前言
HBase客户端是不需要维护连接池的,或者说,Connection对象已经帮我们做好了。创建HBase连接是非常“贵”的操作,并且创建过多的Connection会导致HBase拒绝连接。因此,最科学的方式就是在整个应用(进程)的范围内只维护一个共用的Connection,比如以单例的形式。在应用退出时,再关闭连接。应用中创建的Connection对象过多,会触发zookeeper的连接数限制,导致客户端连不上的。
HBase连接池实现方式
- HTablePool。(废弃)
- HConnectionManager+HConnection。(废弃)
-
常见问题
自己实现一个Connection对象的资源池,每次使用都从资源池中取出一个Connection对象。
- 每个线程一个Connection对象。
- 每次访问HBase的时候临时创建一个Connection对象,使用完之后调用close关闭连接。
从这些做法来看,这些用户显然是把Connection对象当成了单机数据库里面的连接对象来用了。然而,作为一个分布式数据库,HBase客户端需要和多个服务器中的不同服务角色建立连接,所以HBase客户端中的Connection对象并不是简单对应一个socket连接。
HBase Client模型
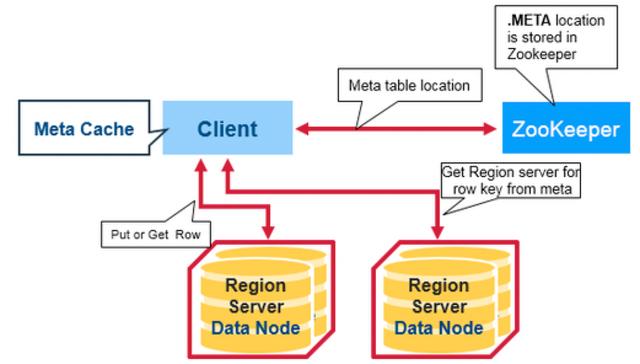
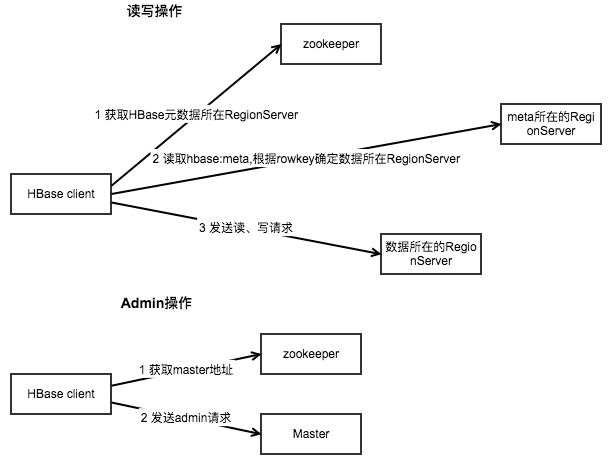
HBase客户端要连接三个不同的服务角色:
- ZooKeeper:主要用于获得meta-region位置,集群Id、master等信息。
- HBase Master:主要用于执行HBaseAdmin接口的一些操作,例如建表等。
- HBase RegionServer:用于读、写数据。
HBase客户端的Connection包含了对以上三种socket连接的封装。Connection对象和实际的socket连接之间的对应关系如下图: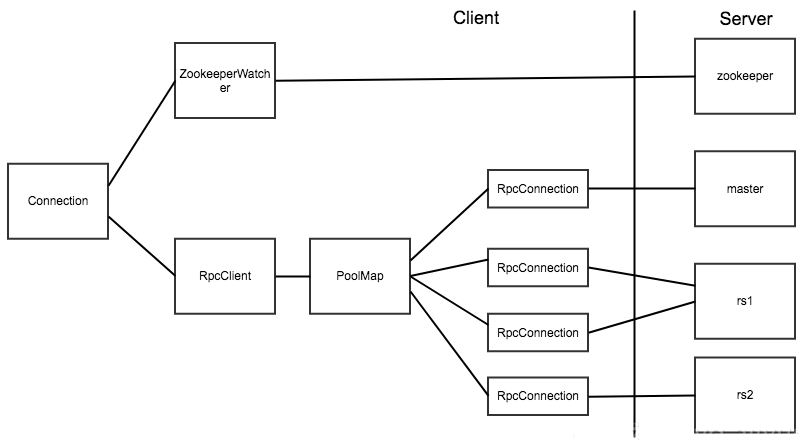
HBase客户端代码真正对应Socket连接的是RpcConnection对象。HBase使用PoolMap这种数据结构来存储客户端到HBase服务器之间的连接。PoolMap封装ConcurrentHashMap的结构,key是ConnectionId(封装服务器地址和用户ticket),value是一个RpcConnection对象的资源池。当HBase需要连接一个服务器时,首先会根据ConnectionId找到对应的连接池,然后从连接池中取出一个连接对象。
HBase Connection源码分析
/*** A cluster connection encapsulating lower level individual connections to actual servers and* a connection to zookeeper. Connections are instantiated through the {@link ConnectionFactory}* class. The lifecycle of the connection is managed by the caller, who has to {@link #close()}* the connection to release the resources.** <p> The connection object contains logic to find the master, locate regions out on the cluster,* keeps a cache of locations and then knows how to re-calibrate after they move. The individual* connections to servers, meta cache, zookeeper connection, etc are all shared by the* {@link Table} and {@link Admin} instances obtained from this connection.** <p> Connection creation is a heavy-weight operation. Connection implementations are thread-safe,* so that the client can create a connection once, and share it with different threads.* {@link Table} and {@link Admin} instances, on the other hand, are light-weight and are not* thread-safe. Typically, a single connection per client application is instantiated and every* thread will obtain its own Table instance. Caching or pooling of {@link Table} and {@link Admin}* is not recommended.** <p>This class replaces {@link HConnection}, which is now deprecated.* @see ConnectionFactory* @since 0.99.0*/@InterfaceAudience.Public@InterfaceStability.Evolvingpublic interface Connection extends Abortable, Closeable {Configuration getConfiguration();Table getTable(TableName tableName) throws IOException;Table getTable(TableName tableName, ExecutorService pool) throws IOException;public BufferedMutator getBufferedMutator(TableName tableName) throws IOException;public BufferedMutator getBufferedMutator(BufferedMutatorParams params) throws IOException;public RegionLocator getRegionLocator(TableName tableName) throws IOException;Admin getAdmin() throws IOException;@Overridepublic void close() throws IOException;boolean isClosed();}
