通用约定
图像操作
img1 = sitk.Image(24,24, sitk.sitkUInt8)img1[0,0] = 0img2 = sitk.Image(img1.GetSize(), sitk.sitkUInt8)img2.SetDirection([0,1,0.5,0.5])img2.SetSpacing([0.5,0.8])img2.SetOrigin([0.000001,0.000001])img2[0,0] = 255img3 = img1 + img2print(img3[0,0])
访问和索引切片
Slicing of SimpleITK images returns a copy of the image data.This is similar to slicing Python lists and differs from the “view” returned by slicing numpy arrays.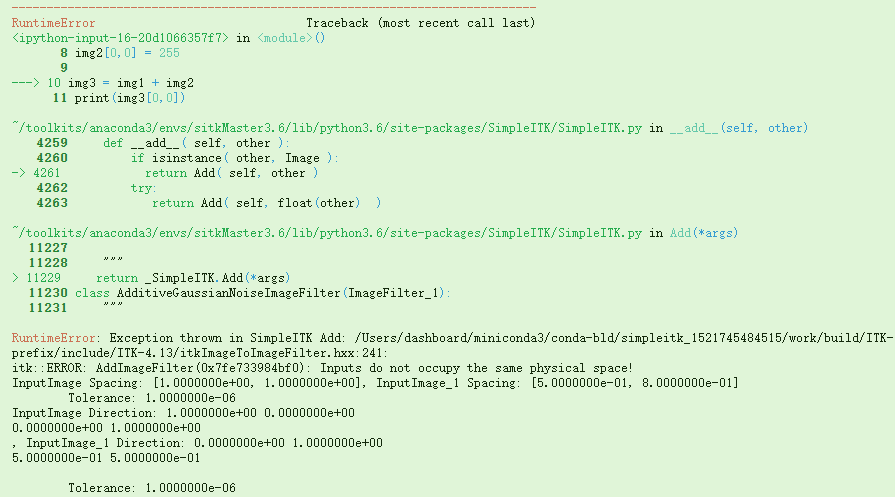
numpy的和SimpleITK之间的转换:
SimpleITK和numpy的索引访问的顺序相反!SimpleITK:图像[X,Y,Z]numpy的:image_numpy_array [Z,Y,X]
1. 从SimplTK到numpy
2. 从numpy到SimpleITK
3. 区别于scikit-image和numpy的转换:
读写图像
SimpleITK可以读写存储在单个文件或一组文件(例如DICOM系列)中的图像。以DICOM格式存储的图像具有与之关联的元数据字典,其中包括了DICOM标签。当将DICOM系列被读为单个图像时,元数据信息不可用,因为DICOM标签是针对每个单独文件的。如果需要元数据,可以使用面向对象的接口的ImageSeriesReader类,或者ImageFileReader类,设置特定切片的文件名,访问元数据图像使用GetMetaDataKeys,HasMetaDataKey和GetMetaData。
例如,读取DICOM格式的图像,并将其写为mhd。文件格式由文件扩展名推导出。还设置了适当的像素类型-您可以覆盖它并强制选择您要的像素类型。
data_directory = os.path.dirname(fdata("CIRS057A_MR_CT_DICOM/readme.txt"))series_ID = '1.2.840.113619.2.290.3.3233817346.783.1399004564.515'# Get the list of files belonging to a specific series ID.reader = sitk.ImageSeriesReader()# Use the functional interface to read the image series.original_image = sitk.ReadImage(reader.GetGDCMSeriesFileNames(data_directory, series_ID))# Write the image.output_file_name_3D = os.path.join(OUTPUT_DIR, '3DImage.mha')sitk.WriteImage(original_image, output_file_name_3D)# Read it back again.written_image = sitk.ReadImage(output_file_name_3D)# Check that the original and written image are the same.statistics_image_filter = sitk.StatisticsImageFilter()statistics_image_filter.Execute(original_image - written_image)# Check that the original and written files are the sameprint('Max, Min differences are : {0}, {1}'.format(statistics_image_filter.GetMaximum(),statistics_image_filter.GetMinimum()))
Fetching CIRS057A_MR_CT_DICOM/readme.txt
Max, Min differences are : 0.0, 0.0
将图像写为jpg格式,并且需要重新调整图像强度(默认为[0,255]),因为JPEG格式的显示需要转换为UInt8像素类型。
sitk.WriteImage(sitk.Cast(sitk.RescaleIntensity(written_image), sitk.sitkUInt8),[os.path.join(OUTPUT_DIR, 'slice{0:03d}.jpg'.format(i))for i in range(written_image.GetSize()[2])])
图像显示
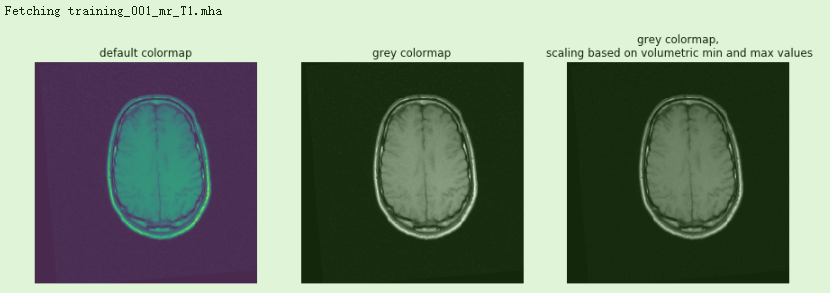
mr_image = sitk.ReadImage(fdata('training_001_mr_T1.mha'))npa = sitk.GetArrayViewFromImage(mr_image)# Display the image slice from the middle of the stack, z axisz = int(mr_image.GetDepth()/2)npa_zslice = sitk.GetArrayViewFromImage(mr_image)[z,:,:]# Three plots displaying the same data, how do we deal with the high dynamic range?fig = plt.figure()fig.set_size_inches(15,30)fig.add_subplot(1,3,1)plt.imshow(npa_zslice)plt.title('default colormap')plt.axis('off')fig.add_subplot(1,3,2)plt.imshow(npa_zslice,cmap=plt.cm.Greys_r);plt.title('grey colormap')plt.axis('off')fig.add_subplot(1,3,3)plt.title('grey colormap,\n scaling based on volumetric min and max values')plt.imshow(npa_zslice,cmap=plt.cm.Greys_r, vmin=npa.min(), vmax=npa.max())plt.axis('off');
参考:
【1】SimpleITK图像基础
【2】SimpleITK-Notebooks-03_Image_Details
【3】scikit-image中的numpy速成
【4】SITK Documentation docs