1.定义
用于存放已被加载的类信息、常量、静态变量、即时编译器编译后的代码等数据。
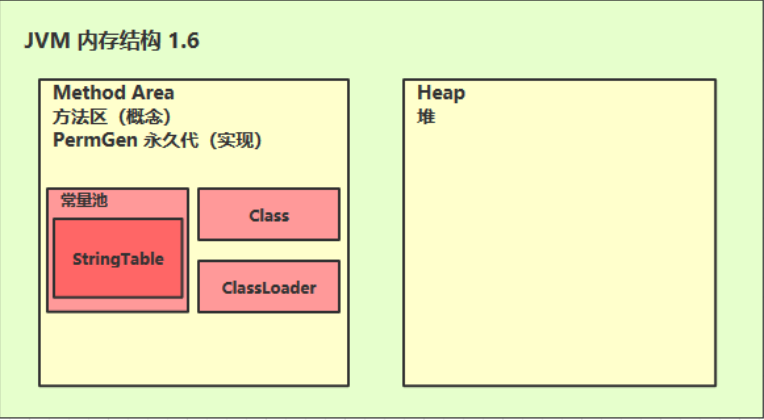
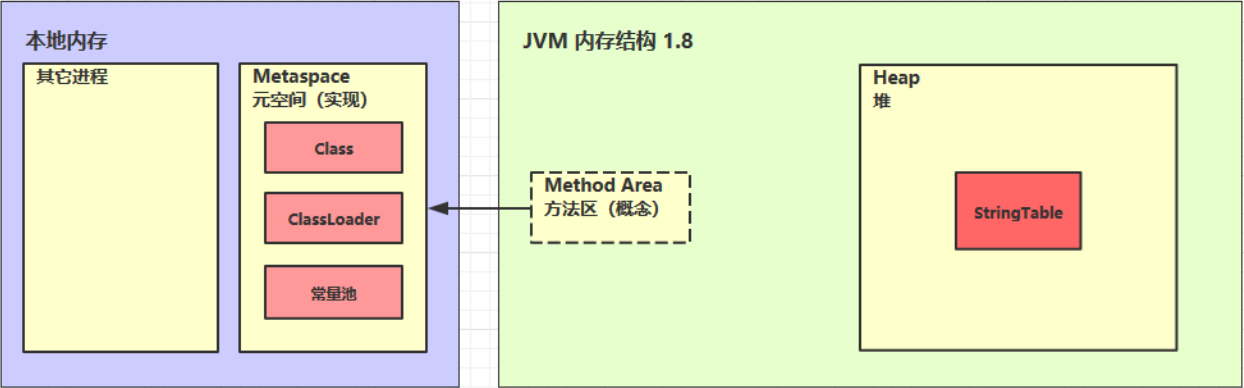
2.结构
- 永久代用的堆内存
- 元空间用的本地内存
3.方法区内存溢出
- 1.8以前会导致永久代内存溢出java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: PermGen space
- 1.8以后会导致元空间内存溢出java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Metaspace
一般情况下元空间不会导致内存溢出,因为他是在本地内存当中的
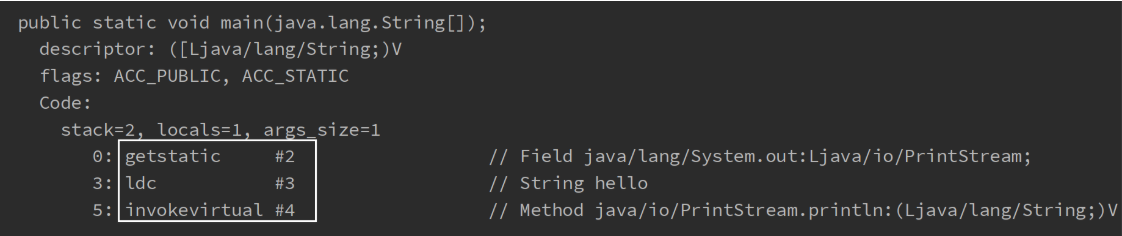
4.常量池
- 类的基本信息
- 常量池
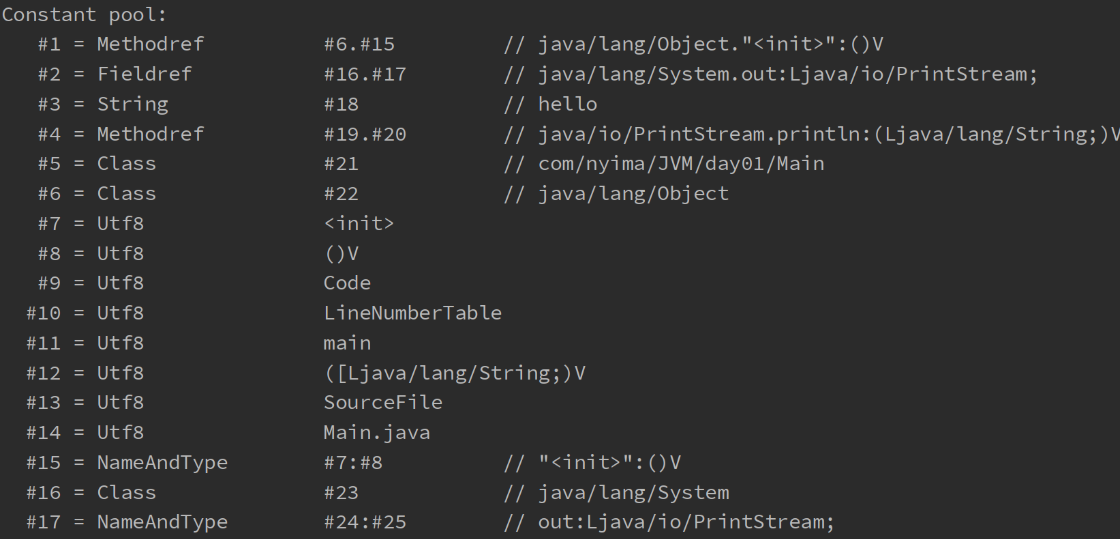
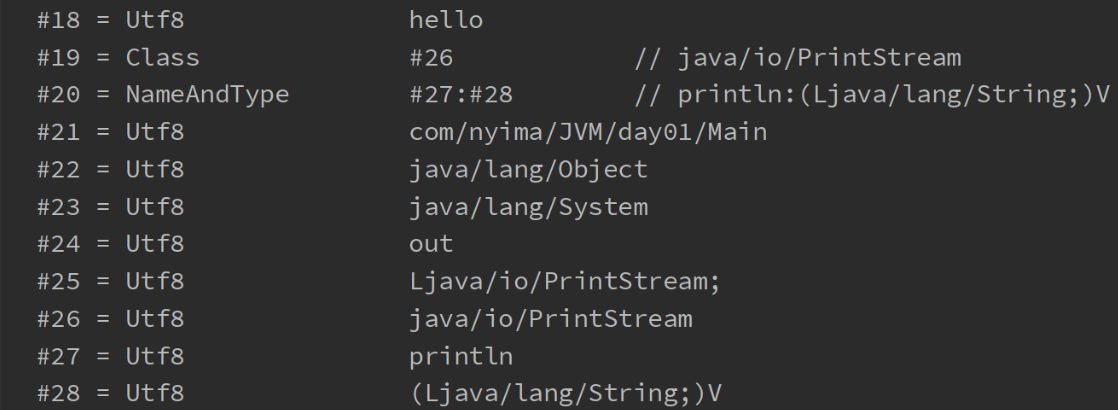
- 虚拟机中执行编译的方法(框内的是真正编译执行的内容,#号的内容需要在常量池中查找)
5.运行时常量池
- 常量池:就是一张表,虚拟机指令根据这张常量表找到要执行的类名、方法名、参数类型、字面量等信息
- 运行时常量池:常量池是 *.class 文件中的,当该类被加载,它的常量池信息就会放入运行时常量池,并把里面的符号地址变为真实地址
StringTable
例子1
- 常量池中的字符串仅是符号,只有在被用到时才会转化为对象
- 利用串池的机制,来避免重复创建字符串对象
常量池中的信息,都会被加载到运行时常量池中,但这是a b ab 仅是常量池中的符号,还没有成为java字符串public class StringTableStudy {public static void main(String[] args) {String a = "a";String b = "b";String ab = "ab";}}
当执行到 ldc #2 时,会把符号 a 变为 “a” 字符串对象,并放入串池中(hashtable结构 不可扩容)0: ldc #2 // String a2: astore_13: ldc #3 // String b5: astore_26: ldc #4 // String ab8: astore_39: return
