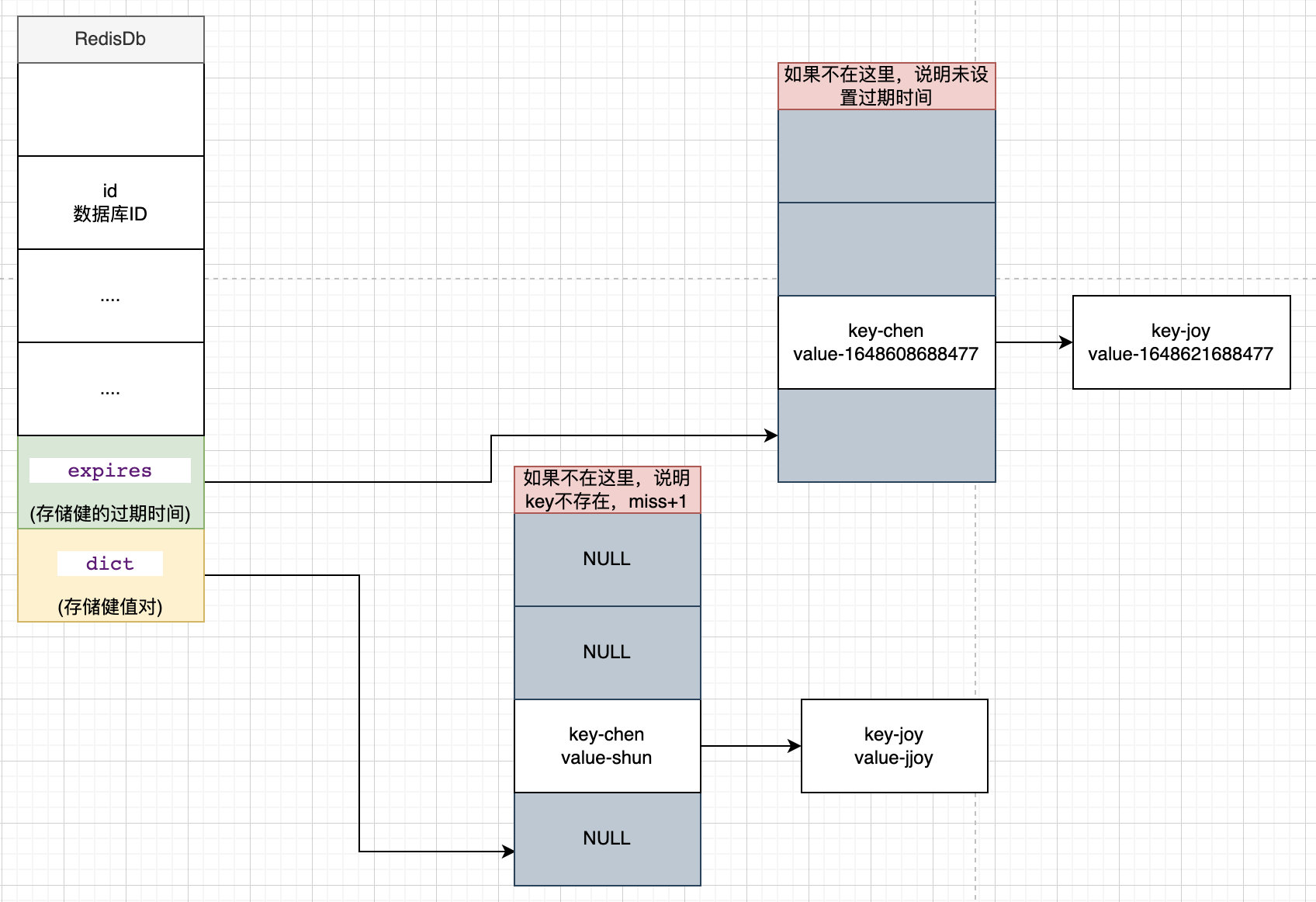
Redis DB数据结构
配置项
volatile: 过期key allkeys: 全部key
内存相关
- maxmemory 最大内存限制
maxmemory-policy 达到最大内存限制的时候,如何驱逐key
lazyfree-lazy-eviction
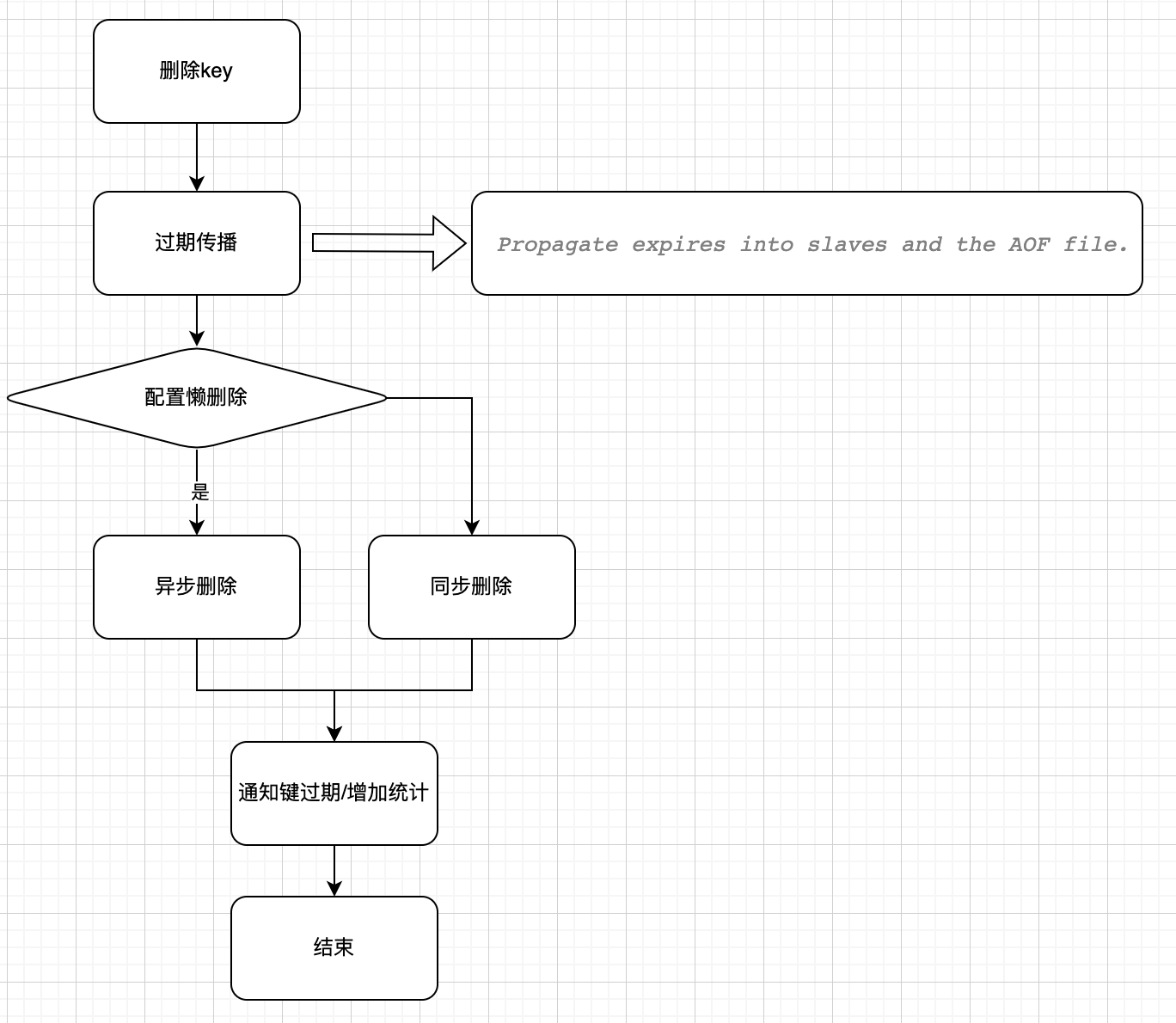
- lazyfree-lazy-expire: 同步删除/异步删除
- lazyfree-lazy-server-del: 同步释放内存/异步释放内存
-
Redis实现
expire.c 过期实现
-
过期删除实现
惰性删除
惰性删除: 不主动删除,等到下次要使用到该key时进行检测是否已过期,由
db.c#expireIfNeeded实现 ```c int expireIfNeeded(redisDb db, robj key) { if (!keyIsExpired(db,key)) return 0; propagateExpire(db,key,server.lazyfree_lazy_expire); notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_EXPIRED,”expired”,key,db->id); return server.lazyfree_lazy_expire ? dbAsyncDelete(db,key) :dbSyncDelete(db,key); }
/ Check if the key is expired. / int keyIsExpired(redisDb db, robj key) { //获取key的过期时间 mstime_t when = getExpire(db,key); if (when < 0) return 0; / No expire for this key / mstime_t now = mstime() return now > when; } ```
定期删除
- 定期删除: 在
server.c#serverCron中定期调用,在expire.c#activeExpireCycle中实现定期删除- 轮训遍历N个数据库
- 从
db->expires中随机挑选20个key,进行过期处理,轮训处理到20个或者是达到指定时间停止遍历
驱逐key实现
It is important to understand that the eviction process works like this:
- A client runs a new command, resulting in more data added.
- Redis checks the memory usage, and if it is greater than the maxmemory limit , it evicts keys according to the policy.
- A new command is executed, and so forth.
So we continuously cross the boundaries of the memory limit, by going over it, and then by evicting keys to return back under the limits.
If a command results in a lot of memory being used (like a big set intersection stored into a new key) for some time, the memory limit can be surpassed by a noticeable amount.
主要由 evict.c#freeMemoryIfNeeded实现,比较maxMemory和 实际使用-AOF/slave使用判定是否需要回收内存。