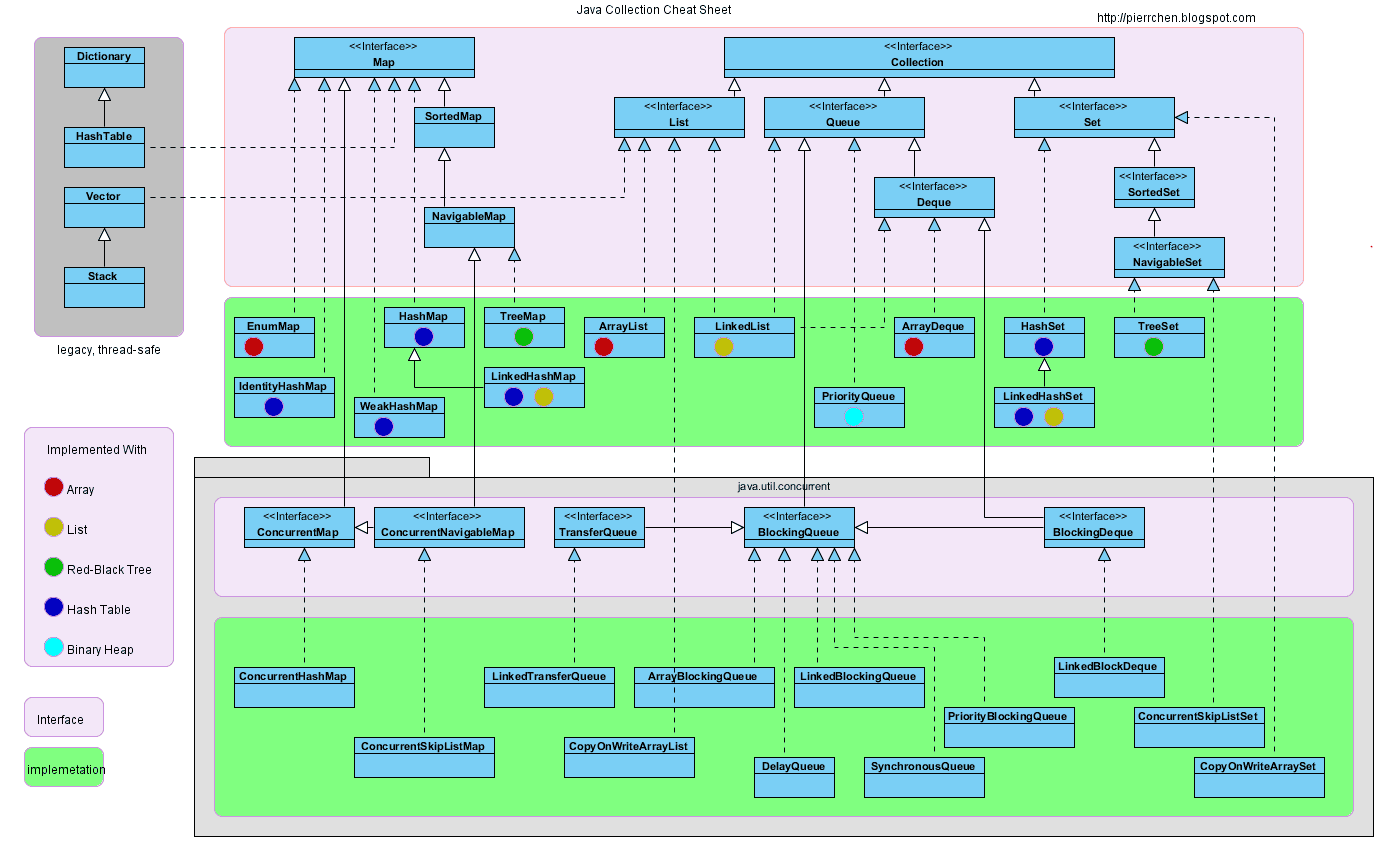
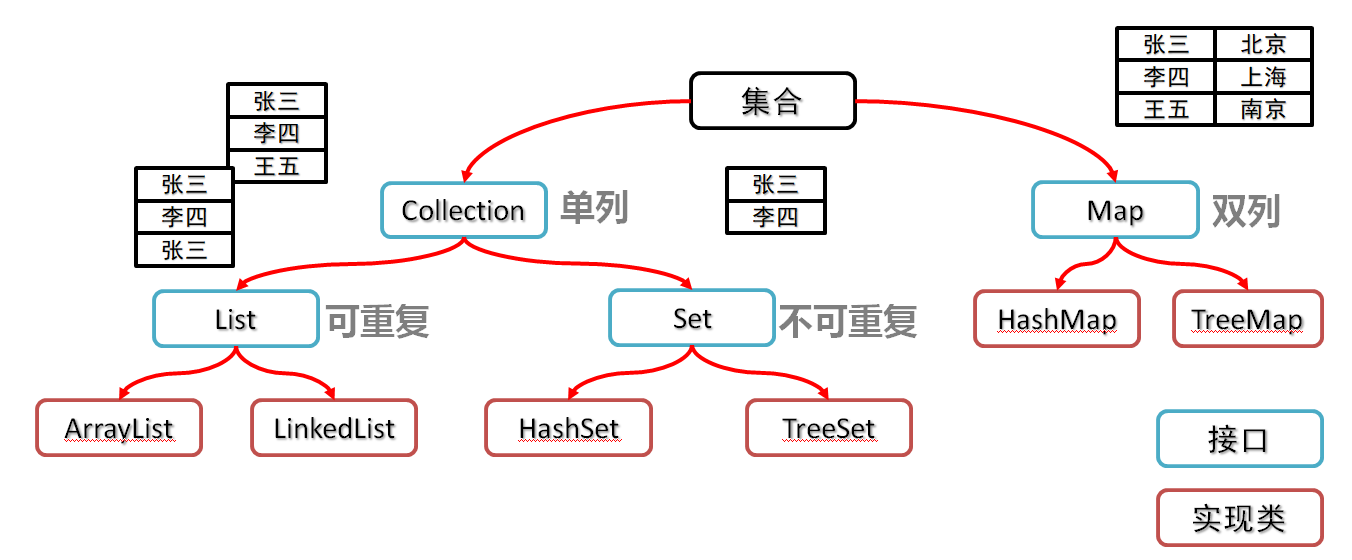
Collection
Collection常见的方法
- Collection集合概述
- 是单例集合的顶层接口,它表示一组对象,这些对象也称为Collection的元素
- JDK 不提供此接口的任何直接实现.它提供更具体的子接口(如Set和List)实现
- 创建Collection集合的对象
- 多态的方式
- 具体的实现类ArrayList
- Collection集合常用方法 | 方法名 | 说明 | | —- | —- | | boolean add(E e) | 添加元素 | | boolean remove(Object o) | 从集合中移除指定的元素 | | boolean removeIf(Object o) | 根据条件进行移除 | | void clear() | 清空集合中的元素 | | boolean contains(Object o) | 判断集合中是否存在指定的元素 | | boolean isEmpty() | 判断集合是否为空 | | int size() | 集合的长度,也就是集合中元素的个数 |
import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collection;public class CollectionDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) {/*注意点:Collection是一个接口,我们不能直接创建他的对象。所以,现在我们学习他的方法时,只能创建他实现类的对象。实现类:ArrayList*///目的:为了学习Collection接口里面的方法Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<>();//1.添加元素//细节1:如果我们要往List系列集合中添加数据,那么方法永远返回true,因为List系列的是允许元素重复的。//细节2:如果我们要往Set系列集合中添加数据,如果当前要添加元素不存在,方法返回true,表示添加成功。// 如果当前要添加的元素已经存在,方法返回false,表示添加失败。// 因为Set系列的集合不允许重复。coll.add("aaa");coll.add("bbb");coll.add("ccc");System.out.println(coll);//2.清空//coll.clear();//3.删除//细节1:因为Collection里面定义的是共性的方法,所以此时不能通过索引进行删除。只能通过元素的对象进行删除。//细节2:方法会有一个布尔类型的返回值,删除成功返回true,删除失败返回false//如果要删除的元素不存在,就会删除失败。System.out.println(coll.remove("aaa"));System.out.println(coll);//4.判断元素是否包含//细节:底层是依赖equals方法进行判断是否存在的。//所以,如果集合中存储的是自定义对象,也想通过contains方法来判断是否包含,那么在javabean类中,一定要重写equals方法。boolean result1 = coll.contains("bbb");System.out.println(result1);//5.判断集合是否为空boolean result2 = coll.isEmpty();System.out.println(result2);//false//6.获取集合的长度coll.add("ddd");int size = coll.size();System.out.println(size);//3}}
Collection集合的遍历
迭代器遍历
迭代器介绍
//迭代器,集合的专用遍历方式Iterator<E> iterator(): 返回此集合中元素的迭代器,通过集合对象的iterator()方法得到
Iterator中的常用方法
boolean hasNext(): 判断当前位置是否有元素可以被取出E next(): 获取当前位置的元素,将迭代器对象移向下一个索引位置
Collection集合的遍历
