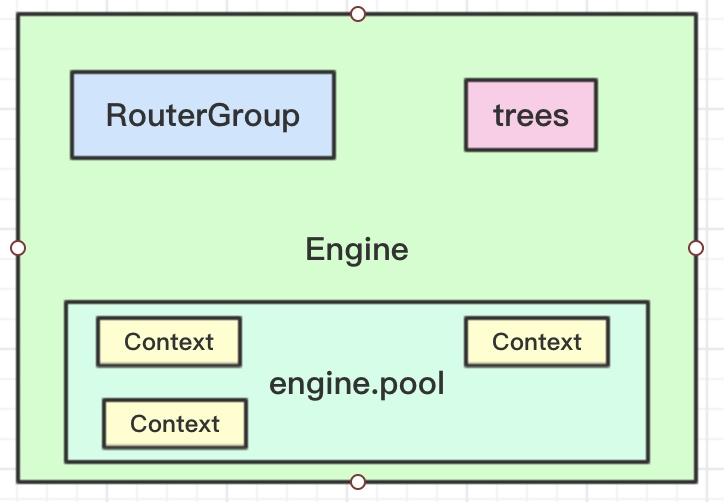
整体结构认识
路由匹配
gin框架处理请求的入口函数ServeHTTP:
// gin.gofunc (engine *Engine) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {// 这里使用了对象池c := engine.pool.Get().(*Context)// Get对象后做初始化c.writermem.reset(w)c.Request = reqc.reset()engine.handleHTTPRequest(c) // 我们要找的处理HTTP请求的函数engine.pool.Put(c) // 处理完请求后将对象放回池子}
处理 handleHTTPRequest
func (engine *Engine) handleHTTPRequest(c *Context) {httpMethod := c.Request.MethodrPath := c.Request.URL.Pathunescape := falseif engine.UseRawPath && len(c.Request.URL.RawPath) > 0 {rPath = c.Request.URL.RawPathunescape = engine.UnescapePathValues}if engine.RemoveExtraSlash {rPath = cleanPath(rPath)}// Find root of the tree for the given HTTP method// 根据请求方法找到对应的路由树t := engine.treesfor i, tl := 0, len(t); i < tl; i++ {if t[i].method != httpMethod {continue}root := t[i].root// Find route in tree 在路由树中根据path查找value := root.getValue(rPath, c.params, unescape)if value.params != nil {c.Params = *value.params}if value.handlers != nil {c.handlers = value.handlersc.fullPath = value.fullPath// 执行函数链条c.Next()c.writermem.WriteHeaderNow()return}if httpMethod != "CONNECT" && rPath != "/" {if value.tsr && engine.RedirectTrailingSlash {redirectTrailingSlash(c)return}if engine.RedirectFixedPath && redirectFixedPath(c, root, engine.RedirectFixedPath) {return}}break}if engine.HandleMethodNotAllowed {for _, tree := range engine.trees {if tree.method == httpMethod {continue}if value := tree.root.getValue(rPath, nil, unescape); value.handlers != nil {c.handlers = engine.allNoMethodserveError(c, http.StatusMethodNotAllowed, default405Body)return}}}c.handlers = engine.allNoRouteserveError(c, http.StatusNotFound, default404Body)}
路由匹配是由节点的 getValue方法实现的。getValue根据给定的路径(键)返回nodeValue值,保存注册的处理函数和匹配到的路径参数数据。
gin框架涉及中间件相关有4个常用的方法,它们分别是c.Next()、c.Abort()、c.Set()、c.Get()。
中间件的注册
gin框架中的中间件设计很巧妙,从最常用的r := gin.Default()的Default函数开始看,它内部构造一个新的engine之后就通过Use()函数注册了Logger中间件和Recovery中间件:
func Default() *Engine {debugPrintWARNINGDefault()engine := New()engine.Use(Logger(), Recovery()) // 默认注册的两个中间件return engine}
Use() 函数
func (engine *Engine) Use(middleware ...HandlerFunc) IRoutes {engine.RouterGroup.Use(middleware...) // 实际上还是调用的RouterGroup的Use函数engine.rebuild404Handlers()engine.rebuild405Handlers()return engine}
注册中间件其实就是将中间件函数追加到group.Handlers中:
// Use adds middleware to the group, see example code in GitHub.func (group *RouterGroup) Use(middleware ...HandlerFunc) IRoutes {group.Handlers = append(group.Handlers, middleware...)return group.returnObj()}
而我们注册路由时会将对应路由的函数和之前的中间件函数结合到一起:
func (group *RouterGroup) handle(httpMethod, relativePath string, handlers HandlersChain) IRoutes {absolutePath := group.calculateAbsolutePath(relativePath)handlers = group.combineHandlers(handlers) // 将处理请求的函数与中间件函数结合group.engine.addRoute(httpMethod, absolutePath, handlers)return group.returnObj()}
package mainimport "github.com/gin-gonic/gin"func main() {r := gin.Default()r.GET("/ping", func(c *gin.Context) {c.JSON(200, gin.H{"message": "success",})})r.Run() // listen and serve on 0.0.0.0:8080}
先看r.Run()
func (engine *Engine) Run(addr ...string) (err error) {defer func() { debugPrintError(err) }()address := resolveAddress(addr)debugPrint("Listening and serving HTTP on %s\n", address)err = http.ListenAndServe(address, engine)return}
https://www.haohongfan.com/post/2019-02-17-gin-01/
https://www.linkinstar.wiki/2019/08/20/golang/open-source-component/gin/