structure.linked.pojo.HeroDoubleNode;
class DoubleLinkedListMain {
/**
* 单链表
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoubleLinkedList linkedList = new DoubleLinkedList();
linkedList.add(new HeroDoubleNode(1, "宋江", "及时雨"));
linkedList.add(new HeroDoubleNode(2,"卢俊义","玉麒麟"));
linkedList.add(new HeroDoubleNode(3,"吴用","智多星"));
linkedList.add(new HeroDoubleNode(4,"林冲","豹子头"));
linkedList.addByOrder(new HeroDoubleNode(50, "燕顺", "锦毛虎"));
linkedList.addByOrder(new HeroDoubleNode(40,"宣赞","丑郡马"));
linkedList.addByOrder(new HeroDoubleNode(7,"秦明","霹雳火"));
linkedList.addByOrder(new HeroDoubleNode(30,"张顺","浪里白条"));
linkedList.addByOrder(new HeroDoubleNode(4,"林冲","豹子头"));
linkedList.printList();
linkedList.update(new HeroDoubleNode(4,"公孙胜","入云龙"));
System.out.println("更新后");
linkedList.printList();
linkedList.delete(30);
System.out.println("删除后");
linkedList.printList();;
System.out.printf("%d\t条数据", linkedList.length());
System.out.println("简单一次翻转");
linkedList.simpleReversal();
linkedList.printList();
}
}
/**
* @author djy
* @createTime 2021/12/22 下午1:47
* @description
*/
public class DoubleLinkedList {
private final HeroDoubleNode headNode = new HeroDoubleNode();
/**
* 添加在最后
* @param node
* @return
*/
public boolean add(HeroDoubleNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return false;
}
HeroDoubleNode tmp = headNode;
while (tmp.next != null) {
if (node.id == tmp.next.id) {
System.out.println("已经存在相同的节点不能重复添加" + node);
return false;
}
tmp = tmp.next;
}
tmp.next = node;
node.pre = tmp;
return true;
}
/**
* 排序添加
* @param node
* @return
*/
public boolean addByOrder(HeroDoubleNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return false;
}
//1、与下一个节点的id进行比对是否是小于该节点,如果是小于的就就添加在该节点前面
HeroDoubleNode tmp = headNode;
while (tmp.next != null) {
if (node.id < tmp.next.id) {
node.next = tmp.next;
tmp.next.pre = node;
node.pre = tmp;
tmp.next = node;
return true;
} else if (node.id == tmp.next.id) {
System.out.println("已经存在相同的节点,无法重复添加" + node);
return false;
}
tmp = tmp.next;
}
tmp.next = node;
node.pre = tmp;
return true;
}
/**
* 更新
* @param node
* @return
*/
public boolean update(HeroDoubleNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return false;
}
HeroDoubleNode tmp = headNode.next;
while (tmp != null) {
if (tmp.id == node.id) {
