昨日内容回顾
多表方案:如何确定表关系呢?表关系是在2张表之间建立的,没有超过2个表的情况。那么相互之间有2条关系线,先来判断一对多的关系。如果其中一张表的记录能够对应另外一张表的多条记录,那么关系线成立!如果只有一条线成立,那么就是一对多的关系。如果有2条线成立,那么就是多对多的关系。比如book和publish。一本书不能对应多个出版社(常规是这样的,否则就盗版了),那么不成立。一个出版社可以对应多本书,关系线成立。所以book和publish表的关系是一对多的关系多对多的关系,就是2张表互相对应多条记录。比如book和author。一本书可以有多个作者,一个作者可以写多本!一对一的关系,就很简单了,彼此唯一。比如author和authordetail是一对一的关系。一对多:book和publish表的关系是一对多的关系一旦确定一对多的关系:在多的表中创建关联字段# 与Publish建立一对多的关系,外键字段建立在多的一方publish=models.ForeignKey(to="Publish",to_field="id",on_delete=models.CASCADE)#创建的字段名为publish_id。它会自动加_id后缀多对多:book和author是多对多的关系一旦确定多对多的关系:创建第三张关系表# 与Author表建立多对多的关系,ManyToManyField可以建在两个模型中的任意一个,自动创建第三张表authors=models.ManyToManyField(to="Author")#注意:表名为应用名+book类名小写+authors,也就是book_authors。#它只有3个字段,分别是主键id,book_id,author_id。#book_id和author_id分别表示book表和author表的主键id一对一:author和authordetail是一对一的关系一旦确定一对一的关系 : 创建关联字段(任意一张表创建都可以)#但是一般,我们会判断谁是重要的,谁是次要的。在重要的表上面创建关联字段!比如author#由于authordetail表是author表的延伸,所以在author表创建关联字段# 与AuthorDetail建立一对一的关系ad=models.OneToOneField(to="AuthorDetail",to_field="id",on_delete=models.CASCADE,)#创建的字段名为ad_id,它会自动加_id后缀。一对一关联字段,必须设置唯一属性!
一、django多表添加
昨天已经把5张表,都创建出来了。models.py里面有4个模型,其中第5张表,是book表和author表的关系表。
由book类的authors属性来创建了关系表,表名为:应用名+book+’_’+authors。
修改urls.py,添加add路径
from app01 import viewsurlpatterns = [path('admin/', admin.site.urls),path('add/', views.add),]
由于pycharm对sqlite数据库的时间字段,添加时,会自动转换为时间戳。
这样很不好,所以我使用navicat来连接。
新建一个连接
找到表publish
添加2条记录
添加表记录
create(**kwargs) 建立新对象
返回值是添加的model对象
一对一
举例:添加一条作者信息
姓名=hong,年龄=25,女朋友=唐安琪,电话=1314
def add(request):#先添加作者详细信息hong_gf = AuthorDetail.objects.create(gf="唐安琪",tel=1314)#再添加作者,因为它依赖AuthorDetail表hong = Author.objects.create(name="hong",age="25",ad=hong_gf)print(hong)return HttpResponse('添加成功')
注意:因为author的ad属性是关联authordetail表,必须添加authordetail表,才能添加author表。
ad必须接收一个model对象。可以从这个model对象中,获取插入的id值。
刷新页面,查看authordetail表,发现多了一条记录

查看author表,发现多了一条记录

一对多
方式1(推荐)
修改views.py,增加add视图函数
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponsefrom app01.models import Book# Create your views here.def add(request):#publish_id就是Book类的publish属性。它的字段为publish_idbook = Book.objects.create(title='西游记',price=100,pub_date="1743-4-12",publish_id=2)print(book.title) #打印titlereturn HttpResponse('添加成功')
访问url:http://127.0.0.1:8000/add/
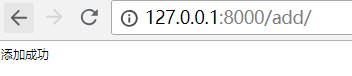
查看book表记录,发现多了一条

方式2
添加一本书《三国演义》,指定出版社为西瓜出版社
首要要导入Publish
def add(request):xigua = Publish.objects.filter(name="西瓜出版社").first() #model对象book = Book.objects.create(title='三国演义',price=300,pub_date="1643-4-12",publish=xigua)print(book.title) #打印标题print(book.publish) # 与这本书籍关联的出版社对象print(type(book.publish)) # 打印属性print(book.publish.id) # 出版社idprint(book.publish.name) # 出版社namereturn HttpResponse('添加成功')
注意:xigua它是一个model对象,它表示publish表的一条记录
create里面的publish只能接收publish表的model对象,不能接收别的表model对象!
查看models.py的Book类的publish属性
publish=models.ForeignKey(to="Publish",to_field="id",on_delete=models.CASCADE)
注意:它只能接收publish表的id字段。
所以执行sql时,它相当于publish_id=xigua.id。
这种添加方式,有严格的限制,必须接收publish的model对象才可以的。不推荐使用
查看控制台信息:
三国演义[29/Jun/2018 16:47:44] "GET /add/ HTTP/1.1" 200 12Publish object (1)<class 'app01.models.Publish'>1西瓜出版社
book.publish 是与这本书籍关联的出版社对象
那么就可以得到出版社的id和name属性值
查看表记录,发现多了一条
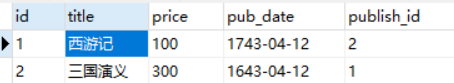
现在书籍和作者还没有绑定关系,先增加作者详细记录
修改authordetail表,增加2条记录
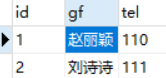
修改author表,增加2条记录

多对多
现在需要在book表里面插入一本书《python》,这本书有2个作者。那么book_authors应该有2条记录
它应该是这样的
id book_id author_id1 3 12 3 2
那么如何将这2条记录,插入进去呢?