当执行到 ldc #3 时,会把符号 b 变为 “b” 字符串对象,并放入串池中
当执行到 ldc #4 时,会把符号 ab 变为 “ab” 字符串对象,并放入串池中
最终StringTable [“a”, “b”, “ab”]
注意:字符串对象的创建都是懒惰的,只有当运行到那一行字符串且在串池中不存在的时候(如 ldc #2)时,该字符串才会被创建并放入串池中。
例子2:
使用拼接字符串变量创建字符串的过程
public class HelloWorld {public static void main(String[] args) {String s1 = "a";String s2 = "b";String s3 = "ab";String s4=s1+s2;//new StringBuilder().append("a").append("b").toString() new String("ab")System.out.println(s3==s4);//false//结果为false,因为s3是存在于串池之中,s4是由StringBuffer的toString方法所返回的一个对象,存在于堆内存之中}}
反编译后的结果
Code:stack=2, locals=5, args_size=10: ldc #2 // String a2: astore_13: ldc #3 // String b5: astore_26: ldc #4 // String ab8: astore_39: new #5 // class java/lang/StringBuilder12: dup13: invokespecial #6 // Method java/lang/StringBuilder."<init>":()V16: aload_117: invokevirtual #7 // Method java/lang/StringBuilder.append:(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/StringBuilder;20: aload_221: invokevirtual #7 // Method java/lang/StringBuilder.append:(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/StringBuilder;24: invokevirtual #8 // Method java/lang/StringBuilder.toString:()Ljava/lang/String;27: astore 429: return