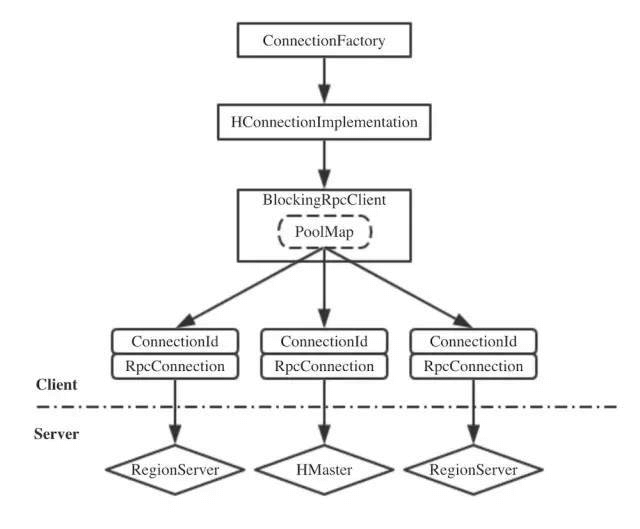
由源码中的JavaDoc可以得出如下结论:
- Connection对象需要知道如何找到HMaster、如何在RegionServer上定位Region,以及感知Region的变动。所以,Connection需要同时与HMaster、RegionServer和ZK建立连接。
- 创建Connection是重量级的,并且它是线程安全的。
由Connection取得的Table和Admin对象是轻量级的,并且不是线程安全的,所以它们应该即用即弃。
连接HBase的正确姿势
从以上分析不难得出,在HBase中Connection类已经实现对连接的管理功能,所以不需要在Connection之上再做额外的管理。另外,Connection是线程安全的,然而Table和Admin则不是线程安全的,因此正确的做法是**一个进程共用一个Connection对象,而在不同的线程中使用单独的Table和Admin对象。**
// 所有进程共用一个Connection对象connection=ConnectionFactory.createConnection(config);...// 每个线程使用单独的Table对象Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf("t1"));try {...} finally {table.close();}
HBase客户端默认的连接池大小是1,也就是每个RegionServer 1个连接,如果是2则client与Master和每个RS均有两个Connection类的实例,也可理解为有2个socket连接。如果应用需要使用更大的连接池或指定其他的资源池类型,也可以通过修改配置实现:
config.set("hbase.client.ipc.pool.type",...);config.set("hbase.client.ipc.pool.size",...);connection = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(config);
对应配置如下:
<!-- socket链接池 --><property><!-- 可选RoundRobinPool(默认)、ThreadLocalPool与ReusablePool三种。 --><name>hbase.client.ipc.pool.type</name><value>RoundRobinPool</value></property><property><!-- 连接池大小,默认值为1 --><name>hbase.client.ipc.pool.size</name><value>10</value></property>
优化实践
只需要对每个HBase集群的connection使用Map保存下来,每次请求的时候拿出对应的connection进去相关操作即可。然后需要注意在系统退出的时候关闭所有的connection。
public class ConnectionManager {private Map<String, Connection> connectionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();public Connection getConnection(String resourceId, Configuration configuration) {ResourceInfo resourceInfo = ResourceInfoCache.getResourceInfoByCache(resourceId);if (resourceInfo == null) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("error resourceid: " + resourceId);}String key = getClusterKey(resourceInfo);if (connectionMap.containsKey(key)) {return connectionMap.get(key);}synchronized (this) {//DCL检查if (connectionMap.containsKey(key)) {return connectionMap.get(key);}Connection connection = null;try {connection = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(configuration);} catch (IOException e) {return null;}connectionMap.put(key, connection);return connection;}}@PreDestroypublic void doDestroy() {for (Map.Entry<String, Connection> entry : connectionMap.entrySet()) {Connection connection = entry.getValue();if (connection != null) {try {connection.close();} catch (IOException e) {//。。。。}}}}}
这里有几个注意点:
将ConnectionManager注册为bean,交给spring容器管理生命周期,同时保证单例。
- 使用@PreDestroy保证应用关闭时,能正确释放所有连接,避免连接泄漏。
- connectionMap使用ConcurrentHashMap保证线程安全。
- DCL检查,避免重复创建同一个connection,浪费资源;并且避免重复创建connection后,无法关闭导致连接泄漏。
在需要查询时,只需要通过getConnection获取已经存在的connection即可。当然,如果是普通的应用使用HBase-client,一般只需要对一个HBase的集群创建全局唯一的一个Connection即可(一般交给spring容器管理),每次请求的时候,创建对应的Table进行CRUD。
参考
腾讯云:科学使用HBase Connection
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1496904
阿里云开发者社区:连接HBase的正确姿势
https://developer.aliyun.com/article/581702
博客园:如何正确管理HBase的连接,从原理到实战
https://www.cnblogs.com/awan-note/p/12731524.html
程序员大本营:连接HBase的正确姿势
https://www.pianshen.com/article/369381828/