修改add视图函数,注意导入author类
先插入一条记录
book = Book.objects.create(title='python',price=122,pub_date="2012-12-12",publish_id=1)
再获取2个作者
xiao = Author.objects.filter(name="xiao").first()zhang = Author.objects.filter(name="zhang").first()
最后插入2条记录,注意:下面2行代码是不能执行的,它是伪代码!
book_authors.objects.create(book_id=book.id,author_id=xiao.id)book_authors.objects.create(book_id=book.id, author_id=zhang.id)
上面2行代码表示在book_authors表中添加2条记录,只增加book_id和author_id。
那么问题来了,book_authors这张表是用orm创建的
但是orm的models.py里面找不到book_authors这张表的模型类。如果存在的话,那肯定没有问题的。
因为第3张表,是在book类里面的authors属性,用ManyToManyField创建的
因为一本书,对应的不止一个作者,所以不能直接赋值操作。
add() 增加多个关系对象
使用方法1:add(obj1, obj2, …)
ORM提供了add方法,来添加多对多的关系表。
def add(request):book = Book.objects.create(title='python',price=122,pub_date="2012-12-12",publish_id=1)xiao = Author.objects.filter(name="xiao").first()zhang = Author.objects.filter(name="zhang").first()book.authors.add(xiao,zhang) # 添加2条数据,接收一个参数,就会产生一条记录return HttpResponse('添加成功')
注意:book.authors.add(xiao,zhang),相当于执行上面2句伪代码!
它会自动获取2个对象的主键id,并插入到对应的字段中。
刷新页面,查看book表,发现多了一条记录
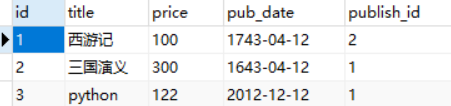
查看book_authors表,发现多2条数据
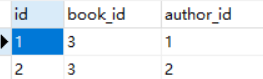
如果需要为书籍绑定所有作者呢?
author_list = Author.objects.all()book.authors.add(*author_list)
上面2行代码,就搞定了,非常简洁!
使用方法2:add(主键1, 主键2, …)
下面这种写法,也是可以的。在html表单页面添加时,会用到此写法!
book.authors.add(1,2)
还有一种写法,是属于python的。*[1,2],表示打散。它相当于上面的写法
book.authors.add(*[1,2])
区别在于:add(1,2)这种写法,它是执行了2次,在book_authors表中插入2条记录。
那么在不知道有多少数值的情况下,需要使用*[args1,args2]这种写法。
注意:在html表单中的复选框中,它提交的数据是多个值,必须使用getlist方法获取,它是列表类型。
因为不知道用户,到底会选择多少个选项。所以就需要使用这种打散写法!
删除记录
remove(obj1, obj2, …) 去除多个关系对象
举例:删除python这本书的xiao作者
那么只需要删除book_authors表,id为1的这一条记录,就可以了
但是,不能直接对这张表,直接删除。因为它是2个表的关联表。
解除绑定的关系
def add(request):book = Book.objects.filter(id=3).first() # 先找到这本书xiao = Author.objects.filter(name="xiao").first() # 再找到作者book.authors.remove(xiao) # 解除绑定的关系return HttpResponse('添加成功')
刷新页面,查看book_authors表记录,发现作者没有了

注意:这里可不是级联删除,book_authors并没有on_delete=models.CASCADE属性
clear() 清理所有关系对象
修改book_authors表记录,添加1条记录
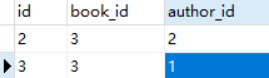
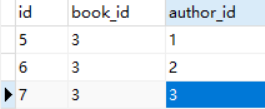
举例:将book_id等于3的所有的作者删除
上面的例子,用remove,可以将一个删除。如果这本书,有5个作者呢?
一个个remove?太累了!django提供了clear方法,可以清理所有关系对象。
def add(request):book = Book.objects.filter(id=3).first()book.authors.clear() # 清理所有关系对象return HttpResponse('添加成功')
刷新页面,再次查看book_authors表记录,发现已经空了!

修改authordetail表,增加一条记录
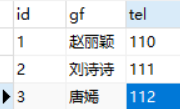
修改author表,增加一条记录
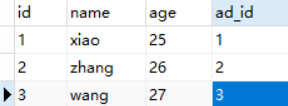
修改book_authors表,增加3条数据
set([obj1,obj2…]) 先清空再设置
set([obj1,obj2,…]) 它接收多个值,可以一个,也可以多个。适用于后台网页修改操作!
举例:
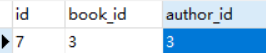
python这本书目前有3个作者,将wang设置为这本书的唯一作者
怎么做呢?将另外2个作者解除关系就可以了。
def add(request):book = Book.objects.filter(id=3).first() # 先找到书xiao = Author.objects.filter(name="xiao").first() # 再找到作者zhang = Author.objects.filter(name="zhang").first()book.authors.remove(xiao,zhang) # 解除绑定的关系return HttpResponse('添加成功')
但是这样将2个作者解除,太麻烦了。
还有一种做法,先清空,再设置
def add(request):book = Book.objects.filter(id=3).first() # 先找到书book.authors.clear() # 清理所有关系对象wang = Author.objects.filter(name="wang").first()book.authors.add(wang)return HttpResponse('添加成功')
django提示了set方法,直接合并了先清空再设置的操作
它必须接收一个数组,因为可以接收多个值
def add(request):book = Book.objects.filter(id=3).first() # 先找到书wang = Author.objects.filter(name="wang").first() # 再找作者book.authors.set([wang]) #先清空再设置return HttpResponse('添加成功')
刷新页面,查看book_authors表记录,发现只有一条了
总结:
重点掌握create,add,remove,clear,set这五个方法!