public class IteratorDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建集合对象Collection<String> c = new ArrayList<>();//添加元素c.add("hello");c.add("world");c.add("java");c.add("javaee");//Iterator<E> iterator():返回此集合中元素的迭代器,通过集合的iterator()方法得到Iterator<String> it = c.iterator();//用while循环改进元素的判断和获取while (it.hasNext()) {String s = it.next();System.out.println(s);}}}
迭代器中删除的方法
void remove(): 删除迭代器对象当前指向的元素public class IteratorDemo2 {public static void main(String[] args) {ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add("a");list.add("b");list.add("b");list.add("c");list.add("d");Iterator<String> it = list.iterator();while(it.hasNext()){String s = it.next();if("b".equals(s)){//指向谁,那么此时就删除谁.it.remove();}}System.out.println(list);}}
迭代器的四个细节
如果当前位置没有元素,还要强行获取,会报NoSuchElementException
- 迭代器遍历完毕,指针不会复位
- 循环中只能用一次next方法
-
增强for循环
介绍
- 它是JDK5之后出现的,其内部原理是一个Iterator迭代器
- 实现Iterable接口的类才可以使用迭代器和增强for
- 简化数组和Collection集合的遍历
格式
```java for(集合/数组中元素的数据类型 变量名 : 集合/数组名) {// 已经将当前遍历到的元素封装到变量中了,直接使用变量即可
}
```javapublic class MyCollectonDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) {ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add("a");list.add("b");list.add("c");list.add("d");list.add("e");list.add("f");//1,数据类型一定是集合或者数组中元素的类型//2,str仅仅是一个变量名而已,在循环的过程中,依次表示集合或者数组中的每一个元素//3,list就是要遍历的集合或者数组for(String str : list){System.out.println(str);}}}
lambda表达式遍历
package com.itheima.a01mycollection;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collection;public class CollectionDemo7 {public static void main(String[] args) {/*lambda表达式遍历:default void forEach(Consumer<? super T> action):*///1.创建集合并添加元素Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<>();coll.add("zhangsan");coll.add("lisi");coll.add("wangwu");//2.利用匿名内部类的形式//底层原理://其实也会自己遍历集合,依次得到每一个元素//把得到的每一个元素,传递给下面的accept方法//s依次表示集合中的每一个数据/* coll.forEach(new Consumer<String>() {@Overridepublic void accept(String s) {System.out.println(s);}});*///lambda表达式coll.forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));}}
List集合的特有方法
- List集合的特点
- 存取有序
- 可以重复
- 有索引
