1 二叉树按层遍历并收集节点
leetcode:https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal-ii/
给定二叉树的根,返回其节点值的自底向上顺序遍历。(即从左到右,从叶到根,一层一层)。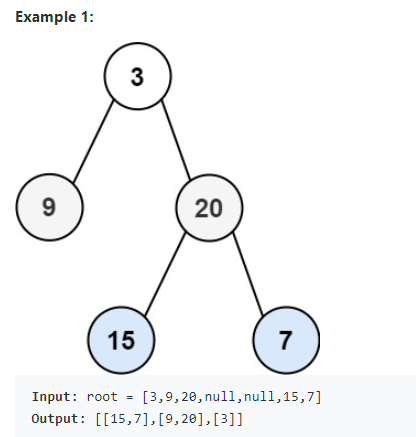
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode root) {List<List<Integer>> ans = new LinkedList<>();if (root == null) {return ans;}Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.add(root);while (!queue.isEmpty()) {List<Integer> curAns = new LinkedList<>();//size 为当前层的节点数量int size = queue.size();for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {TreeNode curNode = queue.poll();curAns.add(curNode.val);if (curNode.left != null) {queue.add(curNode.left);}if (curNode.right != null) {queue.add(curNode.right);}}ans.add(0, curAns);}return ans;}
2 判断是否是平衡二叉树
lettecode:https://leetcode.com/problems/balanced-binary-tree/
给定一棵二叉树,确定它是否是高度平衡的。
对于这个问题,高度平衡二叉树定义为:
一种二叉树,其中每个节点的左右子树高度相差不超过1。
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
return process(root).isBalanced;
}
private Info process(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return new Info(true, 0);
}
Info leftInfo = process(root.left);
Info rightInfo = process(root.right);
boolean isBalanced = leftInfo.isBalanced && rightInfo.isBalanced && Math.abs(leftInfo.height - rightInfo.height) < 2;
int height = Math.max(rightInfo.height, leftInfo.height) + 1;
return new Info(isBalanced, height);
}
//返回是否为平衡二叉树,和二叉树高度信息
private class Info {
boolean isBalanced;
int height;
public Info(boolean isBalanced, int hight) {
this.isBalanced = isBalanced;
this.height = hight;
}
public Info() {
}
}
3 判断是否是搜索二叉树
leetcode:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/validate-binary-search-tree/
- 节点的左子树只包含 小于 当前节点的数。
- 节点的右子树只包含 大于 当前节点的数。
- 所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树。
算法1:利用中序遍历
public static boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
traversal(root,list);
boolean isBinarySearchTree = true;
for (int i = 0; i < list.size() - 1; i++) {
if (list.get(i) > list.get(i + 1)) {
isBinarySearchTree = false;
break;
}
}
return isBinarySearchTree;
}
private static void traversal(TreeNode root, ArrayList<Integer> list) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
traversal(root.left, list);
list.add(root.val);
System.out.println(root.val);
traversal(root.right, list);
}
算法2:
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
return process(root).isBST;
}
private Info process(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
Info leftInfo = process(root.left);
Info rightInfo = process(root.right);
Info info = new Info(true, root.val, root.val);
if (leftInfo != null) {
info.min = Math.min(leftInfo.min, info.min);
info.max = Math.max(leftInfo.max, info.max);
}
if (rightInfo != null) {
info.min = Math.min(rightInfo.min, info.min);
info.max = Math.max(rightInfo.max, info.max);
}
if (leftInfo != null && !leftInfo.isBST) {
info.isBST = false;
}
if (rightInfo != null && !rightInfo.isBST) {
info.isBST = false;
}
boolean leftMaxLessRoot = leftInfo == null ? true : (leftInfo.max < root.val);
boolean lrightMinMoreRoot = rightInfo == null ? true : (rightInfo.min > root.val);
if (!leftMaxLessRoot || !lrightMinMoreRoot) {
info.isBST = false;
}
return info;
}
private class Info {
boolean isBST;
int max;
int min;
public Info() {
}
public Info(boolean isBST, int max, int min) {
this.isBST = isBST;
this.max = max;
this.min = min;
}
}
4 能否组成路径和
leetcode:https://leetcode.com/problems/path-sum/
给定二叉树的根和一个整数targetSum,如果树有根到叶的路径,使得沿着路径的所有值相加等于targetSum,则返回true。
public static boolean isSum = false;
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if (root == null) {
return false;
}
isSum = false;
pathSum(root, 0, targetSum);
return isSum;
}
public void pathSum(TreeNode root, int preSum, int targetSum) {
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
if (root.val + preSum == targetSum) {
isSum = true;
}
return;
}
preSum += root.val;
if (root.left != null) {
pathSum(root.left, preSum, targetSum);
}
if (root.right != null) {
pathSum(root.right, preSum, targetSum);
}
}
5 收集达标路径和
leetcode:https://leetcode.com/problems/path-sum-ii/
给定二叉树的根和一个整数targetSum,返回所有根到叶的路径,其中路径中节点值的和等于targetSum。每个路径应该作为节点值的列表而不是节点引用返回。
根到叶路径是从根开始到任何叶节点结束的路径。叶节点是没有子节点的节点。
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return ans;
}
List<Integer> subList = new ArrayList<>();
process(root, 0, targetSum, subList, ans);
return ans;
}
public void process(TreeNode root, int preSum, int targetSum, List<Integer> subList, List<List<Integer>> ans) {
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
if (preSum + root.val == targetSum) {
subList.add(root.val);
ans.add(copyList(subList));
subList.remove(subList.size() - 1);
}
return;
}
subList.add(root.val);
preSum += root.val;
if (root.left != null) {
process(root.left, preSum, targetSum, subList, ans);
}
if (root.right != null) {
process(root.right, preSum, targetSum, subList, ans);
}
subList.remove(subList.size() - 1);
}
private List<Integer> copyList(List<Integer> list) {
if (list == null) {
return null;
}
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
ans.add(list.get(i));
}
return ans;
}