通过拼接的方式来创建字符串的过程是:StringBuilder().append(“a”).append(“b”).toString()
最后的toString方法的返回值是一个新的字符串,但字符串的值和拼接的字符串一致,但是两个不同的字符串,一个存在于串池之中,一个存在于堆内存之中
例子3:
使用拼接字符串常量的方法创建字符串
public class HelloWorld {public static void main(String[] args) {String s1 = "a";String s2 = "b";String s3 = "ab";String s4=s1+s2;//new StringBuilder().a|ppend("a").append("2").toString() new String("ab")String s5="a"+"b";System.out.println(s5==s3);//true}}
反编译后的结果
Code:stack=2, locals=6, args_size=10: ldc #2 // String a2: astore_13: ldc #3 // String b5: astore_26: ldc #4 // String ab8: astore_39: new #5 // class java/lang/StringBuilder12: dup13: invokespecial #6 // Method java/lang/StringBuilder."<init>":()V16: aload_117: invokevirtual #7 // Method java/lang/StringBuilder.append:(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/StringBuilder;20: aload_221: invokevirtual #7 // Method java/lang/StringBuilder.append:(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/StringBuilder;24: invokevirtual #8 // Method java/lang/StringBuilder.toString:()Ljava/lang/String;27: astore 4//ab3初始化时直接从串池中获取字符串29: ldc #4 // String ab31: astore 533: return