方法介绍 | 方法名 | 描述 | | —- | —- | | void add(int index,E element) | 在此集合中的指定位置插入指定的元素 | | E remove(int index) | 删除指定索引处的元素,返回被删除的元素 | | E set(int index,E element) | 修改指定索引处的元素,返回被修改的元素 | | E get(int index) | 返回指定索引处的元素 |
示例代码
public class MyListDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add("aaa");list.add("bbb");list.add("ccc");//method1(list);//method2(list);//method3(list);//method4(list);}private static void method4(List<String> list) {// E get(int index) 返回指定索引处的元素String s = list.get(0);System.out.println(s);}private static void method3(List<String> list) {// E set(int index,E element) 修改指定索引处的元素,返回被修改的元素//被替换的那个元素,在集合中就不存在了.String result = list.set(0, "qqq");System.out.println(result);System.out.println(list);}private static void method2(List<String> list) {// E remove(int index) 删除指定索引处的元素,返回被删除的元素//在List集合中有两个删除的方法//第一个 删除指定的元素,返回值表示当前元素是否删除成功//第二个 删除指定索引的元素,返回值表示实际删除的元素String s = list.remove(0);System.out.println(s);System.out.println(list);}private static void method1(List<String> list) {// void add(int index,E element) 在此集合中的指定位置插入指定的元素//原来位置上的元素往后挪一个索引.list.add(0,"qqq");System.out.println(list);}}
List集合的实现类
List集合子类的特点
ArrayList集合 底层是数组结构实现,查询快、增删慢
- LinkedList集合 底层是链表结构实现,查询慢、增删快
LinkedList集合的特有功能
- 特有方法 | 方法名 | 说明 | | —- | —- | | public void addFirst(E e) | 在该列表开头插入指定的元素 | | public void addLast(E e) | 将指定的元素追加到此列表的末尾 | | public E getFirst() | 返回此列表中的第一个元素 | | public E getLast() | 返回此列表中的最后一个元素 | | public E removeFirst() | 从此列表中删除并返回第一个元素 | | public E removeLast() | 从此列表中删除并返回最后一个元素 |
public class MyLinkedListDemo4 {public static void main(String[] args) {LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList<>();list.add("aaa");list.add("bbb");list.add("ccc");// public void addFirst(E e) 在该列表开头插入指定的元素//method1(list);// public void addLast(E e) 将指定的元素追加到此列表的末尾//method2(list);// public E getFirst() 返回此列表中的第一个元素// public E getLast() 返回此列表中的最后一个元素//method3(list);// public E removeFirst() 从此列表中删除并返回第一个元素// public E