树状结构专用结构
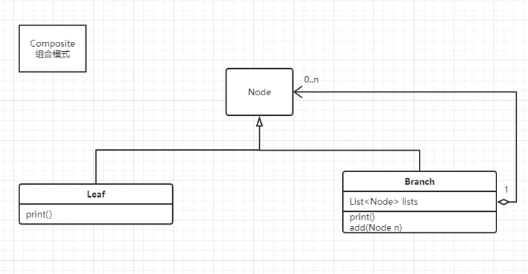
UML类图
生成树状结构
- Node接口:有输出方法
- LeafNode实现类:包含内容,可以输出内容
- BranchNode实现类:包含名字和子节点列表(子节点可以是LeafNode也可以是BranchNode),并且可以添加子节点与输出名字 ```java package com.mashibing.dp.composite;
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List;
abstract class Node { abstract public void p(); }
class LeafNode extends Node { String content; public LeafNode(String content) {this.content = content;}
@Overridepublic void p() {System.out.println(content);}
}
class BranchNode extends Node {
List
String name;public BranchNode(String name) {this.name = name;}@Overridepublic void p() {System.out.println(name);}public void add(Node n) {nodes.add(n);}
}
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) {
BranchNode root = new BranchNode("root");BranchNode chapter1 = new BranchNode("chapter1");BranchNode chapter2 = new BranchNode("chapter2");Node r1 = new LeafNode("r1");Node c11 = new LeafNode("c11");Node c12 = new LeafNode("c12");BranchNode b21 = new BranchNode("section21");Node c211 = new LeafNode("c211");Node c212 = new LeafNode("c212");root.add(chapter1);root.add(chapter2);root.add(r1);chapter1.add(c11);chapter1.add(c12);chapter2.add(b21);b21.add(c211);b21.add(c212);tree(root, 0);}// 递归显示static void tree(Node b, int depth) {// 按树状结构的目录层次进行输出for(int i=0; i<depth; i++) System.out.print("--");b.p();if(b instanceof BranchNode) {// 强转for (Node n : ((BranchNode)b).nodes) {tree(n, depth + 1);}}}
} ```
🤏随想
- 递归本身就是一个压栈过程,任何递归都可以自己写成栈式结构,自己压栈弹栈
- 有的情况用到递归方便,而栈式结构就不一定方便
- 二叉树的栈式遍历是面试时经常考的

