概念
AC 自动机(Aho-Corasick)算法。其实,Trie 树跟 AC 自动机之间的关系,就像单串匹配中朴素的串匹配算法,跟 KMP 算法之间的关系一样,只不过Trie 树跟 AC 自动机针对的是多模式串而已。所以,AC 自动机实际上就是在 Trie 树之上,加了类似 KMP 的 next 数组,只不过此处的 next 数组是构建在树上罢了。
所以,AC 自动机的构建,包含两个操作:
- 将多个模式串构建成 Trie 树;
- 在 Trie 树上构建失败指针(相当于 KMP 中的失效函数 next 数组)。
假设沿 Trie 树走到 p 节点,即下图中的紫色节点,那 p 的失败指针就是从 root 走到紫色节点形成的字符串 abc,跟所有模式串前缀匹配的最长可匹配后缀子串,就是箭头指的 bc 模式串。将 p 节点的失败指针指向那个最长匹配后缀子串对应的模式串的前缀的最后一个节点,就是下图中箭头指向的节点。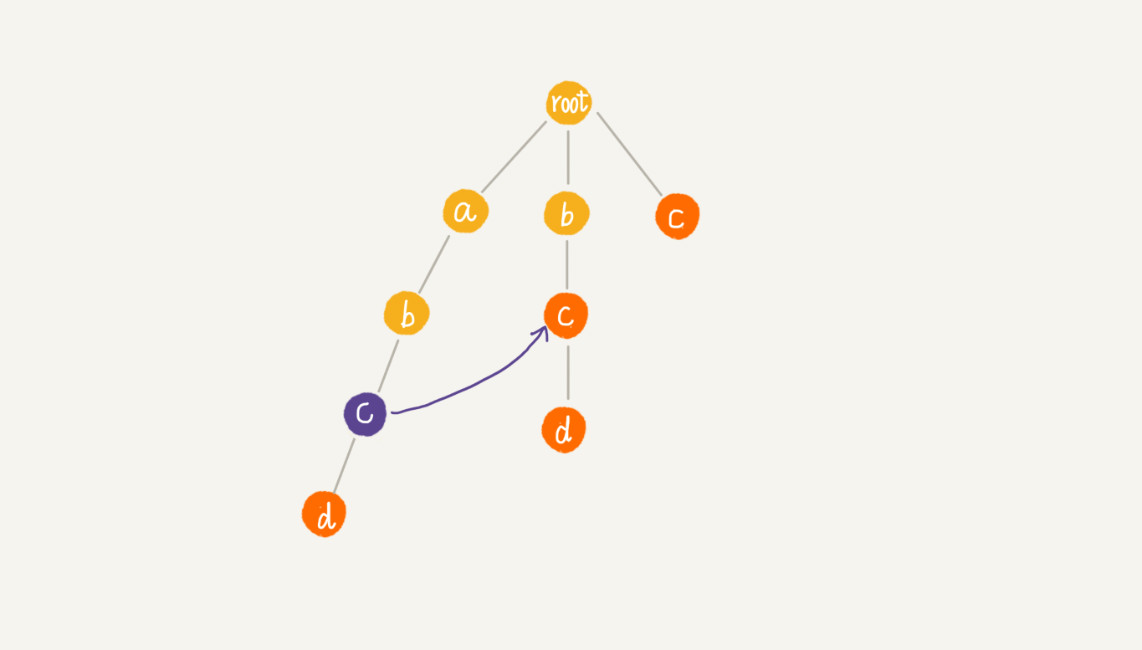
计算每个节点的失败指针这个过程看起来有些复杂。其实把树中相同深度的节点放到同一层,那么某个节点的失败指针只出现在它所在层的上一层。像 KMP 算法那样,当要求某个节点的失败指针的时候,通过已经求得的、深度更小的那些节点的失败指针来推导。即可以逐层依次来求解每个节点的失败指针。所以,失败指针的构建过程,是一个按层遍历树的过程。
首先 root 的失败指针为 NULL,也就是指向自己。当已经求得某个节点 p 的失败指针之后,如何寻找它的子节点的失败指针呢?