removeLast() 从此列表中删除并返回最后一个元素//method4(list);}private static void method4(LinkedList<String> list) {String first = list.removeFirst();System.out.println(first);String last = list.removeLast();System.out.println(last);System.out.println(list);}private static void method3(LinkedList<String> list) {String first = list.getFirst();String last = list.getLast();System.out.println(first);System.out.println(last);}private static void method2(LinkedList<String> list) {list.addLast("www");System.out.println(list);}private static void method1(LinkedList<String> list) {list.addFirst("qqq");System.out.println(list);}}
Set集合
特点
- 不可以存储重复元素
- 没有索引,不能使用普通for循环遍历
Set集合的使用
public class MySet1 {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建集合对象Set<String> set = new TreeSet<>();//添加元素set.add("ccc");set.add("aaa");set.add("aaa");set.add("bbb");// for (int i = 0; i < set.size(); i++) {// //Set集合是没有索引的,所以不能使用通过索引获取元素的方法// }//遍历集合Iterator<String> it = set.iterator();while (it.hasNext()){String s = it.next();System.out.println(s);}System.out.println("-----------------------------------");for (String s : set) {System.out.println(s);}}}
TreeSet集合
TreeSet集合概述和特点
- 不可以存储重复元素
- 没有索引
可以将元素按照规则进行排序
- TreeSet():根据其元素的自然排序进行排序
TreeSet(Comparator comparator) :根据指定的比较器进行排序
TreeSet集合基本使用
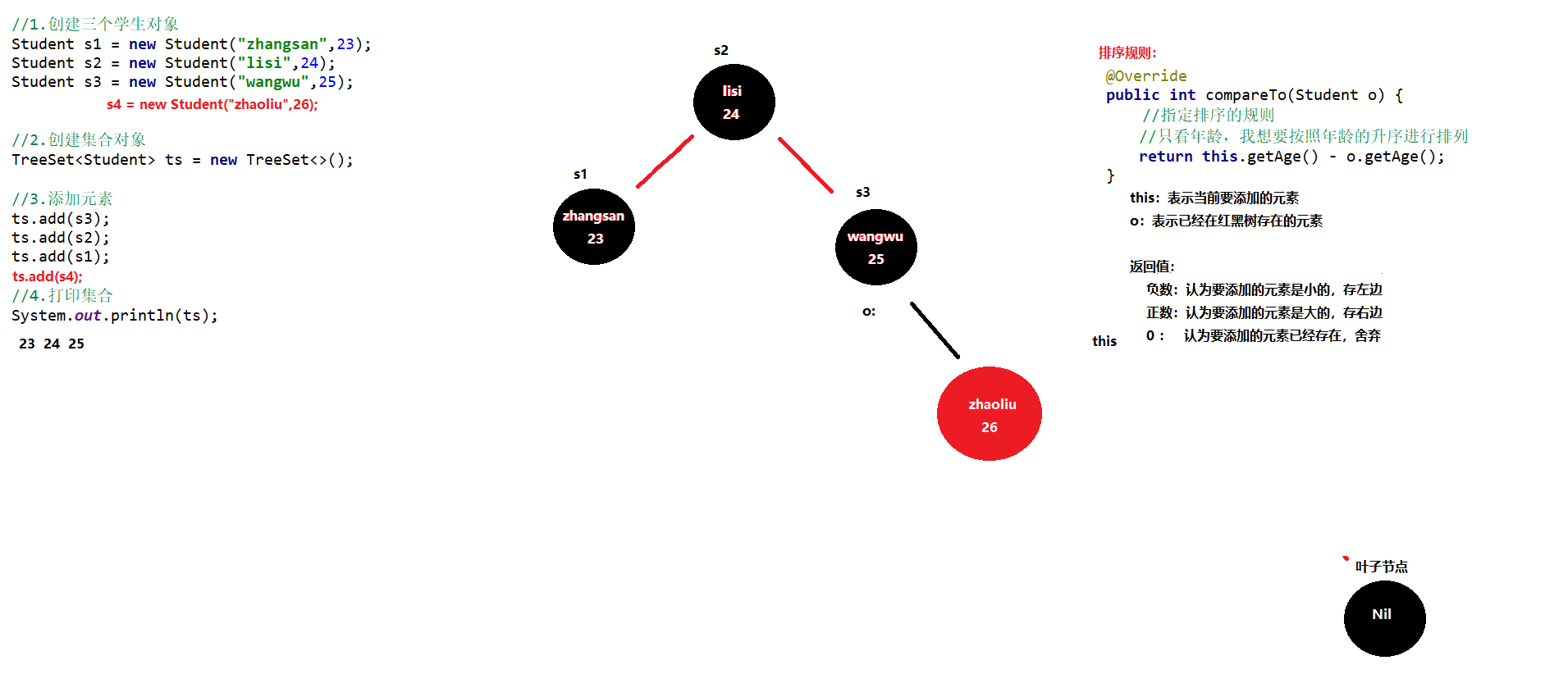
public class TreeSetDemo01 {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建集合对象TreeSet<Integer> ts = new TreeSet<Integer>();//添加元素ts.add(10);ts.add(40);ts.add(30);ts.add(50);ts.add(20);ts.add(30);//遍历集合for(Integer i : ts) {System.out.println(i);}}}
自然排序Comparable的使用
案例需求
- 存储学生对象并遍历,创建TreeSet集合使用无参构造方法
- 要求:按照年龄从小到大排序,年龄相同时,按照姓名的字母顺序排序
实现步骤
- 使用空参构造创建TreeSet集合
- 用TreeSet集合存储自定义对象,无参构造方法使用的是自然排序对元素进行排序的
- 自定义的Student类实现Comparable接口
- 自然排序,就是让元素所属的类实现Comparable接口,重写compareTo(T o)方法
重写接口中的compareTo方法
- 重写方法时,一定要注意排序规则必须按照要求的主要条件和次要条件来写
```java
public class Student implements Comparable
{ private String name; private int age;
public Student() { }