添加表记录:
一对一和一对多,使用create方法。它有2种使用方法:
1.** create(字段名1=值1…)。适用于表单添加操作!**注意,这里面的字段名是ORM创建表之后的的字段名
比如: book类的publish属性,它是关联字段,ORM创建之后,字段名为publish_id
2.create(模型类属性1=值1…)。比如book类的publish属性,它是关联字段。
直接create(publish=obj1),注意,它接收一个model对象,对象包含了主键id
多对多使用add方法。add用2种使用方法:
1.add(obj1,obj2…) 它接收一个model对象,对象包含了主键id
2.**add(主键id1,主键id2…) 它接收一个主键id。适用于表单添加操作!**
**还有一个python的打散语法,前面加一个就可以了。比如[1,2],它会依次调用前置方法,每次只取一个值。表单操作,会用到!**
删除记录:
适用于一对一,一对多,多对一。
remove(obj1, obj2, …) 去除多个关系对象。它需要指定一个或者多个对象
clear() 清理所有关系对象。不管现有的关系有多少,一律清空!
**set([obj1,obj2…]) 先清空再设置。不管现有的关系有多少,一律清空再设置。适用于网页后台修改操作**
基于对象的跨表查询(子查询)
先来查询id为3的书籍,打印publish和authors是什么?
def add(request):book = Book.objects.filter(id=3).first()print(book.publish) # 查看publish属性print(book.authors)print(type(book.authors)) # 查看类型print(book.authors.all()) # 返回所有book的关联对象print(book.authors.all().values()) # 查看关联对象的值return HttpResponse('添加成功')
刷新页面,查看控制台信息
Publish object (1)app01.Author.None<class 'django.db.models.fields.related_descriptors.create_forward_many_to_many_manager.<locals>.ManyRelatedManager'><QuerySet [<Author: Author object (3)>]><QuerySet [{'name': 'wang', 'age': 27, 'id': 3, 'ad_id': 3}]>
注意:book.authors不能直接print,否则返回的值是None。它是一个多对多的关系管理器,必须用all()才能取值。
book.authors.all() 表示返回所有book的关联对象。注意:这里的book对象,是一个model对象,它是表示id为3的一条记录。从最后一条打印信息中,就可以看出来!
修改book_authors表,添加2条记录
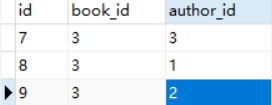
再次刷新页面,查看控制台信息
Publish object (1)app01.Author.None<class 'django.db.models.fields.related_descriptors.create_forward_many_to_many_manager.<locals>.ManyRelatedManager'><QuerySet [<Author: Author object (1)>, <Author: Author object (2)>, <Author: Author object (3)>]><QuerySet [{'name': 'xiao', 'id': 1, 'ad_id': 1, 'age': 25}, {'name': 'zhang', 'id': 2, 'ad_id': 2, 'age': 26}, {'name': 'wang', 'id': 3, 'ad_id': 3, 'age': 27}]>
注意最后一条信息,它返回了3个model对象。为什么会返回3条信息呢?
它实际是执行了下面这句SQL
SELECTauthor.id,author.name,author.age,author.ad_idFROMauthorINNER JOIN book_authors ON (author.id = book_authors.author_id)WHEREbook_authors.book_id = 3LIMIT 21;
因为book的id为3,它先从关系表book_authors,查找book_id=3的记录。此时有3条记录!
再和author表关联查询,找出3个作者的记录。所以最终结果就是author的3条记录!
book.authors.all()是与这本书关联的作者对象queryset对象集合
django有2个日期类型,一个是DateField(),它的格式是yyyy-mm-dd
还有一个类型是DateTimeField(),它的格式是yyyy-mm-dd h:i:s。它是带时分秒的!
python中的datetime
举例:
import datetimenow = datetime.datetime.now()print(now) # 当前时间print(now.today()) # 当前时间print(now.date()) # 日期print(now.time()) # 排除日期,取时分秒print(now.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%I:%S")) # 格式化时间delta = datetime.timedelta(days=3) # 时间差print(delta)print(now+delta) # 3天后print(now-delta) # 3天后
输出:
2018-06-29 20:59:02.7417802018-06-29 20:59:02.7417812018-06-2920:59:02.7417802018-06-29 20:08:023 days, 0:00:002018-07-02 20:59:02.7417802018-06-26 20:59:02.741780
一对多查询(Publish 与 Book)
book_authors表添加2条数据
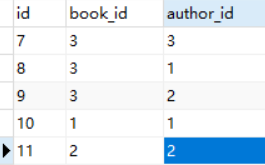
举例:
查询西游记这本书的出版社的名字
普通写法
先找出这本书,然后取出publish_id。在publish表中,通过publish_id找到对应记录。
def add(request):book = Book.objects.filter(title="西游记").first()publish_id = book.publish_idpublish = Publish.objects.filter(id=publish_id).first()print(publish.name)return HttpResponse('添加成功')
刷新网页,查看控制台,输出:
榴莲出版社
推荐写法:
上面的步骤太麻烦了,下面使用简洁写法,2行就搞定了!
def add(request):book = Book.objects.filter(title="西游记").first()print(book.publish.name)return HttpResponse('添加成功')
举例:查询西瓜出版社出版过的所有书籍的名称
def add(request):publish = Publish.objects.filter(name="西瓜出版社").first() # 先找出版社ret = Book.objects.filter(publish_id=publish.id).values("title") # 再找书籍print(ret)return HttpResponse('添加成功')
刷新网页,查看控制台,效果同上
上面写的太麻烦,下面来介绍正向查询和反向查询
正向和反向,就看关键字段在哪里?
如果是通过关联字段查询,就是正向。否则是反向!
简单来说:正向,按照字段。反向,按照表名
正向与反向查询
正向查询:关联属性在book表中,所以book对象找出关联出版社对象,正向查询
反向查询:关联属性在book表中,所以publish对象找出关联书籍,正向查询
正向:按字段:publish book —————-> publish <—————- 反向:按表名小写_set() 例如:publish.obj.book_set()
正向查询
还是上面的例子:查询西瓜出版社出版过的所有书籍的名称
简洁写法:
def add(request):publish = Publish.objects.filter(name="西瓜出版社").first() # 先找出版社# ret = Book.objects.filter(publish_id=publish.id).values("title") # 再找书籍# print(ret)#正向查询--简洁写法ret = publish.book_set.all().values("title")print(ret)return HttpResponse('添加成功')
刷新网页,控制台输出:
<QuerySet [{'title': '三国演义'}, {'title': 'python'}]>
推荐使用简洁写法,为什么呢?因为如果表越来越多,那么SQL就非常复杂。使用简洁写法,就能避免!
那么它是如何实现的呢?通过Book模型类的authors属性
authors=models.ManyToManyField(to="Author")
反向查询
举例:查询与西瓜出版社关联的所有书籍的名字
def add(request):publish = Publish.objects.filter(name="西瓜出版社").first() # 先找出版社ret = publish.book_set.all().values("title") # 再找书籍,过滤titleprint(ret)return HttpResponse('添加成功')
刷新网页,控制台输出:
<QuerySet [{'title': '三国演义'}, {'title': 'python'}]>
多对多查询 (Author 与 Book)
正向查询:关联属性在book表中,所以book对象找出关联作者集合,正向查询
反向查询:关联属性在book表中,所以author对象找出关联书籍,正向查询
因为记录有多条,所以结尾要加.all()
正向:按字段:authors.all() book —————-> author <—————- 反向:按表名小写_set().all() 例如:author.obj.book_set().all()
正向查询
举例:查询西游记这本书籍的所有作者的姓名和年龄
def add(request):book = Book.objects.filter(title="西游记").first() # 先找书籍ret = book.authors.all().values("name","age") # 再找作者,过滤name和ageprint(ret)return HttpResponse('添加成功')
刷新网页,控制台输出:
<QuerySet [{'age': 25, 'name': 'xiao'}]>
反向查询
举例:查询作者xiao出版过的所有书籍名称
def add(request):xiao = Author.objects.filter(name="xiao").first() # 先找作者ret = xiao.book_set.all().values("title") # 再找书籍,过滤titleprint(ret)return HttpResponse('添加成功')
刷新网页,控制台输出:
<QuerySet [{'title': 'python'}, {'title': '西游记'}]>
一对一查询(Author 与 AuthorDetail)
正向查询:关联属性在author表中,所以author对象找出关联作者详细信息对象,正向查询
反向查询:关联属性在book表中,所以author对象找出关联书籍,正向查询
因为记录只有一条,所以直接.ad就可以了。ad是关联字段
正向:按字段:.ad author —————-> authordetail <—————- 反向:按表名小写 例如:authordetail_obj.author
正向查询
举例:查询xiao的女朋友的名字
def add(request):xiao = Author.objects.filter(name="xiao").first() # 先找作者ret = xiao.ad.gf # 再找女朋友print(ret)return HttpResponse('添加成功')
刷新网页,控制台输出:
赵丽颖
反向查询
举例:查询手机号为112的作者名字
def add(request):phone = AuthorDetail.objects.filter(tel="112").first() # 先找号码ret = phone.author.name # 再找作者的名字print(ret)
刷新网页,控制台输出:
wang
周末作业
基于多表的图书管理系统
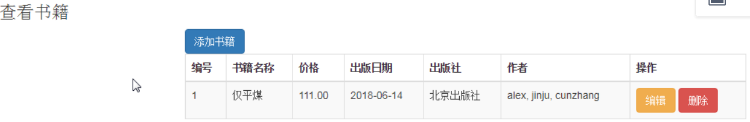
注意:出版社和作者,是从数据库中读取的。
作业是复选框,可以选择多个
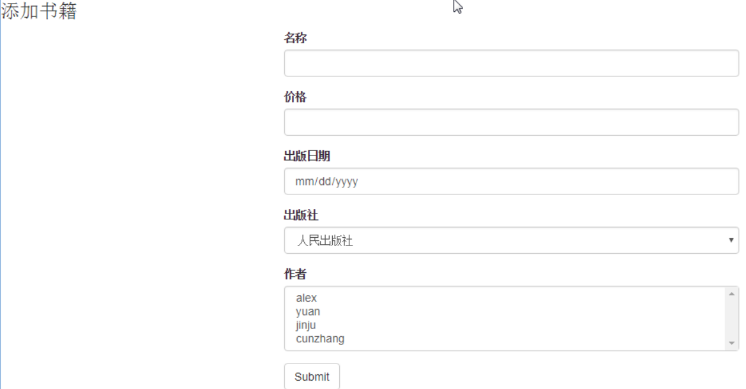
编辑页面,作者一栏的灰色背景。表示现有绑定的作者!
它是选择状,使用selected属性
提示:
视图函数接收复选框的值,需要使用request.POST.getlist()。使用get只能获取一个值!
答案
修改urls.py,添加路径
from django.contrib import adminfrom django.urls import path,re_pathfrom book import viewsurlpatterns = [path('admin/', admin.site.urls),path('', views.index),path('index/', views.index),path('books/add/', views.add),path('books/manage/', views.manage),re_path('books/delete/(?P<id>\d+)', views.delete),re_path('books/modify/(?P<id>\d+)', views.modify),]
修改settings.py
注册app
INSTALLED_APPS = ['django.contrib.admin','django.contrib.auth','django.contrib.contenttypes','django.contrib.sessions','django.contrib.messages','django.contrib.staticfiles','book',]
指定模板路径
TEMPLATES = [{'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates','DIRS': [os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'templates')],'APP_DIRS': True,'OPTIONS': {'context_processors': ['django.template.context_processors.debug','django.template.context_processors.request','django.contrib.auth.context_processors.auth','django.contrib.messages.context_processors.messages',],},},]
默认使用sqlite3数据库,有需要的使用其他数据库的,自行更改
指定静态资源路径
STATIC_URL = '/static/'STATICFILES_DIRS=[os.path.join(BASE_DIR,"static")]
手动创建templates和static目录。
在static目录创建css目录,下载bootstrap 3.3.7的数据包。将将bootstrap.min.css放到css目录
修改models.py
from django.db import models# Create your models here.class Book(models.Model):title=models.CharField(max_length=32,unique=True)price=models.DecimalField(max_digits=8,decimal_places=2,null=True)pub_date=models.DateField()# 与Publish建立一对多的关系,外键字段建立在多的一方publish=models.ForeignKey(to="Publish",to_field="id",on_delete=models.CASCADE)# 与Author表建立多对多的关系,ManyToManyField可以建在两个模型中的任意一个,自动创建关系表book_authorsauthors=models.ManyToManyField(to="Author")class Publish(models.Model):name=models.CharField(max_length=32)email=models.CharField(max_length=32)addr=models.CharField(max_length=32)class Author(models.Model):name=models.CharField(max_length=32)age=models.IntegerField()# 与AuthorDetail建立一对一的关系# ad=models.ForeignKey(to="AuthorDetail",to_field="id",on_delete=models.CASCADE,unique=True)ad=models.OneToOneField(to="AuthorDetail",to_field="id",on_delete=models.CASCADE,)class AuthorDetail(models.Model):gf=models.CharField(max_length=32)tel=models.CharField(max_length=32)
使用2个命令生成表
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate
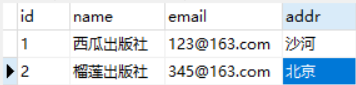
使用navicat打开sqlite数据库,5个表,添加初始数据
注意修改应用名,因为每个人的应用名不一样!下面是sql语句:
#作者详情表
INSERT INTO book_authordetail (`id`, `gf`, `tel`) VALUES (1, '赵丽颖',110);
INSERT INTO book_authordetail (`id`, `gf`, `tel`) VALUES (2, '刘诗诗',111);
INSERT INTO book_authordetail (`id`, `gf`, `tel`) VALUES (3, '唐嫣',112);
#作者表
INSERT INTO book_author (`id`, `name`, `age`, `ad_id`) VALUES (1, 'xiao',25,1);
INSERT INTO book_author (`id`, `name`, `age`, `ad_id`) VALUES (2, 'zhang',26,2);
INSERT INTO book_author (`id`, `name`, `age`, `ad_id`) VALUES (3, 'wang',27,3);
#出版社表
INSERT INTO book_publish (`id`, `name`, `email`, `addr`) VALUES (1, '人民教育出版社', 'rm@qq.com', '北京');
INSERT INTO book_publish (`id`, `name`, `email`, `addr`) VALUES (2, '中国农业出版社', 'zg@qq.com', '北京');
INSERT INTO book_publish (`id`, `name`, `email`, `addr`) VALUES (3, '中国林业出版社', 'ly@qq.com', '云南');
#书籍表
INSERT INTO book_book (`id`, `title`, `price`, `pub_date`, `publish_id`) VALUES (1, '西游记',2, '1501-01-23',1);
INSERT INTO book_book (`id`, `title`, `price`, `pub_date`, `publish_id`) VALUES (2, '红楼梦',3, '1715-02-13',2);
INSERT INTO book_book (`id`, `title`, `price`, `pub_date`, `publish_id`) VALUES (3, '三国演义',4, '1330-03-25',3);
#书籍和作者关系表
INSERT INTO book_book_authors (`id`, `book_id`, `author_id`) VALUES (1,1,1);
INSERT INTO book_book_authors (`id`, `book_id`, `author_id`) VALUES (2,2,2);
INSERT INTO book_book_authors (`id`, `book_id`, `author_id`) VALUES (3,3,3);
