类型定义和类型别名的区别
类型别名与类型定义表面上看只有一个等号的差异,我们通过下面的这段代码来理解它们之间的区别。
//类型定义type NewInt int//类型别名type MyInt = intfunc main() {var a NewIntvar b MyIntfmt.Printf("type of a:%T\n", a) //type of a:main.NewIntfmt.Printf("type of b:%T\n", b) //type of b:int}
结果显示a的类型是main.NewInt,表示main包下定义的NewInt类型。b的类型是int。MyInt类型只会在代码中存在,编译完成时并不会有MyInt类型。
构造函数
Go语言的结构体没有构造函数,可以自己实现。 例如,下方的代码就实现了一个person的构造函数。 因为struct是值类型,如果结构体比较复杂的话,值拷贝性能开销会比较大,所以该构造函数返回的是结构体指针类型。
func newPerson(name, city string, age int8) *person {return &person{name: name,city: city,age: age,}}
匿名结构体
结构体允许其成员字段在声明时没有字段名而只有类型,这种没有名字的字段就称为匿名字段。
var apr = struct {Name stringAge int}{Name: "zhangsan",Age: 13,}
go中的结构体内存布局和c结构体布局类似,每个成员的内存分布是连续的,在以下示例中通过反射进行进一步说明:
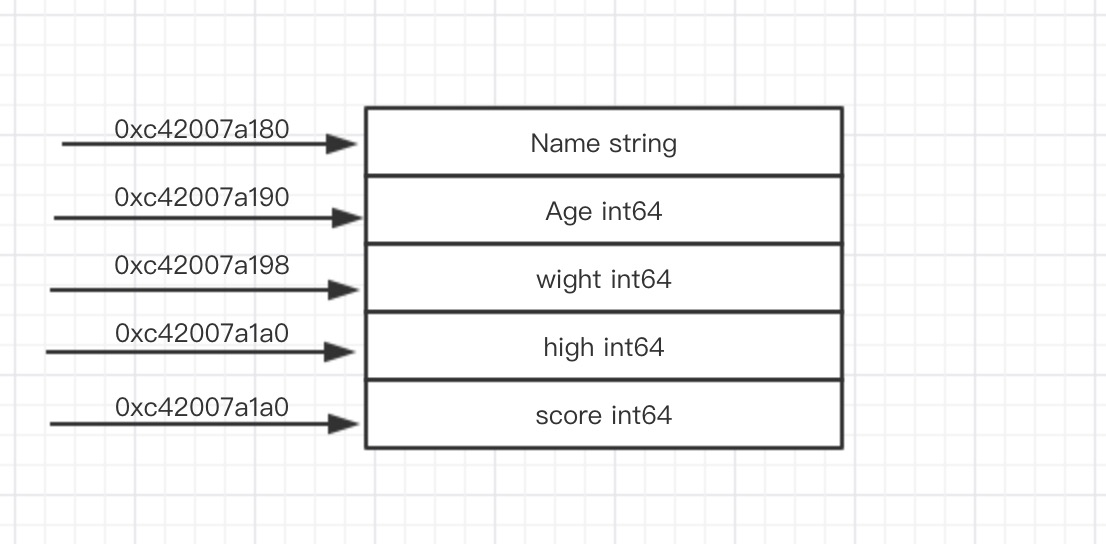
package mainimport ("fmt""reflect")type Student struct {Name stringAge int64wight int64high int64score int64}func main() {var stu1 = new(Student)fmt.Printf("%p\n", &stu1.Name)fmt.Printf("%p\n", &stu1.Age)fmt.Printf("%p\n", &stu1.wight)fmt.Printf("%p\n", &stu1.high)fmt.Printf("%p\n", &stu1.score)typ := reflect.TypeOf(Student{})fmt.Printf("Struct is %d bytes long\n", typ.Size())// We can run through the fields in the structure in ordern := typ.NumField()for i := 0; i < n; i++ {field := typ.Field(i)fmt.Printf("%s at offset %v, size=%d, align=%d\n",field.Name, field.Offset, field.Type.Size(),field.Type.Align())}}// result0xc0000981800xc0000981900xc0000981980xc0000981a00xc0000981a8Struct is 48 bytes longName at offset 0, size=16, align=8Age at offset 16, size=8, align=8wight at offset 24, size=8, align=8high at offset 32, size=8, align=8score at offset 40, size=8, align=8
可以看到内存地址的偏移总是以8字节偏移(使用的是int64,刚好是8字节),在观察其内存地址,也是连续的,所以go语言中的结构体内存布局是连续的。如下图:
因为空结构体是不占用内存的,所以size为0,在内存分配时,size为0会统一返回zerobase的地址,所以空结构体在进行参数传递时,发生值拷贝后地址都是一样的,才造成了这个质疑Go不是值传递的假象。
所以在判断是否存在的时候可以 map[type]struct{}
空结构体在结构体中的前面和中间时,是不占用空间的,但是当空结构体放到结构体中的最后时,会进行特殊填充,struct { } 作为最后一个字段,会被填充对齐到前一个字段的大小,地址偏移对齐规则不变;
- 空结构体也是一个结构体,不过他的size为0,所有的空结构体内存分配都是同一个地址,都是zerobase的地址;
- 空结构体作为内嵌字段时要注意放置的顺序,当作为最后一个字段时会进行特殊填充,会被填充对齐到前一个字段的大小,地址偏移对齐规则不变;