public Student(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; }
public String getName() { return name; }
public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; }
public int getAge() { return age; }
public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; }
@Override public String toString() { return “Student{“ +
"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';
}
@Override public int compareTo(Student o) { //按照对象的年龄进行排序 //主要判断条件: 按照年龄从小到大排序 int result = this.age - o.age; //次要判断条件: 年龄相同时,按照姓名的字母顺序排序 result = result == 0 ? this.name.compareTo(o.getName()) : result; return result; } }
```javapublic class MyTreeSet2 {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建集合对象TreeSet<Student> ts = new TreeSet<>();//创建学生对象Student s1 = new Student("zhangsan",28);Student s2 = new Student("lisi",27);Student s3 = new Student("wangwu",29);Student s4 = new Student("zhaoliu",28);Student s5 = new Student("qianqi",30);//把学生添加到集合ts.add(s1);ts.add(s2);ts.add(s3);ts.add(s4);ts.add(s5);//遍历集合for (Student student : ts) {System.out.println(student);}}}
比较器排序Comparator的使用
- 重写方法时,一定要注意排序规则必须按照要求的主要条件和次要条件来写
```java
public class Student implements Comparable
- 使用空参构造创建TreeSet集合
案例需求
- 存储老师对象并遍历,创建TreeSet集合使用带参构造方法
- 要求:按照年龄从小到大排序,年龄相同时,按照姓名的字母顺序排序
- 实现步骤
- 用TreeSet集合存储自定义对象,带参构造方法使用的是比较器排序对元素进行排序的
- 比较器排序,就是让集合构造方法接收Comparator的实现类对象,重写compare(T o1,T o2)方法
- 重写方法时,一定要注意排序规则必须按照要求的主要条件和次要条件来写
代码实现
public class Teacher {private String name;private int age;public Teacher() {}public Teacher(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Teacher{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}}
public class MyTreeSet4 {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建集合对象TreeSet<Teacher> ts = new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<Teacher>() {@Overridepublic int compare(Teacher o1, Teacher o2) {//o1表示现在要存入的那个元素//o2表示已经存入到集合中的元素//主要条件int result = o1.getAge() - o2.getAge();//次要条件result = result == 0 ? o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName()) : result;return result;}});//创建老师对象Teacher t1 = new Teacher("zhangsan",23);Teacher t2 = new Teacher("lisi",22);Teacher t3 = new Teacher("wangwu",24);Teacher t4 = new Teacher("zhaoliu",24);//把老师添加到集合ts.add(t1);ts.add(t2);ts.add(t3);ts.add(t4);//遍历集合for (Teacher teacher : ts) {System.out.println(teacher);}}}
比较
两种比较方式小结
- 自然排序: 自定义类实现Comparable接口,重写compareTo方法,根据返回值进行排序
- 比较器排序: 创建TreeSet对象的时候传递Comparator的实现类对象,重写compare方法,根据返回值进行排序
- 在使用的时候,默认使用自然排序,当自然排序不满足现在的需求时,必须使用比较器排序
两种方式中关于返回值的规则
底层数据结构是哈希表
- 存取无序
- 不可以存储重复元素
没有索引,不能使用普通for循环遍历
public class HashSetDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建集合对象HashSet<String> set = new HashSet<String>();//添加元素set.add("hello");set.add("world");set.add("java");//不包含重复元素的集合set.add("world");//遍历for(String s : set) {System.out.println(s);}}}
案例需求
- 创建一个存储学生对象的集合,存储多个学生对象,使用程序实现在控制台遍历该集合
- 要求:学生对象的成员变量值相同,我们就认为是同一个对象
代码实现
public class Student {private String name;private int age;public Student() {}public Student(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object o) {if (this == o) return true;if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;Student student = (Student) o;if (age != student.age) return false;return name != null ? name.equals(student.name) : student.name == null;}@Overridepublic int hashCode() {int result = name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0;result = 31 * result + age;return result;}}
public class HashSetDemo02 {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建HashSet集合对象HashSet<Student> hs = new HashSet<Student>();//创建学生对象Student s1 = new Student("林青霞", 30);Student s2 = new Student("张曼玉", 35);Student s3 = new Student("王祖贤", 33);Student s4 = new Student("王祖贤", 33);//把学生添加到集合hs.add(s1);hs.add(s2);hs.add(s3);hs.add(s4);//遍历集合(增强for)for (Student s : hs) {System.out.println(s.getName() + "," + s.getAge());}}}
总结 HashSet集合存储自定义类型元素,要想实现元素的唯一,要求必须重写hashCode方法和equals方法