修改views.py
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse
#导入4个表模型
from book.models import Book,Publish,Author,AuthorDetail
# Create your views here.
def index(request): #首页
ret = Book.objects.all().exists() # 判断表是否有记录
if ret:
book_list = Book.objects.all() # 查询表的所有记录
return render(request, "index.html", {"book_list": book_list})
else:
hint = '<script>alert("没有书籍,请添加书籍");window.location.href="/books/add"</script>'
return HttpResponse(hint) # js跳转到添加页面
def add(request): # 添加
if request.method=="POST":
# print(request.POST)
title=request.POST.get("title")
the_book = Book.objects.filter(title=title).exists()
if the_book:
hint = '<script>alert("书籍已存在!不能重复添加");window.location.href="/books/add/"</script>'
return HttpResponse(hint) # js跳转到添加页面
else:
price=request.POST.get("price")
pub_date=request.POST.get("pub_date")
publish_id=request.POST.get("publish_id")
author_id=request.POST.getlist("author_id") # 返回列表
print(title,price,pub_date,publish_id,author_id)
#先插入书籍
book = Book.objects.create(title=title, price=price, pub_date=pub_date, publish_id=publish_id)
#再插入作者
book.authors.add(*author_id)
hint = '<script>alert("添加成功");window.location.href="/index/"</script>'
return HttpResponse(hint) # js跳转到首页
#读取所有出版社,过滤出id和name
publish_list = Publish.objects.all().values("id","name")
# 读取所有作者,过滤出id和name
author_list = Author.objects.all().values("id","name")
return render(request, "add.html", {"publish_list": publish_list,"author_list":author_list})
def delete(request,id): # 删除
# 先删除关系表中的作者
book_ad = Book.objects.filter(id=id).first()
book_ad.authors.clear()
# 再删除书籍
ret = Book.objects.filter(id=id).delete() # 返回元组
print(ret)
if ret[0]: # 取值为1的情况下
hint = '<script>alert("删除成功");window.location.href="/index/"</script>'
return HttpResponse(hint)
else: # 取值为0的情况下
hint = '<script>alert("删除失败");window.location.href="/index/"</script>'
return HttpResponse(hint)
def manage(request): # 管理页面
ret = Book.objects.all().exists()
if ret:
book_list = Book.objects.all()
#加载管理页面
return render(request, "manage.html", {"book_list": book_list})
else:
hint = '<script>alert("没有书籍,请添加书籍");window.location.href="/books/add"</script>'
return HttpResponse(hint)
def modify(request,id): # 修改
if request.method == "POST":
title = request.POST.get("title")
price = request.POST.get("price")
pub_date = request.POST.get("pub_date")
publish_id = request.POST.get("publish_id")
author_id = request.POST.getlist("author_id") # 返回列表
# 先修改书籍
ret = Book.objects.filter(id=id).update(title=title, price=price, pub_date=pub_date, publish_id=publish_id)
# 获取当前书籍
book_ad = Book.objects.filter(id=id).first()
book_ad.authors.set(author_id) # 先清空再设置
if ret: # 判断返回值为1
hint = '<script>alert("修改成功");window.location.href="/index/"</script>'
return HttpResponse(hint) # js跳转
else: # 返回为0
hint = '<script>alert("修改失败");window.location.href="/index/"</script>'
return HttpResponse(hint) # js跳转
book = Book.objects.get(id=id) # 默认获取id值
# print(book)
# 读取所有出版社,过滤出id和name
publish_list = Publish.objects.all().values("id", "name")
# 读取所有作者,过滤出id和name
author_list = Author.objects.all().values("id", "name")
the_author = [] # 当前书籍的作者
for i in book.authors.all():
the_author.append(i.name) # 最加到列表中
print(the_author)
return render(request, "modify.html", {"book":book,"publish_list": publish_list, "author_list": author_list,"the_author":the_author})
在templates目录新建几个html文件
base.html,这个是所有html的母版文件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
{% block title %}
<title>title</title>
{% endblock title %}
{#bootstrap,版本为3.3.7#}
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/css/bootstrap.min.css">
{#美化复选框#}