假设节点 p 的失败指针指向节点 q,看节点 p 的子节点 pc 对应的字符,是否也可以在节点 q 的子节点中找到。如果找到了则将节点 pc 的失败指针指向节点 qc。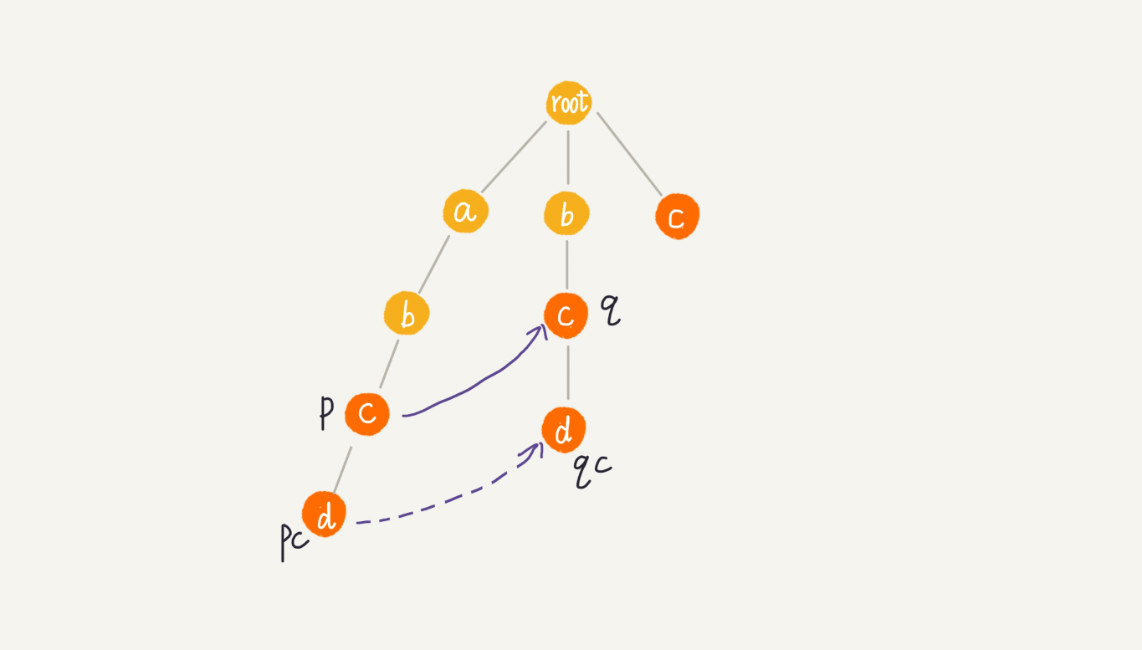
如果没找到,则令 q=q -> fail(fail 表示失败指针),继续上面的查找,直到 q 是 root 为止,如果还没有找到,就让节点 pc 的失败指针指向 root。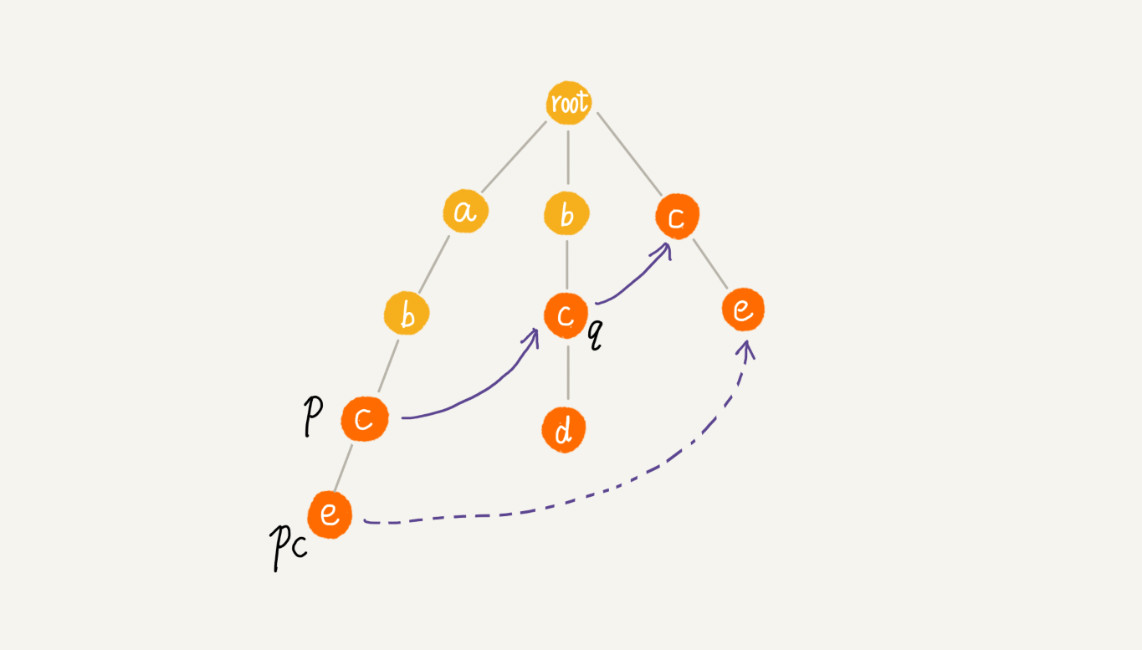
代码实现
class TrieNode {constructor(value) {this.value = value //value为单个字符this.num = 1this.deep = 0//根节点默认0this.son = []this.isEnd = false}findNode(value) {for (let i = 0; i < this.son.length; i++) {const node = this.son[i]if (node.value == value) {return node}}return null}}class Trie {constructor() {this.root = new TrieNode(null)this.size = 1//一开始的时候只有根节点这一个节点}insert(str) {let node = this.rootfor (let c of str) {let snode = node.findNode(c)if (snode == null) {snode = new TrieNode(c)snode.deep = node.deep + 1node.son.push(snode)} else {snode.num++//有N个字符串经过它}node = snode}//如果当前的node已经是一个word,则不需要添加if (!node.isEnd) {this.size++node.isEnd = true}}has(str) {let node = this.rootfor (let c of str) {const snode = node.findNode(c)if (snode) {node = snode} else {return false}}return node.isEnd}}//构建字典树失败指针function build_ac_automation(root) {root.fail = nullconst queue = [root]let i = 0while (i < queue.length) {const temp = queue[i]for (let j = 0; j < temp.son.length; j++) {const node = temp.son[j]if (temp === root) {node.fail = root} else {node.fail = temp.fail.findNode(node.value) || root}queue.push(node)}i++}}// AC算法多字符查询function acSearch(arr, str) {//生成字典树const tr = new Trie()arr.forEach(function (item) {tr.insert(item)})//构造字典树的失败指针build_ac_automation(tr.root)let node = tr.rootconst data = []for (let i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {let cnode = node.findNode(str[i])//匹配不到字符,进入失败匹配,while (!cnode && node !== tr.root) {node = node.failcnode = node.findNode(str[i])}if (cnode) {node = cnode}if (node.isEnd) {data.push({start: i + 1 - node.deep,len: node.deep,str: str.substr(i + 1 - node.deep, node.deep),num: node.num,})}}return data}// 测试const result = acSearch(['she', 'shr', 'her', 'her'], 'sher')console.log(result)/*** [ { start: 0, len: 3, str: 'she', num: 1 },{ start: 1, len: 3, str: 'her', num: 2 } ]*/
场景
实现一个高性能的敏感词过滤系统:就要用到多模式串匹配算法。
单模式与多模式区别:尽管单模式串匹配算法也能完成多模式串的匹配工作。例如通过单模式串匹配算法(比如 KMP 算法)与用户输入的文字内容进行匹配。但是每个匹配过程都需要扫描一遍用户输入的内容。整个过程下来就要扫描很多遍用户输入的内容。如果敏感词很多,比如几千个,并且用户输入的内容很长,假如有上千个字符,那就需要扫描几千遍这样的输入内容,这种处理思路比较低效。多模式匹配算法只需要扫描一遍主串,就能在主串中一次性查找多个模式串是否存在,从而大大提高匹配效率。
具体做法:可以对敏感词字典进行预处理,构建成 Trie 树结构。这个预处理的操作只需要做一次,如果敏感词字典动态更新了,比如删除、添加了一个敏感词,只需要动态更新一下 Trie 树就可以。当用户输入一个文本内容后,把用户输入的内容作为主串,从第一个字符开始,在 Trie 树中匹配。当匹配到 Trie 树的叶子节点,或者中途遇到不匹配字符的时候,将主串的开始匹配位置后移一位,重新在 Trie 树中匹配。利用AC 自动机算法对多模式串 Trie 树进行改进,进一步提高 Trie 树的效率。

