Variables are a generic way to store and retrieve arbitrary content or settings as a simple key value store within Airflow. Variables can be listed, created, updated and deleted from the UI (Admin -> Variables), code or CLI.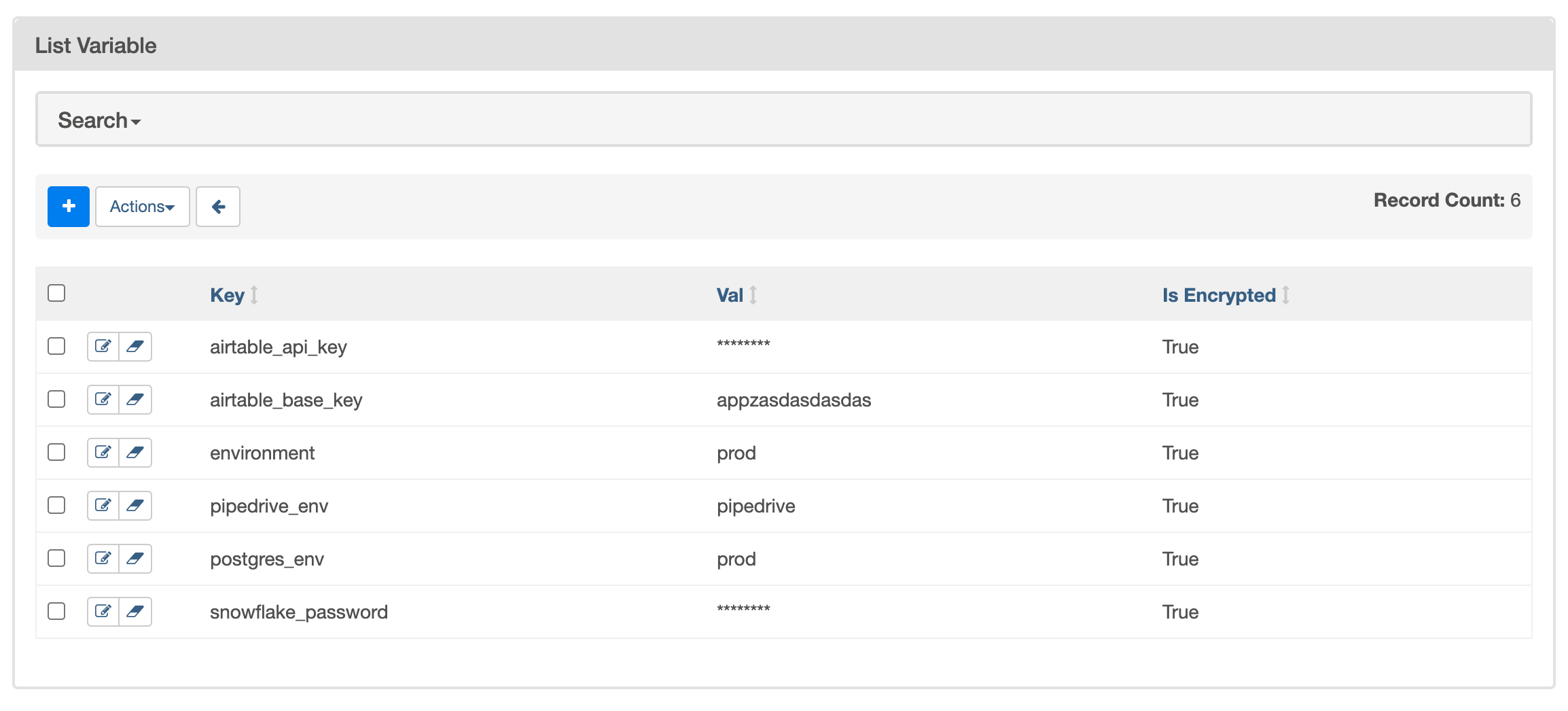
See the Variables Concepts documentation for more information.
1. Storing Variables in Environment Variables
New in version 1.10.10.
Airflow Variables can also be created and managed using Environment Variables. The environment variable naming convention is AIRFLOW_VAR_{VARIABLE_NAME}, all uppercase. So if your variable key is FOO then the variable name should be AIRFLOW_VAR_FOO.
For example:
$ export AIRFLOW_VAR_FOO=BAR# To use JSON, store them as JSON strings$ export AIRFLOW_VAR_FOO_BAZ='{"hello":"world"}'
You can use them in your DAGs as:
from airflow.models import Variablefoo = Variable.get("foo")foo_json = Variable.get("foo_baz", deserialize_json=True)
:::tips
🔖 Note
:::
:::info
Single underscores surround VAR. This is in contrast with the way airflow.cfg parameters are stored, where double underscores surround the config section name. Variables set using Environment Variables would not appear in the Airflow UI but you will be able to use them in your DAG file
:::
2. Securing Variables
Airflow uses Fernet to encrypt variables stored in the metastore database. It guarantees that without the encryption password, content cannot be manipulated or read without the key. For information on configuring Fernet, look at Fernet.
In addition to retrieving variables from environment variables or the metastore database, you can enable a secrets backend to retrieve variables. For more details see Secrets backend.