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.bootcss.com/awesome-bootstrap-checkbox/0.3.7/awesome-bootstrap-checkbox.css">
<link href="http://cdn.bootcss.com/font-awesome/4.6.3/css/font-awesome.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.header {
width: 100%;
height: 60px;
background-color: #369;
}
.title {
line-height: 60px;
color: white;
font-weight: 100;
margin-left: 20px;
font-size: 20px;
}
.container {
margin-top: 20px;
}
.table th, .table td {
text-align: center;
vertical-align: middle !important;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="header">
<p class="title">
图书管理系统
</p>
</div>
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-3">
<div class="panel panel-danger">
<div class="panel-heading"><a href="/index/">查看书籍</a></div>
<div class="panel-body">
Panel content
</div>
</div>
<div class="panel panel-success">
<div class="panel-heading"><a href="/books/add/">添加书籍</a></div>
<div class="panel-body">
Panel content
</div>
</div>
<div class="panel panel-warning">
<div class="panel-heading"><a href="/books/manage/">管理书籍</a></div>
<div class="panel-body">
Panel content
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="col-md-9">
{% block content %}
{% endblock %}
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
index.html,首页
{% extends 'base.html' %}
{% block title %}
<title>查看书籍</title>
{% endblock title %}
{% block content %}
<h3>查看书籍</h3>
<table class="table table-hover table-striped ">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>编号</th>
<th>书籍名称</th>
<th>价格</th>
<th>出版日期</th>
<th>出版社</th>
<th>作者</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{#遍历所有书籍#}
{% for book in book_list %}
<tr>
<td>{{ book.id }}</td>
<td>{{ book.title }}</td>
<td>{{ book.price }}</td>
<td>{{ book.pub_date|date:"Y-m-d" }}</td>
<td>{{ book.publish.name }}</td>
<td>
{#遍历所有书籍相关的作者#}
{% for j in book.authors.all %}
{#使用forloop.last判断,如果如果是最后一个,不增加逗号#}
{{ j.name }}{% if not forloop.last %},{% endif %}
{% endfor %}
</td>
</tr>
{% endfor %}
</tbody>
</table>
{% endblock content %}
add.html,添加页面
{% extends 'base.html' %}
{% block title %}
<title>添加书籍</title>
{% endblock title %}
{% block content %}
<h3>添加书籍</h3>
<form action="" method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
<div class="form-group">
<label for="">书籍名称</label>
<input type="text" name="title" class="form-control">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="">价格</label>
<input type="text" name="price" class="form-control">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="">出版日期</label>
<input type="date" name="pub_date" class="form-control">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="">出版社</label>
<select name="publish_id" id="" class="form-control">
{#使用for循环遍历所有出版社#}
{% for p in publish_list %}
{#由于表关系是通过id关联的,所以value值必须是id#}
<option value="{{ p.id }}">{{ p.name }}</option>
{% endfor %}
</select>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="">作者</label>
<ul class="list-group">
{#使用for循环遍历所有作者#}
{% for author in author_list %}
<li class="list-group-item">
<div class="checkbox checkbox-success ">
{#由于表关系是通过id关联的,所以value值必须是id#}
<input class="styled" type="checkbox" name="author_id" value="{{ author.id }}">
<label class="checkbox-inline">
{{ author.name }}
</label>
</div>
</li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
</div>
<input type="submit" class="btn btn-success pull-right" value="添加">
</form>
{% endblock content %}
manage.html,管理页面,用来删除和修改的
{% extends 'base.html' %}
{% block title %}
<title>管理书籍</title>
{% endblock title %}
{% block content %}
<h3>管理书籍</h3>
<table class="table table-hover table-striped ">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>编号</th>