使用拼接字符串常量的方法来创建新的字符串时,因为内容是常量,javac在编译期会进行优化,结果已在编译期确定为ab,而创建ab的时候已经在串池中放入了“ab”,所以s5直接从串池中获取值,所以进行的操作和 s3= “ab” 一致。
使用拼接字符串变量的方法来创建新的字符串时,因为内容是变量,只能在运行期确定它的值,所以需要使用StringBuilder来创建
intern方法 1.8
调用字符串对象的intern方法,会将该字符串对象尝试放入到串池中
- 如果串池中没有该字符串对象,则放入成功
- 如果有该字符串对象,则放入失败
无论放入是否成功,都会返回串池中的字符串对象
例子:(分析)
public class HelloWorld {//["a","b"]public static void main(String[] args) {String s = new String("a") + new String("b");// new String("a") new String("b") new String("ab") 注意字符串常量池中是没有"ab"的}}
例子:
public class HelloWorld {public static void main(String[] args) {String x = "ab";String s = new String("a") + new String("b");String s2 = s.intern();//将这个字符串对象尝试放入串池,如果有则并不会放入,如果没有则放入串池,这两种情况都会把串池中的对象返回System.out.println(s2 == x);//trueSystem.out.println(s == x);//false}}
intern方法 1.6:
调用字符串对象的intern方法,会将该字符串对象尝试放入到串池中
- 如果串池中没有该字符串对象,会将该字符串对象复制一份,再放入到串池中
- 如果有该字符串对象,则放入失败
无论放入是否成功,都会返回串池中的字符串对象
面试题(1.8)