tmp.name = node.name;
tmp.nickName = node.nickName;
return true;
}
tmp = tmp.next;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 删除双向链表可双向删除
* @param id
* @return
*/
public boolean delete(int id){
HeroDoubleNode tmp = headNode.next;
while (tmp != null){
if (tmp.id == id){
//删除
tmp.pre.next = tmp.next;
if (tmp.next != null){
//最后一个节点的时候
tmp.next.pre = tmp.pre;
}
return true;
}
tmp = tmp.next;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 节点个数
* @return
*/
public int length(){
HeroDoubleNode tmp = headNode;
int count = 0;
while (tmp.next != null){
count++;
tmp = tmp.next;
}
return count;
}
public void printList() {
HeroDoubleNode tmp = headNode.next;
if (tmp == null) {
System.out.println("数据为空");
return;
}
do {
System.out.println(tmp);
tmp = tmp.next;
} while (tmp != null);
}
/**
* 一次翻转
*/
public void simpleReversal(){
HeroDoubleNode head = headNode;
if (head.next == null || head.next.next == null){
return;
}
HeroDoubleNode tmpHead = new HeroDoubleNode();
HeroDoubleNode currentNode = head.next;
HeroDoubleNode next = null;
while (currentNode != null){
next = currentNode.next;
//从原来的链表自我删除
if (currentNode.next != null){
currentNode.next.pre = currentNode.pre;
}
currentNode.pre.next = currentNode.next;
//插入到新添加第一个上
//先挂新节点后面的链表到当前节点上
currentNode.next = tmpHead.next;
if (tmpHead.next != null){
tmpHead.next.pre = currentNode;
}
//挂载自己到临时新头节点上
tmpHead.next = currentNode;
currentNode.pre = tmpHead;
currentNode = next;
}
head.next = tmpHead.next;
tmpHead.next.pre = head;
}
}
4、单向环形链表应用
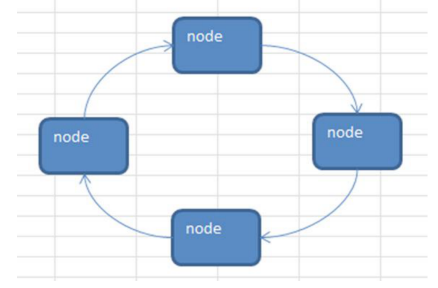
1、单向环形链表介绍
- 最后一个节点的next指向第一个节点
2、约瑟夫问题
1、实际应用场景
- Josephu(约瑟夫、约瑟夫环) 问题
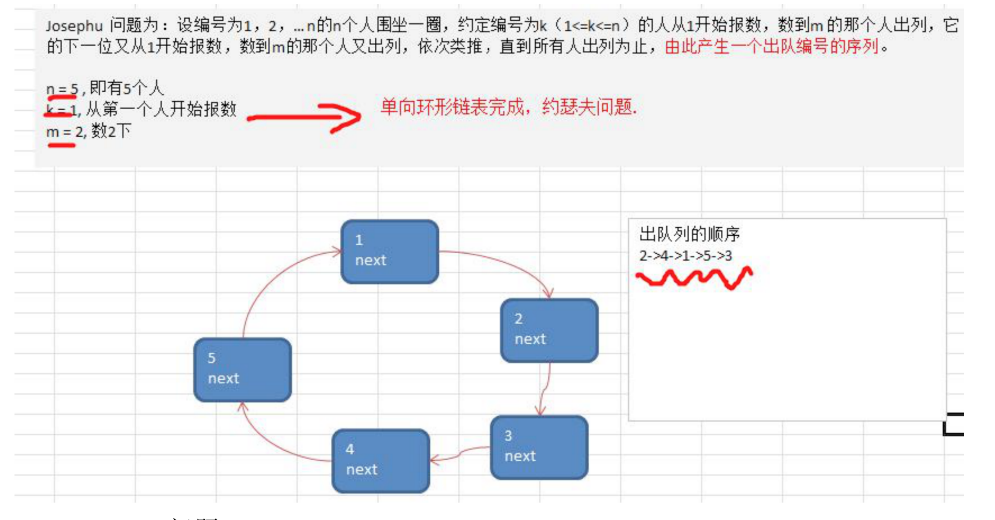
- Josephu 问题为:设编号为 1,2,… n 的 n 个人围坐一圈,约定编号为 k(1<=k<=n)的人从1 开始报数,数到 m 的那个人出列,它的下一位又从1开始报数,数到 m 的那个人又出列,依次类推,直到所有人出列为止,由此产生一个出队编号的序列。
- 提示:用一个不带头结点的循环链表来处理Josephu问题:先构成一个有n个结点的单循环链表,然后由k结点起从1开始计数,计到m时,对应结点从链表中删除,然后再从被删除结点的下一个结点又从1开始计数,直到最后一个结点从链表中删除算法结束。
-
2、问题分析
1、问题
Josephu 问题为:设编号为 1,2,… n 的 n 个人围坐一圈,约定编号为 k(1<=k<=n)的人从1开始报数,数到m 的那个人出列,它的下一位又从1开始报数,数到 m 的那个人又出列,依次类推,直到所有人出列为止,由此产生一个出队编号的序列。
2、解决方法
用一个不带头结点的循环链表来处理Josephu 问题:先构成一个有 n 个结点的单循环链表,然后由 k 结点起从 1 开始计数,计到 m 时,对应结点从链表中删除,然后再从被删除结点的下一个结点又从 1 开始计数,直到最后一个结点从链表中删除算法结束。
约瑟夫问题-创建环形链路表的思想图解
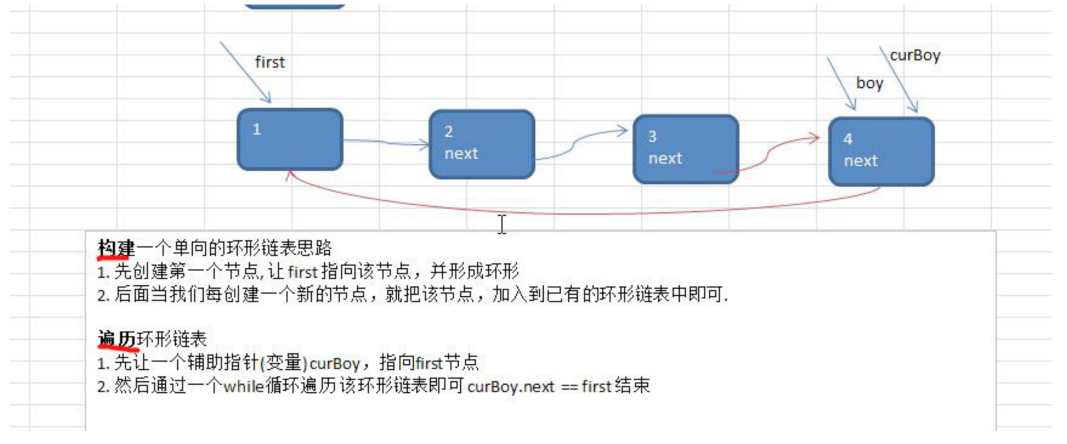
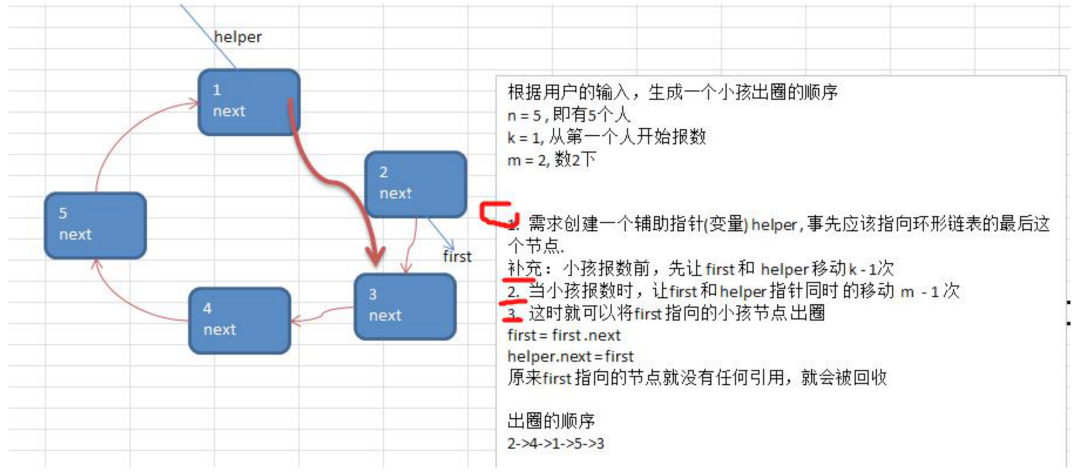
