课程ppt

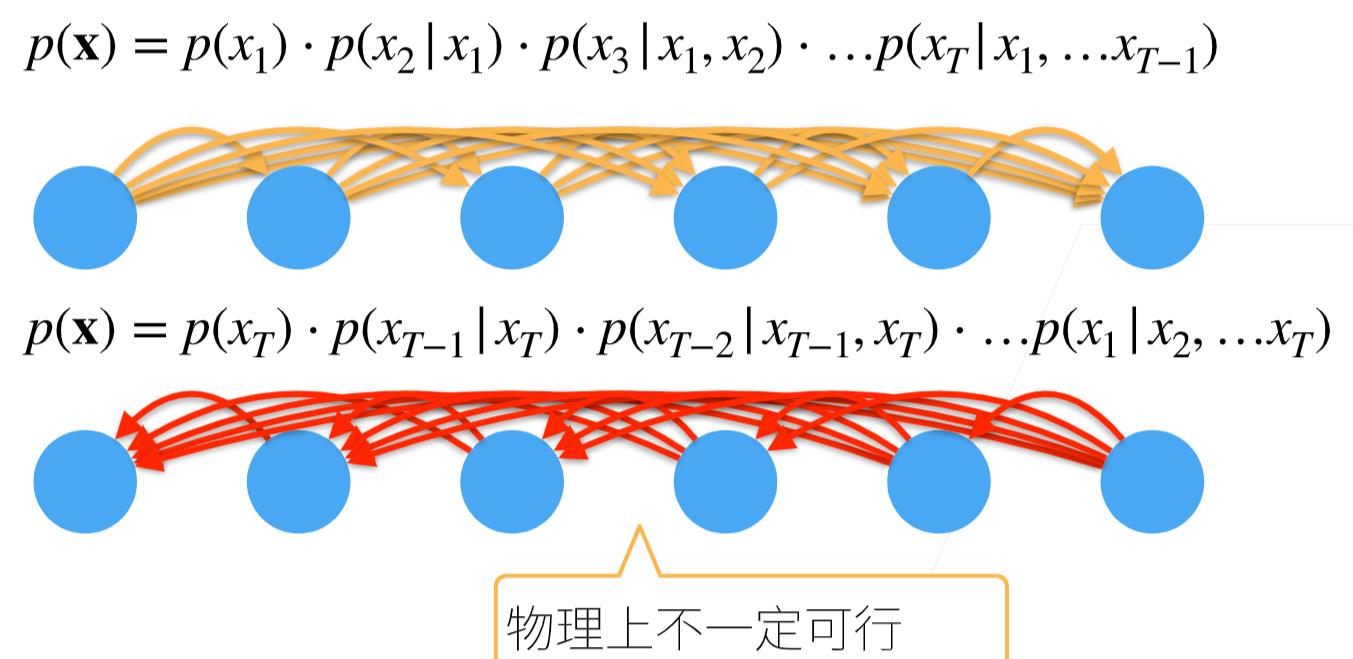
对见过的数据建模,也称自回归模型
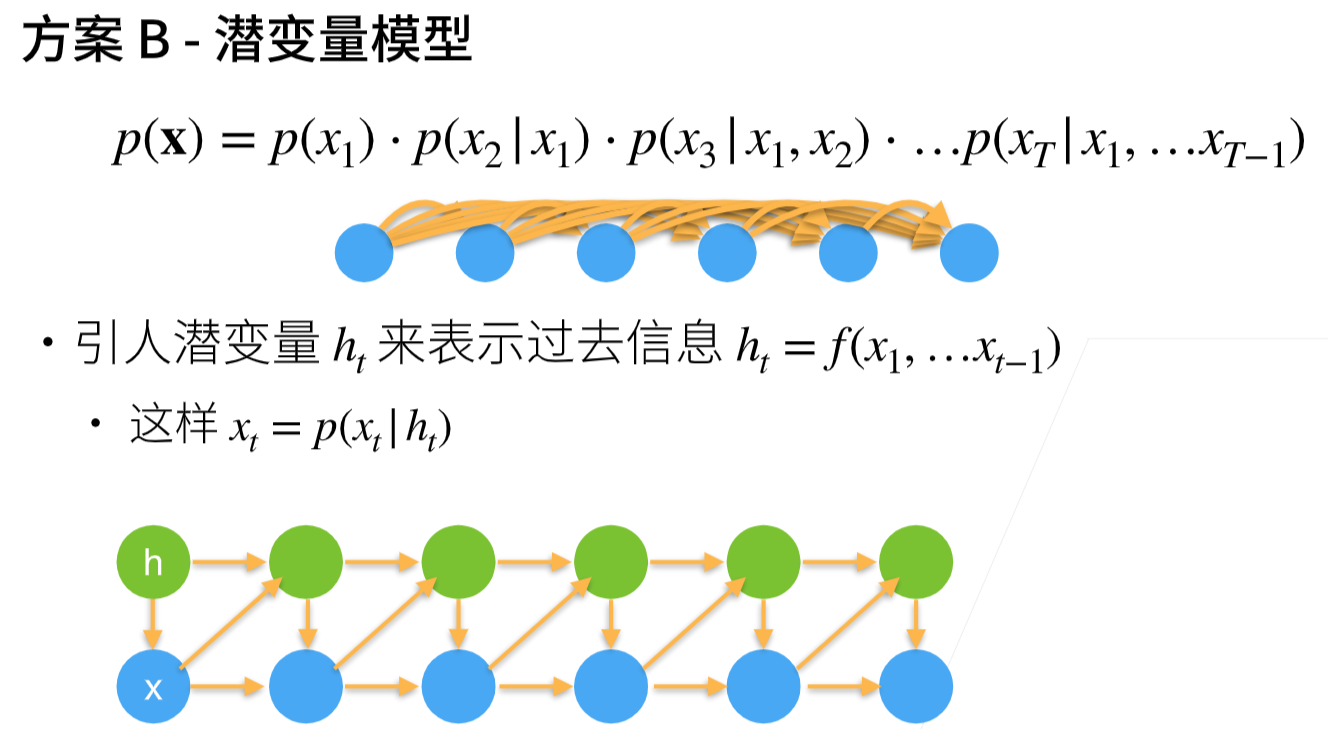
引入潜变量ht来表示过去信息,ht = f(x1,x2,…,xt-1)
xt = p(xt|ht)
模型1:
x’ 和前一个时间的x和潜变量h’有关
模型2:
h’和前一个时间的x和前一个时间的潜变量h有关
总结:
- 时序模型中,当前数据跟之前观察到的数据相关
- 自回归模型使用自身过去数据来预测未来
- 马尔可夫模型假设当前只跟最近少数数据相关,从而简化模型
- 潜变量模型使用潜变量来概括历史信息
代码
labels = x[tau:].reshape((-1, 1))
这里-1是指未设定行数,程序随机分配,所以这里-1表示任一正整数
所以reshape(-1,1)表示(任意行,1列)
import torchfrom torch import nnfrom d2l import torch as d2l# 序列模型# 使用正弦函数和一些可加性噪声来生成序列数据,时间步为1,2,..., 1000T = 1000time = torch.arange(1,T+1,dtype=torch.float32)x = torch.sin(0.01*time)+torch.normal(0,0.2,(T,))d2l.plot(time,[x],'time','x',xlim=[1,1000],figsize=(6,3))tau = 4features = torch.zeros((T - tau, tau))for i in range(tau):features[:, i] = x[i:T - tau + i]labels = x[tau:].reshape((-1, 1))batch_size, n_train = 16, 600train_iter = d2l.load_array((features[:n_train], labels[:n_train]),batch_size, is_train=True)### 使用一个相当简单的结构:只是一个拥有两个全连接层的多层感知机def init_weights(m):if type(m) == nn.Linear:nn.init.xavier_uniform_(m.weight)def get_net():net = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(4,10),nn.ReLU(),nn.Linear(10,1))net.apply(init_weights)return netloss = nn.MSELoss()def train(net,train_iter,loss,epochs,lr):trainer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(),lr)for epoch in range(epochs):for X,y in train_iter:trainer.zero_grad() #梯度设为0l = loss(net(X),y)l.backward()trainer.step()print(f'epoch {epoch+1},'f'loss {d2l.evaluate_loss(net,train_iter,loss)}')net = get_net()train(net,train_iter,loss,5,0.01)### 模型预测下一个时间步onestep_preds = net(features)d2l.plot([time,time[tau:]],[x.detach().numpy(),onestep_preds.detach().numpy()],'time','x',legend=['data','1-step preds'],xlim=[1,1000],figsize=(6,3))

