搜索查询
全文查询
如果查询日期(date)或整数(integer)字段,会将查询字符串分别作为日期或整数对待。
如果查询一个未分析的(not_analyzed)精确值字符串字段,会将查询字符串作为单个词项对待。
但如果要查询一个已分析的(analyzed)全文字段,会将查询字符串传递到一个合适的分析器,然后生成一个供查询的词项列表。
- query_string:query 支持紧凑的 Lucene 查询字符串语法。
- match_query:用于执行全文查询的标准查询,包括模糊匹配和短语或邻近查询。
- match_phrase:query 像匹配查询一样,但用于匹配确切的短语或单词接近度匹配。
-
querystring 语法
全文检索:
GET /school/_search?q=zhangsan
单字段全文索引:
- GET /school/_search?q=name:zhangsan
单字段精确检索:
- GET /school/_search?q=mark:”good day”
多个检索条件的组合:
- GET /school/_search?q=name:(“zhangsan” OR “lisi”) AND NOT course:spring
字段是否存在:
- GET /school/search?q=_exists:mark
- GET /school/search?q=NOT _exists:mark
通配符,用 ? 表示单字母,* 表示任意字母:
- GET /school/_search?q=name:zh???san
GET /school/_search?q=name:zh*san
正则搜索
用 / / 包裹。ES 中正则性能不高,尽量不用。
保留转义字符:. ? + | { } [ ] “ \ # @ & < > ~。转义字符用 \,例如 \、\。GET /school/_search?q=name:/zh.*san
GET /school/_search?q=name:/zh…san(三个字符)
match_all 搜索查询
空查询,查询该索引下的所有文档:
GET school/_search
{
“query”: {
“match_all”: {}
}
}
不匹配任何文档:
GET school/_search
{
“query”: {
“match_none”: {}
}
}match 匹配查询
GET school/_search
{
“query”: {
“match”: {
“mark”: “Day” // 检查字段类型;分析查询字符串->”day”
}
}
}
match 匹配查询步骤:检查字段类型
- 分析查询字符串
- 查找匹配文档
-
match 多词匹配查询
多词匹配:
GET school/_search
{
“query”: {
“match”: {
// 分析后 包含 good 或 day
“mark”: “good day”
}
}
}
提高精度:
GET school/_search
{
“query”: {
“match”: {
“mark”: {
// 分析后 包含 good 和 day
“query”: “good day”,
“operator”: “and”
}
}
}
}
控制精度:
GET school/_search
{
“query”: {
“match”: {
“mark”: {