- 约瑟夫问题-小孩出圈的思路分析图
3、代码实现
1、创建JosephBoy
package com.daijunyi.structure.linked.pojo;
/**
* @author djy
* @createTime 2021/12/22 下午3:00
* @description
*/
public class JosephBoy {
private int no;
private JosephBoy next;
public JosephBoy(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public int getNo() {
return no;
}
public void setNo(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public JosephBoy getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(JosephBoy next) {
this.next = next;
}
}
2、JosephLinkedListMain
package com.daijunyi.structure.linked;
import com.daijunyi.structure.linked.pojo.JosephBoy;
import com.sun.scenario.animation.shared.ClipEnvelope;
class JosephLinkedListMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JosephLinkedList linkedList = new JosephLinkedList(5);
linkedList.print();
linkedList.countBoy(1,2);
}
}
/**
* @author djy
* @createTime 2021/12/22 下午2:58
* @description
*/
public class JosephLinkedList {
private JosephBoy first = null;
private int size;
/**
* 创建一个环形单向链表
* @param size
*/
public JosephLinkedList(int size) {
if (size < 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("最少大于1个");
}
this.size = size;
//临时
JosephBoy tmp = null;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
JosephBoy boy = new JosephBoy(i+1);
if (i == 0) {
first = boy;
} else {
tmp.setNext(boy);
}
tmp = boy;
}
tmp.setNext(first);
}
public void print(){
JosephBoy tmp = first;
while (true){
System.out.printf("%d\t",tmp.getNo());
if (tmp.getNext() == first){
break;
}
tmp = tmp.getNext();
}
}
public void countBoy(int startNo,int countNum){
if (first == null || startNo < 1 || startNo >= size){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("参数异常");
}
//因为是单向链表所以,在出圈的时候需要知道自己的上一个节点,单向链表不能自我删除,所以需要先找出最后一个节点
JosephBoy tmp = first;
while (true){
if (tmp.getNext() == first){
break;
}
tmp = tmp.getNext();
}
//找到从第几个小孩开始喊
for (int i = 0;i<startNo-1;i++){
first = first.getNext();
tmp = tmp.getNext();
}
while (true){
if (first.getNext() == first){
break;
}
//喊两次
for (int i=0;i<countNum-1;i++){
first = first.getNext();
tmp = tmp.getNext();
}
System.out.printf("%d->",first.getNo());
first = first.getNext();
tmp.setNext(first);
}
System.out.printf("%d",first.getNo());
}
}
3、运行结果
1 2 3 4 5 2->4->1->5->3
Process finished with exit code 0