package com.itcast.itheima.xpp;public class main {public static void main(String[] args) {String s1="a";String s2="b";String s3="a"+"b";String s4=s1+s2;String s5="ab";String s6=s4.intern();System.out.println(s3==s4);//falseSystem.out.println(s3==s5);//trueSystem.out.println(s3==s6);//trueString x2=new String("c")+new String("d");String x1="cd";x2.intern();System.out.println(x1==x2);//falseString x4=new String("e")+new String("f");x4.intern();String x3="ef";System.out.println(x3==x4);//true}}
6.StringTable垃圾回收
StringTable中的字符串常量不再引用后,也会被垃圾回收。
-Xmx10m 指定堆内存大小
-XX:+PrintStringTableStatistics 打印字符串常量池信息
-XX:+PrintGCDetails
-verbose:gc 打印 gc 的次数,耗费时间等信息
/*** 演示 StringTable 垃圾回收* -Xmx10m -XX:+PrintStringTableStatistics -XX:+PrintGCDetails -verbose:gc*/public class Demo1_23 {public static void main(String[] args) {int i = 0;try {} catch (Throwable e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {System.out.println(i);}}}
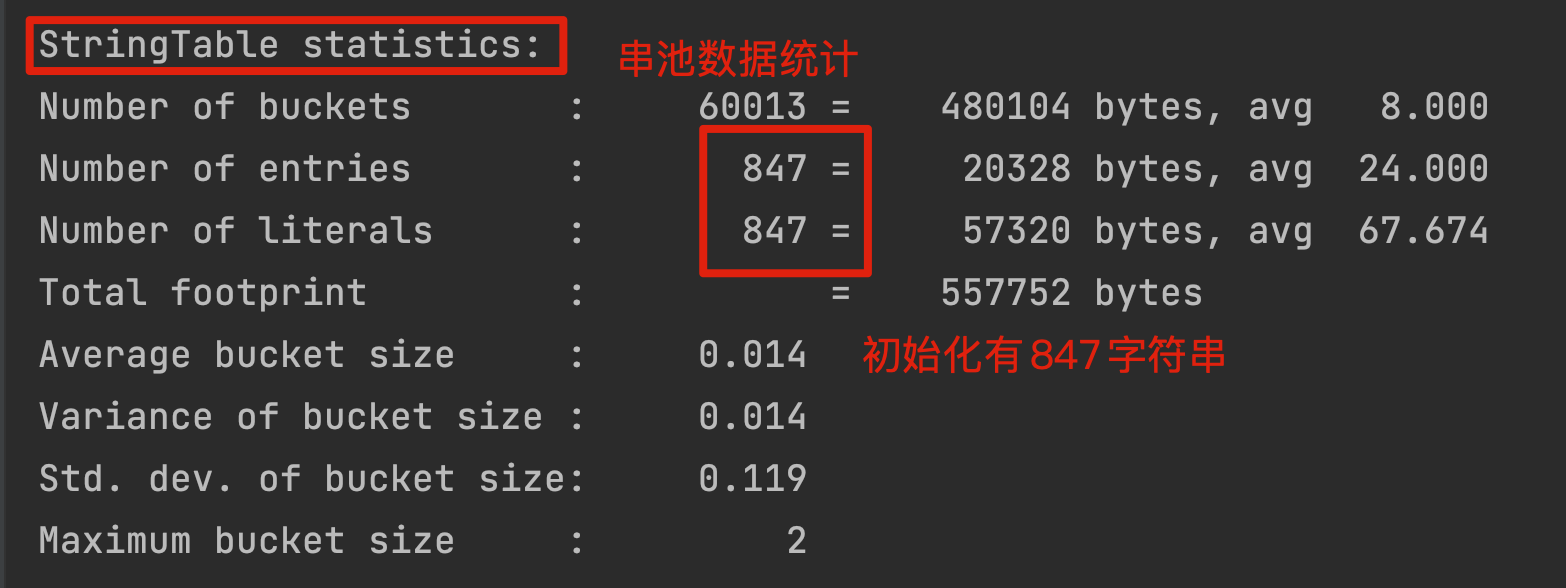
public class Demo1_23 {public static void main(String[] args) {int i = 0;try {for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {String.valueOf(j).intern();i++;}} catch (Throwable e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {System.out.println(i);}}}
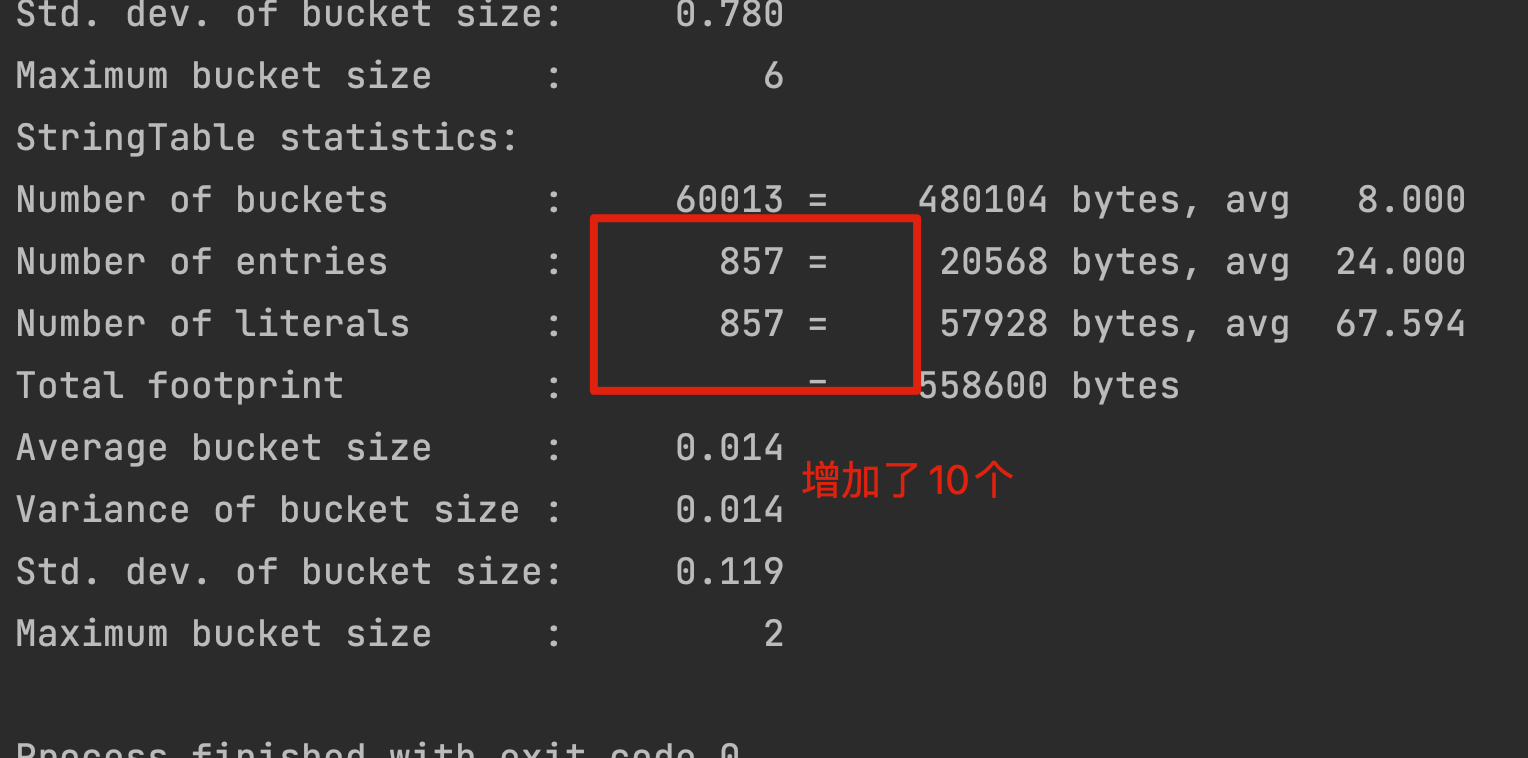
for (int j = 0; j < 100000; j++) {String.valueOf(j).intern();i++;}
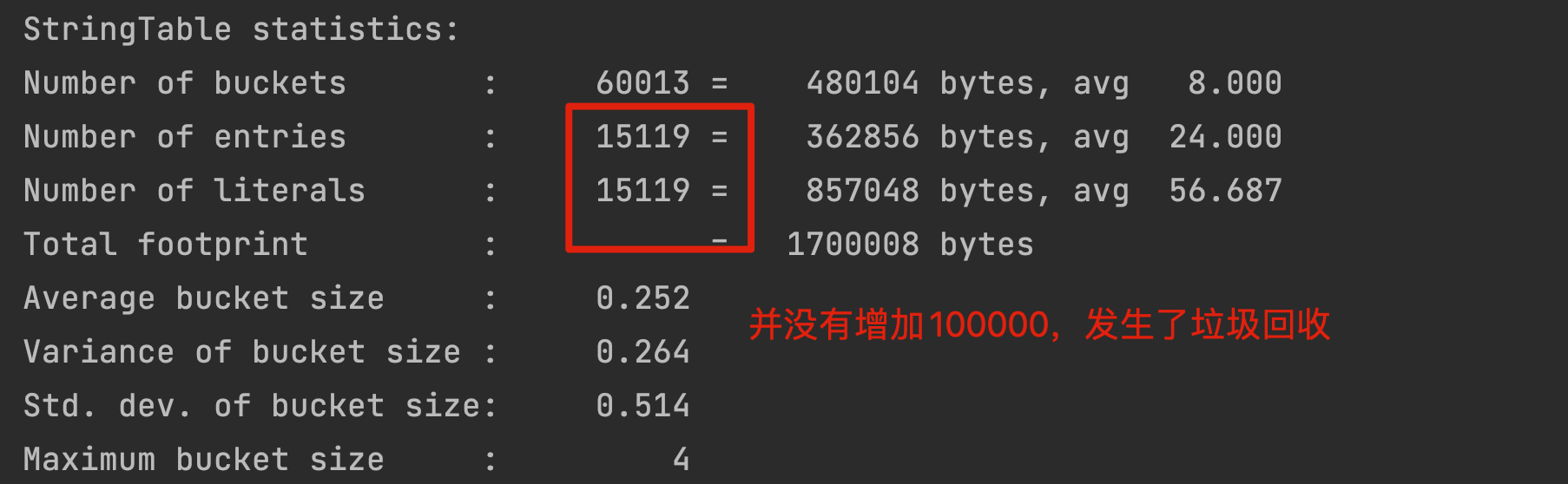
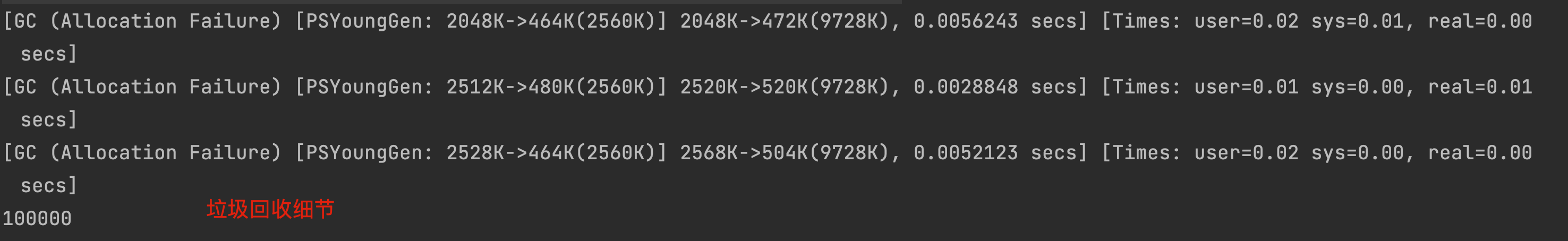 [
[
清理了一些未引用的字符串常量。
](https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45966440/article/details/120824295)
7.StringTable性能调优
- 调整 -XX:StringTableSize=桶个数
- 考虑是否将字符串对象放入池中,即用intern
参数调优
StringTable的数据结构实现是哈希表,调优即对哈希表的桶的个数的调整。
jvm 参数
-XX:StringTableSize=1009
*** 演示串池大小对性能的影响* -Xms500m -Xmx500m -XX:+PrintStringTableStatistics -XX:StringTableSize=1009*/public class Demo1_24 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("linux.words"), "utf-8"))) {String line = null;long start = System.nanoTime();while (true) {line = reader.readLine();if (line == null) {break;}line.intern(); //入池}System.out.println("cost:" + (System.nanoTime() - start) / 1000000);}}}
由于入池时候会先去查找StringTable中有无这个字符串,hash表的的寻找,桶个数越多越快。
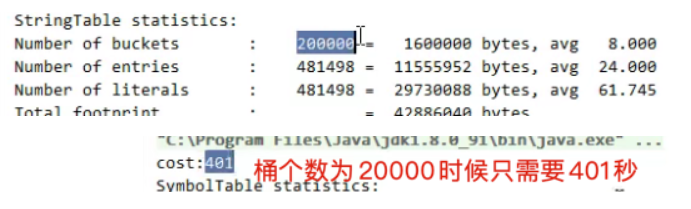
当桶个数为1009时,耗费12097毫秒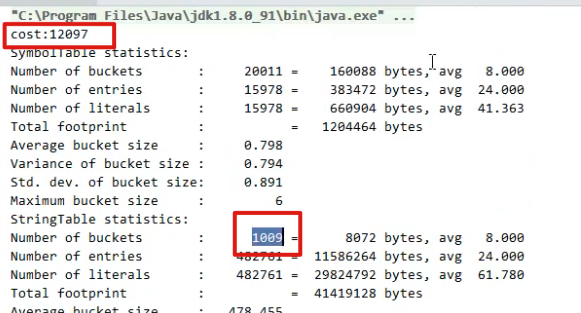
实习生调优
当有大量的重复的字符串的时候,考虑加入到串池。 ```java /**
- 演示 intern 减少内存占用
- -XX:StringTableSize=200000 -XX:+PrintStringTableStatistics
-Xsx500m -Xmx500m -XX:+PrintStringTableStatistics -XX:StringTableSize=200000 */ public class Demo1_25 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
List<String> address = new ArrayList<>();System.in.read();// 按回车进行下面的程序for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { //实现重复数据添加try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("linux.words"), "utf-8"))) {String line = null;long start = System.nanoTime();while (true) {line = reader.readLine();if(line == null) {break;}// address.add(line); 这样会把字符串全部加入到堆中address.add(line.intern()); //重复的字符串加入不了串池(1-9),会被垃圾收回}System.out.println("cost:" +(System.nanoTime()-start)/1000000);}}System.in.read();/ 按回车进行下面的程序
} }
```
[
](https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45966440/article/details/120824295)
[
](https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45966440/article/details/120824295)