<th>书籍名称</th>
<th>价格</th>
<th>出版日期</th>
<th>出版社</th>
<th>作者</th>
<th>删除</th>
<th>编辑</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{% for book in book_list %}
<tr>
<td>{{ book.id }}</td>
<td>{{ book.title }}</td>
<td>{{ book.price }}</td>
<td>{{ book.pub_date|date:"Y-m-d" }}</td>
<td>{{ book.publish.name }}</td>
<td>
{#遍历所有书籍相关的作者#}
{% for j in book.authors.all %}
{#使用forloop.last判断,如果如果是最后一个,不增加逗号#}
{{ j.name }}{% if not forloop.last %},{% endif %}
{% endfor %}
</td>
<td>
{#由于表关系是通过id关联的,所以参数必须是id#}
<a href="/books/delete/{{ book.id }}">
<button type="button" class="btn btn-danger" data-toggle="modal" id="modelBtn">删除</button>
</a>
</td>
<td>
<a href="/books/modify/{{ book.id }}">
<button type="button" class="btn btn-success" data-toggle="modal">编辑</button>
</a>
</td>
</tr>
{% endfor %}
</tbody>
</table>
{% endblock content %}
modify.html,修改页面
{% extends 'base.html' %}
{% block title %}
<title>修改书籍</title>
{% endblock title %}
{% block content %}
<h3>修改书籍</h3>
<form action="" method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
<div class="form-group">
<label for="">书籍名称</label>
<input type="text" name="title" class="form-control" value="{{ book.title }}">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="">价格</label>
<input type="text" name="price" class="form-control" value="{{ book.price }}">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="">出版日期</label>
<input type="date" name="pub_date" class="form-control" value="{{ book.pub_date|date:"Y-m-d" }}">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="">出版社</label>
<select name="publish_id" id="" class="form-control">
{#遍历所有出版社#}
{% for p in publish_list %}
{#判断当前书籍的出版社id等于出版社表的id时#}
{% if book.publish_id == p.id %}
{#添加选中状态selected="selected"#}
{#由于表关系是通过id关联的,所以value值必须是id#}
<option value="{{ p.id }}" selected="selected">{{ p.name }}</option>
{% else %}
<option value="{{ p.id }}">{{ p.name }}</option>
{% endif %}
{% endfor %}
</select>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="">作者</label>
<ul class="list-group">
{% for author in author_list %}
<li class="list-group-item">
<div class="checkbox checkbox-success ">
{#判断作者的名字在当前书籍作者列表中#}
{% if author.name in the_author %}
{#添加选中状态checked="checked"#}
{#由于表关系是通过id关联的,所以value值必须是id#}
<input class="styled" type="checkbox" checked="checked" name="author_id"
value="{{ author.id }}">
<label class="checkbox-inline">{{ author.name }}</label>
{% else %}
<input class="styled" type="checkbox" name="author_id" value="{{ author.id }}">
<label class="checkbox-inline">{{ author.name }}</label>
{% endif %}
</div>
</li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
</div>
<input type="submit" class="btn btn-default pull-right" value="修改">
</form>
{% endblock content %}
项目文件结构如下:
bms_mto
├── bms_mto
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── settings.py
│ ├── urls.py
│ └── wsgi.py
├── book
│ ├── admin.py
│ ├── apps.py
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── models.py
│ ├── tests.py
│ └── views.py
├── db.sqlite3
├── manage.py
├── static
│ └── css
│ ├── bootstrap.min.css
└── templates
├── add.html
├── base.html
├── index.html
├── manage.html
└── modify.html
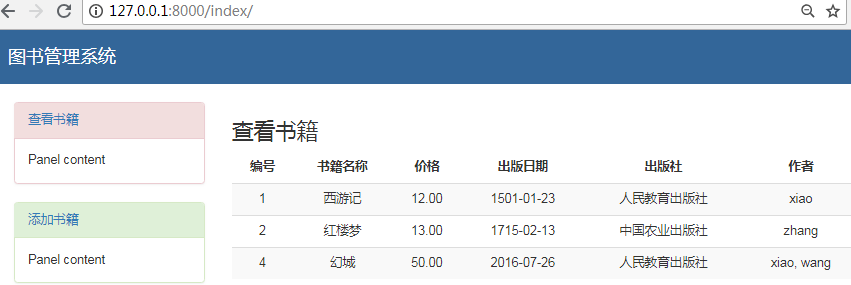
启动项目访问首页:http://127.0.0.1:8000/
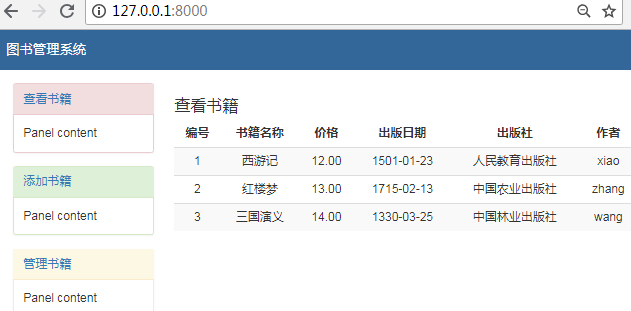
点击左侧的添加书籍
添加一本书,选择2个作者
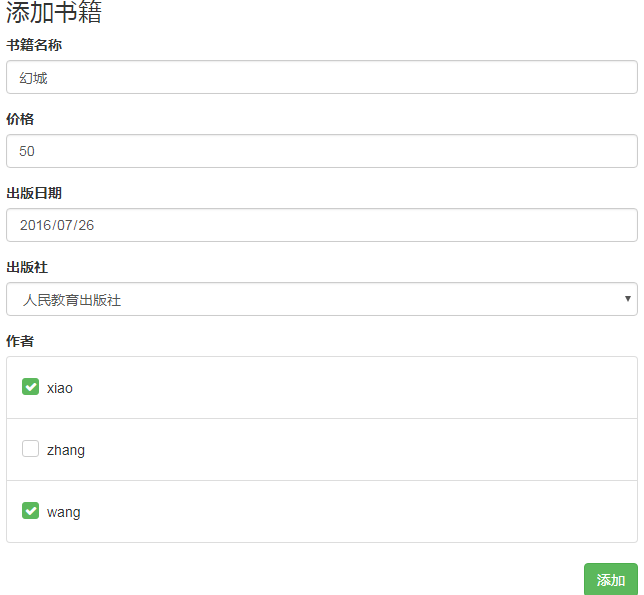
提示添加成功
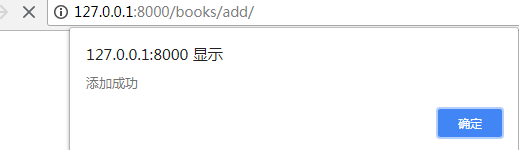
首页就会多一本书籍
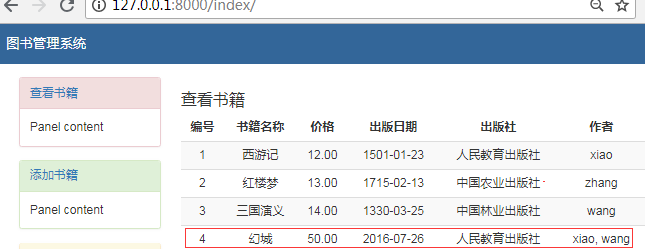
点击编辑按钮
修改价格,增加一个作者
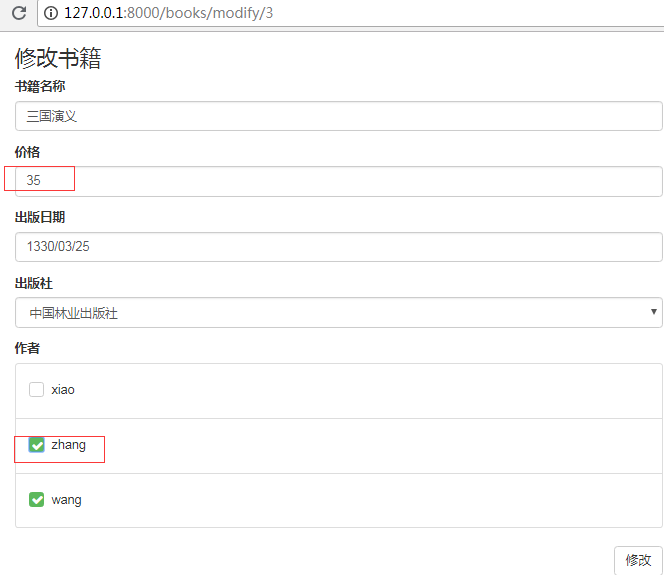
提示修改成功
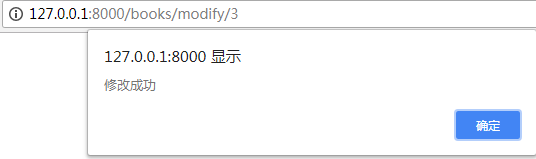
首页的书籍,价格和作者更新过来了
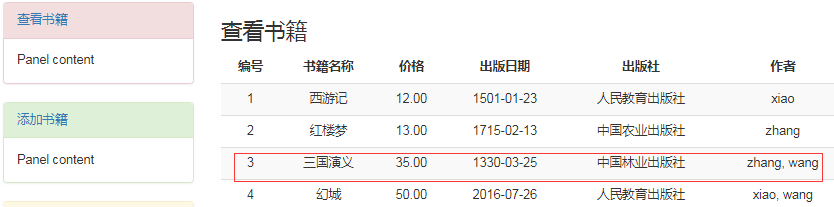
点击删除
提示删除成功
首页少了一条数据