// 分析后 包含 good、day、happy 中至少两个单词
“query”: “good happy day”,
“minmum_should_match”: “2”
}
}
}
}match_phrase 短语匹配
GET school/_search
{
“query”: {
“match_phrase”: {
“mark”: “good day”
}
}
}
GET school/_search
{
“query”: {
“match_phrase”: {
“mark”: {
‘query’: “good day”, // good happy day 满足条件
“slop”: 1
}
}
}
}
执行步骤: 分析查询字符串,分解成词项
- 查找匹配文档
- 只保留包含全部词项的文档,并且词项位置也相同,即 “good” 和 “day” 紧挨着
slop 指定词项间的范围,即 “good” 和 “day” 之间可以有一个词
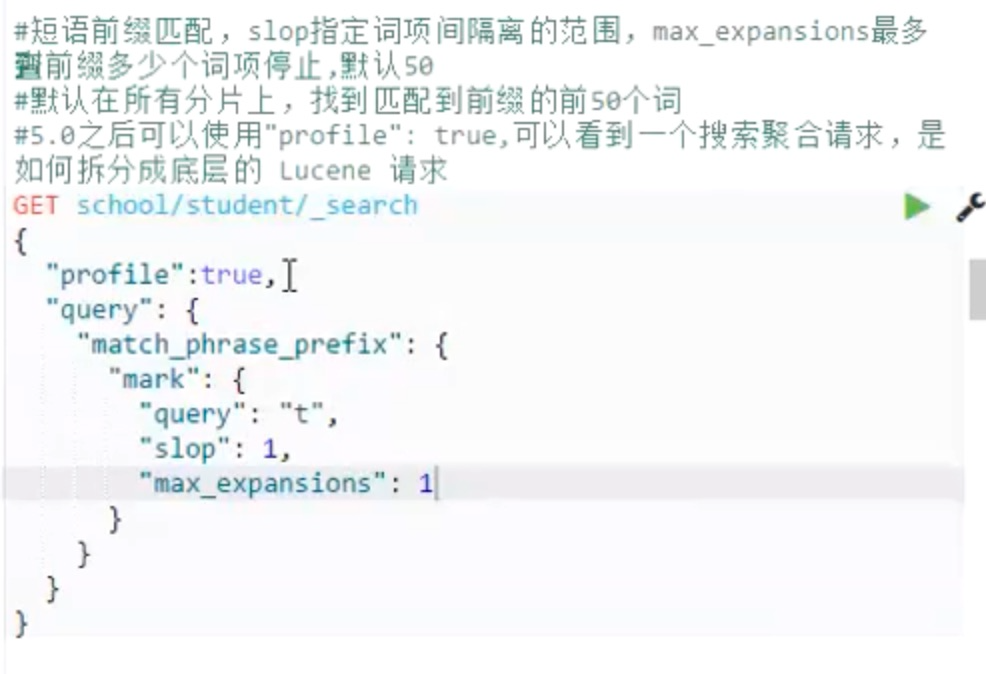
match_phrase_prefix 短语前缀匹配
GET school/_search
{
“query”: {
“match_phrase_prefix”: {
“mark”: {
‘query’: “t”,
“slop”: 1,
“max_expansions”: 50
}
}
}
}
执行步骤:分析查询字符串,查找前 50 个前缀是 t 的词项
-
multi_match 查询
GET school/_search
{
“query”: {
“multi_match”:{
“query”: “elasticsearch”,
“fields”: [“mark”, “co*”]
}
}
}
在多字段上执行 match 查询,字段名可以写通配符。term 精确查询
term 查询被用于精确值匹配,这些精确值可以使数字(number)、日期(date)、布尔值(bool)、未经分析的字符串(keyword)。
- term 查询对于输入的文本不分析,所以它将给定的值进行精确查询。
sql 中如下查询:SELECT document FROM school WHERE age=25;
对应 ES 中如下查询:
GET school/_search
{
“query”: {
“term”: {
“age”: 25
}
}
}
term 查询不需要经过查询词分析,mapping 定义中,mark 字段是 text,是经过词分析的,索引在倒排索引中没有 happy day 这个词,所以该查询查不出任何结果。
terms 查询
GET school/_search
{
“query”: {
“terms”: {
“name”: [“zhangsan”, “lisi”]
}
}
}
- terms 查询允许指定多值进行匹配。
- 如果这个字段包含了指定值中的任何一个值,那么这个文档满足条件。
和 term 查询一样,terms 查询对于输入的文本不分析。
range 范围查询
GET school/_search
{
“query”: {
“range”: {
“age”: { // 数字类型
“gte”: 20,
“lt”: 30
},
“study_date”: { // 日期类型
“gte”: “2017-01-01”,
“lte”: “2018”,
“format”: “yyyy-MM-dd||yyyy”
},
“study_date”: {
“gte”: “now-10d/d”,
“lt”: “now+1M/d”
}
}
}
}
gt 大于,gte 大于等于,lt 小于,lte 小于等于。bool 组合查询

must:所有语句都 必须(must)匹配,与 AND 等价;
- must_not:所有语句都 不能(must_not)匹配,与 NOT 等价;
- should:至少有一个语句要匹配,与 OR 等价;
查询与过滤
- 尽量使用 Filter 代替 Query
- query 搜索需要计算相关度评分并排序,无法使用缓存。
- filter 过滤无序计算相关度评分,可以使用缓存。
- 尽量使用 Bool 组合代替 AND OR
- bool 使用 must、must_not、should、filter 条件可以服用,结果保存在 bitset 中,做交集效率高。
- and / or 逐个文档处理、检查是否匹配,效率低,把选择性高的文档条件放在最前面。
=> 使用查询语句做全文本搜索或其他需要进行相关性评分,剩下的全部用过滤语句。
实例
聚合分析
每个聚合都是一个或者多个桶和零个或者多个指标的组合。
- 桶(Buckets):满足特定条件的文档的组合。
- 指标(Metrics):对桶内的文档进行统计计算。
SELECT COUNT(field) FROM table1 GROUP BY field;
指标 桶
聚合语法结构
“aggregations”: {
“
“
[, “meta”: { [
[, “aggregations”: { [
}
[, “
}
Bucket Aggregation - 分桶
- Filter Aggregation:过滤分桶
- Filters Aggregation:过滤分桶
- Date Histogram:按日期自动分桶
- Date Range Aggregation:给定日期范围分桶
- Histogram Aggregation:直方图分桶
- Range Aggregation:给定范围分桶
- IP Range Aggregation:按给定的 ip 范围分桶
- Terms Aggregation:按最多的词条分桶
- Geo Distance Aggregation:按地理位置指定的中心点圆环分桶
GeoHash grid Aggregation:按 geohash 分桶
Metric Aggregation - 指标
Avg Aggregation:平均值
- Max Aggregation:最大值
- Min Aggregation:最小值
- Sum Aggregation:求和
- Cardinality Aggregation:基数(去重值)
- Percentiles Aggregation:百分位
- percentile Aggregation:百分位排名
- Stats Aggregation:统计(包含 min、max、sim、avg)
- Geo Bounds Aggregation:地理坐标边框
- Geo Centroid Aggregation:图心
添加指标

嵌套桶

例:
统计图表
直方图: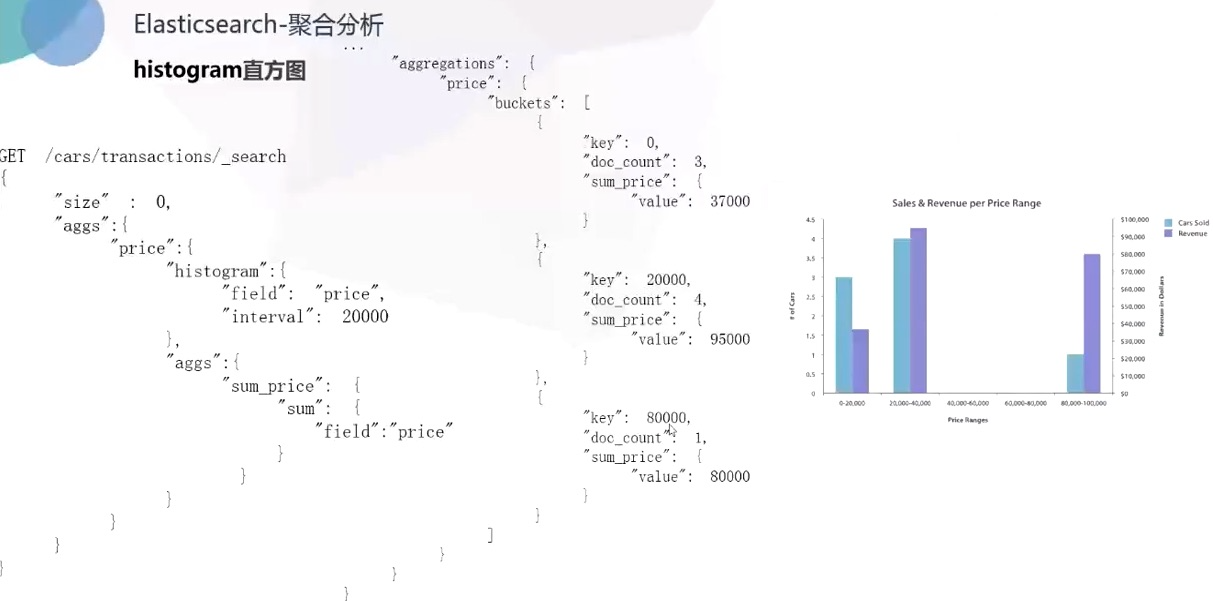
按季度、按每个汽车品牌计算销售总额:
Kibana 用聚合构建实时分析面板: