一.介绍
LinkedList简介
LinkedList 是一个继承于AbstractSequentialList的双向链表。它也可以被当作堆栈、队列或双端队列进行操作。
LinkedList 实现 List 接口,能对它进行队列操作。
LinkedList 实现 Deque 接口,即能将LinkedList当作双端队列使用。
LinkedList 实现了Cloneable接口,即覆盖了函数clone(),能克隆。
LinkedList 实现java.io.Serializable接口,这意味着LinkedList支持序列化,能通过序列化去传输。
LinkedList 是非同步的。
LinkedList构造函数
// 默认构造函数LinkedList() // 创建一个LinkedList,保护Collection中的全部元素。LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> collection)
LinkedList的API
LinkedList的APIboolean add(E object) //将指定的元素的列表。void add(int location, E object) //在指定位置插入指定元素在这个列表中。boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> collection) //将指定集合的所有元素附加到这个列表,它们的顺序返回的指定集合的迭代器。boolean addAll(int location, Collection<? extends E> collection)//将指定集合中的所有元素插入此列表,从指定的位置。void addFirst(E object) //将某个元素添加到列表的头部void addLast(E object) //将某个元素添加到列表的尾部void clear() //从这个列表中删除所有的元素。Object clone() //返回一个 LinkedList浅拷贝。boolean contains(Object object) //返回 true如果该列表包含指定的元素。Iterator<E> descendingIterator() //返回一个迭代器在反向双端队列中的元素顺序排列的。E element() //检索,但不删除这个列表的头(第一个元素)。E get(int location) //返回此列表的元素在指定的位置。E getFirst() //返回此列表的第一个元素。E getLast() //返回此列表中最后一个元素。int indexOf(Object object) //返回第一次出现的指定元素的索引列表,或1如果该列表不包含的元素。int lastIndexOf(Object object) //返回最后出现的指定元素的索引列表,或1如果该列表不包含的元素。ListIterator<E> listIterator(int location) //返回一个list-iterator这个列表的元素(在适当的序列),开始在指定的位置在列表中。boolean offer(E o) //添加指定的元素作为这个列表的尾部(最后一个元素)。boolean offerFirst(E e) //插入指定元素在这个列表的前面。boolean offerLast(E e) //插入指定元素在这个列表。E peek() //检索,但不删除这个列表的头(第一个元素)。E peekFirst() //检索,但不删除这个列表的第一个元素,或返回 null如果该列表是空的。E peekLast() //检索,但不删除最后一个元素的列表,或返回 null如果该列表是空的。E poll() //获取和删除这个列表的头(第一个元素)。E pollFirst() //获取和删除这个列表的第一个元素,或返回 null如果该列表是空的。E pollLast() //获取和删除最后一个元素的列表,或返回 null如果该列表是空的。E pop() //从堆栈中弹出一个元素代表了这个列表。void push(E e) //将一个元素放入堆栈中由这个列表。E remove() //获取和删除这个列表的头(第一个元素)。E remove(int location) //这个列表中删除指定位置的元素。boolean remove(Object object) //删除第一次出现的指定元素从这个列表,如果它存在。E removeFirst() //从这个列表中删除并返回第一个元素。boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) //删除第一次出现的指定元素在这个列表(从头到尾遍历列表时)。E removeLast() //从这个列表中删除并返回最后一个元素。boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) //删除此列表中最后出现的指定元素(如果从头到尾遍历列表)。E set(int location, E object) //取代在指定位置上的元素在此列表中指定的元素。int size() //返回此列表的元素数量。<T> T[] toArray(T[] contents) //返回一个数组,其中包含所有的元素在这个列表中正确的顺序(从第一个到最后一个元素),返回数组的运行时类型是指定数组中Object[] toArray() //返回一个数组,其中包含所有的元素在这个列表中适当顺序(从第一个到最后一个元素)。
AbstractSequentialList简介
在介绍LinkedList的源码之前,先介绍一下AbstractSequentialList。毕竟,LinkedList是AbstractSequentialList的子类。
AbstractSequentialList 实现了get(int index)、set(int index, E element)、add(int index, E element) 和 remove(int index)这些函数。这些接口都是随机访问List的,LinkedList是双向链表;既然它继承于AbstractSequentialList,就相当于已经实现了“get(int index)这些接口”。
此外,我们若需要通过AbstractSequentialList自己实现一个列表,只需要扩展此类,并提供 listIterator() 和 size() 方法的实现即可。若要实现不可修改的列表,则需要实现列表迭代器的 hasNext、next、hasPrevious、previous 和 index 方法即可。
二.数据结构
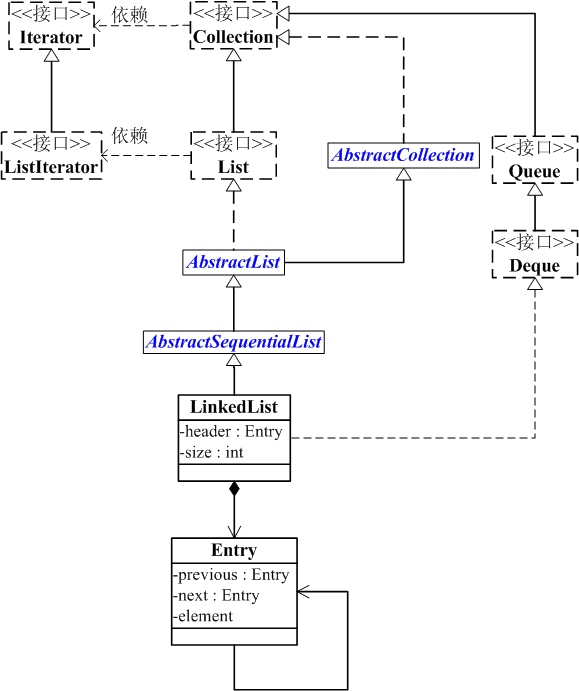
LinkedList的继承关系
java.lang.Object↳ java.util.AbstractCollection<E>↳ java.util.AbstractList<E>↳ java.util.AbstractSequentialList<E>↳ java.util.LinkedList<E>public class LinkedList<E>extends AbstractSequentialList<E>implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {}
LinkedList与Collection关系如下图:
LinkedList的本质是双向链表。
(01) LinkedList继承于AbstractSequentialList,并且实现了Dequeue接口。
(02) LinkedList包含两个重要的成员:header 和 size。
header是双向链表的表头,它是双向链表节点所对应的类Entry的实例。Entry中包含成员变量: previous, next, element。其中,previous是该节点的上一个节点,next是该节点的下一个节点,element是该节点所包含的值。
size是双向链表中节点的个数。
三.源码解析(基于JDK1.6.0_45)
为了更了解LinkedList的原理,下面对LinkedList源码代码作出分析。
在阅读源码之前,我们先对LinkedList的整体实现进行大致说明:
LinkedList实际上是通过双向链表去实现的。既然是双向链表,那么它的顺序访问会非常高效,而随机访问效率比较低。
既然LinkedList是通过双向链表的,但是它也实现了List接口{也就是说,它实现了get(int location)、remove(int location)等“根据索引值来获取、删除节点的函数”}。LinkedList是如何实现List的这些接口的,如何将“双向链表和索引值联系起来的”?
实际原理非常简单,它就是通过一个计数索引值来实现的。例如,当我们调用get(int location)时,首先会比较“location”和“双向链表长度的1/2”;若前者大,则从链表头开始往后查找,直到location位置;否则,从链表末尾开始先前查找,直到location位置。
这就是“双线链表和索引值联系起来”的方法。
好了,接下来开始阅读源码(只要理解双向链表,那么LinkedList的源码很容易理解的)。
package java.util;public class LinkedList<E>extends AbstractSequentialList<E>implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable{// 链表的表头,表头不包含任何数据。Entry是个链表类数据结构。private transient Entry<E> header = new Entry<E>(null, null, null);// LinkedList中元素个数private transient int size = 0;// 默认构造函数:创建一个空的链表public LinkedList() {header.next = header.previous = header;}// 包含“集合”的构造函数:创建一个包含“集合”的LinkedListpublic LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {this();addAll(c);}// 获取LinkedList的第一个元素public E getFirst() {if (size==0)throw new NoSuchElementException();// 链表的表头header中不包含数据。// 这里返回header所指下一个节点所包含的数据。return header.next.element;}// 获取LinkedList的最后一个元素public E getLast() {if (size==0)throw new NoSuchElementException();// 由于LinkedList是双向链表;而表头header不包含数据。// 因而,这里返回表头header的前一个节点所包含的数据。return header.previous.element;}// 删除LinkedList的第一个元素public E removeFirst() {return remove(header.next);}// 删除LinkedList的最后一个元素public E removeLast() {return remove(header.previous);}// 将元素添加到LinkedList的起始位置public void addFirst(E e) {addBefore(e, header.next);}// 将元素添加到LinkedList的结束位置public void addLast(E e) {addBefore(e, header);}// 判断LinkedList是否包含元素(o)public boolean contains(Object o) {return indexOf(o) != -1;}// 返回LinkedList的大小public int size() {return size;}// 将元素(E)添加到LinkedList中public boolean add(E e) {// 将节点(节点数据是e)添加到表头(header)之前。// 即,将节点添加到双向链表的末端。addBefore(e, header);return true;}// 从LinkedList中删除元素(o)// 从链表开始查找,如存在元素(o)则删除该元素并返回true;// 否则,返回false。public boolean remove(Object o) {if (o==null) {// 若o为null的删除情况for (Entry<E> e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next) {if (e.element==null) {remove(e);return true;}}} else {// 若o不为null的删除情况for (Entry<E> e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next) {if (o.equals(e.element)) {remove(e);return true;}}}return false;}// 将“集合(c)”添加到LinkedList中。// 实际上,是从双向链表的末尾开始,将“集合(c)”添加到双向链表中。public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {return addAll(size, c);}// 从双向链表的index开始,将“集合(c)”添加到双向链表中。public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {if (index < 0 || index > size)throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index+", Size: "+size);Object[] a = c.toArray();// 获取集合的长度int numNew = a.length;if (numNew==0)return false;modCount++;// 设置“当前要插入节点的后一个节点”Entry<E> successor = (index==size ? header : entry(index));// 设置“当前要插入节点的前一个节点”Entry<E> predecessor = successor.previous;// 将集合(c)全部插入双向链表中for (int i=0; i<numNew; i++) {Entry<E> e = new Entry<E>((E)a[i], successor, predecessor);predecessor.next = e;predecessor = e;}successor.previous = predecessor;// 调整LinkedList的实际大小size += numNew;return true;}// 清空双向链表public void clear() {Entry<E> e = header.next;// 从表头开始,逐个向后遍历;对遍历到的节点执行一下操作:// (01) 设置前一个节点为null// (02) 设置当前节点的内容为null// (03) 设置后一个节点为“新的当前节点”while (e != header) {Entry<E> next = e.next;e.next = e.previous = null;e.element = null;e = next;}header.next = header.previous = header;// 设置大小为0size = 0;modCount++;}// 返回LinkedList指定位置的元素public E get(int index) {return entry(index).element;}// 设置index位置对应的节点的值为elementpublic E set(int index, E element) {Entry<E> e = entry(index);E oldVal = e.element;e.element = element;return oldVal;}// 在index前添加节点,且节点的值为elementpublic void add(int index, E element) {addBefore(element, (index==size ? header : entry(index)));}// 删除index位置的节点public E remove(int index) {return remove(entry(index));}// 获取双向链表中指定位置的节点private Entry<E> entry(int index) {if (index < 0 || index >= size)throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index+", Size: "+size);Entry<E> e = header;// 获取index处的节点。// 若index < 双向链表长度的1/2,则从前先后查找;// 否则,从后向前查找。if (index < (size >> 1)) {for (int i = 0; i <= index; i++)e = e.next;} else {for (int i = size; i > index; i--)e = e.previous;}return e;}// 从前向后查找,返回“值为对象(o)的节点对应的索引”// 不存在就返回-1public int indexOf(Object o) {int index = 0;if (o==null) {for (Entry e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next) {if (e.element==null)return index;index++;}} else {for (Entry e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next) {if (o.equals(e.element))return index;index++;}}return -1;}// 从后向前查找,返回“值为对象(o)的节点对应的索引”// 不存在就返回-1public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {int index = size;if (o==null) {for (Entry e = header.previous; e != header; e = e.previous) {index--;if (e.element==null)return index;}} else {for (Entry e = header.previous; e != header; e = e.previous) {index--;if (o.equals(e.element))return index;}}return -1;}// 返回第一个节点// 若LinkedList的大小为0,则返回nullpublic E peek() {if (size==0)return null;return getFirst();}// 返回第一个节点// 若LinkedList的大小为0,则抛出异常public E element() {return getFirst();}// 删除并返回第一个节点// 若LinkedList的大小为0,则返回nullpublic E poll() {if (size==0)return null;return removeFirst();}// 将e添加双向链表末尾public boolean offer(E e) {return add(e);}// 将e添加双向链表开头public boolean offerFirst(E e) {addFirst(e);return true;}// 将e添加双向链表末尾public boolean offerLast(E e) {addLast(e);return true;}// 返回第一个节点// 若LinkedList的大小为0,则返回nullpublic E peekFirst() {if (size==0)return null;return getFirst();}// 返回最后一个节点// 若LinkedList的大小为0,则返回nullpublic E peekLast() {if (size==0)return null;return getLast();}// 删除并返回第一个节点// 若LinkedList的大小为0,则返回nullpublic E pollFirst() {if (size==0)return null;return removeFirst();}// 删除并返回最后一个节点// 若LinkedList的大小为0,则返回nullpublic E pollLast() {if (size==0)return null;return removeLast();}// 将e插入到双向链表开头public void push(E e) {addFirst(e);}// 删除并返回第一个节点public E pop() {return removeFirst();}// 从LinkedList开始向后查找,删除第一个值为元素(o)的节点// 从链表开始查找,如存在节点的值为元素(o)的节点,则删除该节点public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) {return remove(o);}// 从LinkedList末尾向前查找,删除第一个值为元素(o)的节点// 从链表开始查找,如存在节点的值为元素(o)的节点,则删除该节点public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) {if (o==null) {for (Entry<E> e = header.previous; e != header; e = e.previous) {if (e.element==null) {remove(e);return true;}}} else {for (Entry<E> e = header.previous; e != header; e = e.previous) {if (o.equals(e.element)) {remove(e);return true;}}}return false;}// 返回“index到末尾的全部节点”对应的ListIterator对象(List迭代器)public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) {return new ListItr(index);}// List迭代器private class ListItr implements ListIterator<E> {// 上一次返回的节点private Entry<E> lastReturned = header;// 下一个节点private Entry<E> next;// 下一个节点对应的索引值private int nextIndex;// 期望的改变计数。用来实现fail-fast机制。private int expectedModCount = modCount;// 构造函数。// 从index位置开始进行迭代ListItr(int index) {// index的有效性处理if (index < 0 || index > size)throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index+ ", Size: "+size);// 若 “index 小于 ‘双向链表长度的一半’”,则从第一个元素开始往后查找;// 否则,从最后一个元素往前查找。if (index < (size >> 1)) {next = header.next;for (nextIndex=0; nextIndex<index; nextIndex++)next = next.next;} else {next = header;for (nextIndex=size; nextIndex>index; nextIndex--)next = next.previous;}}// 是否存在下一个元素public boolean hasNext() {// 通过元素索引是否等于“双向链表大小”来判断是否达到最后。return nextIndex != size;}// 获取下一个元素public E next() {checkForComodification();if (nextIndex == size)throw new NoSuchElementException();lastReturned = next;// next指向链表的下一个元素next = next.next;nextIndex++;return lastReturned.element;}// 是否存在上一个元素public boolean hasPrevious() {// 通过元素索引是否等于0,来判断是否达到开头。return nextIndex != 0;}// 获取上一个元素public E previous() {if (nextIndex == 0)throw new NoSuchElementException();// next指向链表的上一个元素lastReturned = next = next.previous;nextIndex--;checkForComodification();return lastReturned.element;}// 获取下一个元素的索引public int nextIndex() {return nextIndex;}// 获取上一个元素的索引public int previousIndex() {return nextIndex-1;}// 删除当前元素。// 删除双向链表中的当前节点public void remove() {checkForComodification();Entry<E> lastNext = lastReturned.next;try {LinkedList.this.remove(lastReturned);} catch (NoSuchElementException e) {throw new IllegalStateException();}if (next==lastReturned)next = lastNext;elsenextIndex--;lastReturned = header;expectedModCount++;}// 设置当前节点为epublic void set(E e) {if (lastReturned == header)throw new IllegalStateException();checkForComodification();lastReturned.element = e;}// 将e添加到当前节点的前面public void add(E e) {checkForComodification();lastReturned = header;addBefore(e, next);nextIndex++;expectedModCount++;}// 判断 “modCount和expectedModCount是否相等”,依次来实现fail-fast机制。final void checkForComodification() {if (modCount != expectedModCount)throw new ConcurrentModificationException();}}// 双向链表的节点所对应的数据结构。// 包含3部分:上一节点,下一节点,当前节点值。private static class Entry<E> {// 当前节点所包含的值E element;// 下一个节点Entry<E> next;// 上一个节点Entry<E> previous;/*** 链表节点的构造函数。* 参数说明:* element —— 节点所包含的数据* next —— 下一个节点* previous —— 上一个节点*/Entry(E element, Entry<E> next, Entry<E> previous) {this.element = element;this.next = next;this.previous = previous;}}// 将节点(节点数据是e)添加到entry节点之前。private Entry<E> addBefore(E e, Entry<E> entry) {// 新建节点newEntry,将newEntry插入到节点e之前;并且设置newEntry的数据是eEntry<E> newEntry = new Entry<E>(e, entry, entry.previous);newEntry.previous.next = newEntry;newEntry.next.previous = newEntry;// 修改LinkedList大小size++;// 修改LinkedList的修改统计数:用来实现fail-fast机制。modCount++;return newEntry;}// 将节点从链表中删除private E remove(Entry<E> e) {if (e == header)throw new NoSuchElementException();E result = e.element;e.previous.next = e.next;e.next.previous = e.previous;e.next = e.previous = null;e.element = null;size--;modCount++;return result;}// 反向迭代器public Iterator<E> descendingIterator() {return new DescendingIterator();}// 反向迭代器实现类。private class DescendingIterator implements Iterator {final ListItr itr = new ListItr(size());// 反向迭代器是否下一个元素。// 实际上是判断双向链表的当前节点是否达到开头public boolean hasNext() {return itr.hasPrevious();}// 反向迭代器获取下一个元素。// 实际上是获取双向链表的前一个节点public E next() {return itr.previous();}// 删除当前节点public void remove() {itr.remove();}}// 返回LinkedList的Object[]数组public Object[] toArray() {// 新建Object[]数组Object[] result = new Object[size];int i = 0;// 将链表中所有节点的数据都添加到Object[]数组中for (Entry<E> e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next)result[i++] = e.element;return result;}// 返回LinkedList的模板数组。所谓模板数组,即可以将T设为任意的数据类型public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {// 若数组a的大小 < LinkedList的元素个数(意味着数组a不能容纳LinkedList中全部元素)// 则新建一个T[]数组,T[]的大小为LinkedList大小,并将该T[]赋值给a。if (a.length < size)a = (T[])java.lang.reflect.Array.newInstance(a.getClass().getComponentType(), size);// 将链表中所有节点的数据都添加到数组a中int i = 0;Object[] result = a;for (Entry<E> e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next)result[i++] = e.element;if (a.length > size)a[size] = null;return a;}// 克隆函数。返回LinkedList的克隆对象。public Object clone() {LinkedList<E> clone = null;// 克隆一个LinkedList克隆对象try {clone = (LinkedList<E>) super.clone();} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {throw new InternalError();}// 新建LinkedList表头节点clone.header = new Entry<E>(null, null, null);clone.header.next = clone.header.previous = clone.header;clone.size = 0;clone.modCount = 0;// 将链表中所有节点的数据都添加到克隆对象中for (Entry<E> e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next)clone.add(e.element);return clone;}// java.io.Serializable的写入函数// 将LinkedList的“容量,所有的元素值”都写入到输出流中private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)throws java.io.IOException {// Write out any hidden serialization magics.defaultWriteObject();// 写入“容量”s.writeInt(size);// 将链表中所有节点的数据都写入到输出流中for (Entry e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next)s.writeObject(e.element);}// java.io.Serializable的读取函数:根据写入方式反向读出// 先将LinkedList的“容量”读出,然后将“所有的元素值”读出private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {// Read in any hidden serialization magics.defaultReadObject();// 从输入流中读取“容量”int size = s.readInt();// 新建链表表头节点header = new Entry<E>(null, null, null);header.next = header.previous = header;// 从输入流中将“所有的元素值”并逐个添加到链表中for (int i=0; i<size; i++)addBefore((E)s.readObject(), header);}}
总结:
(01) LinkedList 实际上是通过双向链表去实现的。
它包含一个非常重要的内部类:Entry。Entry是双向链表节点所对应的数据结构,它包括的属性有:当前节点所包含的值,上一个节点,下一个节点。
(02) 从LinkedList的实现方式中可以发现,它不存在LinkedList容量不足的问题。
(03) LinkedList的克隆函数,即是将全部元素克隆到一个新的LinkedList对象中。
(04) LinkedList实现java.io.Serializable。当写入到输出流时,先写入“容量”,再依次写入“每一个节点保护的值”;当读出输入流时,先读取“容量”,再依次读取“每一个元素”。
(05) 由于LinkedList实现了Deque,而Deque接口定义了在双端队列两端访问元素的方法。提供插入、移除和检查元素的方法。每种方法都存在两种形式:一种形式在操作失败时抛出异常,另一种形式返回一个特殊值(null 或 false,具体取决于操作)。
总结起来如下表格:
第一个元素(头部) 最后一个元素(尾部)
抛出异常 特殊值 抛出异常 特殊值
插入 addFirst(e) offerFirst(e) addLast(e) offerLast(e)
移除 removeFirst() pollFirst() removeLast() pollLast()
检查 getFirst() peekFirst() getLast() peekLast()
(06) LinkedList可以作为FIFO(先进先出)的队列,作为FIFO的队列时,下表的方法等价:
队列方法 等效方法
add(e) addLast(e)
offer(e) offerLast(e)
remove() removeFirst()
poll() pollFirst()
element() getFirst()
peek() peekFirst()
(07) LinkedList可以作为LIFO(后进先出)的栈,作为LIFO的栈时,下表的方法等价:
栈方法 等效方法
push(e) addFirst(e)
pop() removeFirst()
peek() peekFirst()
四.遍历方式
LinkedList遍历方式
LinkedList支持多种遍历方式。建议不要采用随机访问的方式去遍历LinkedList,而采用逐个遍历的方式。
(01) 第一种,通过迭代器遍历。即通过Iterator去遍历。
for(Iterator iter = list.iterator(); iter.hasNext();)
iter.next();
(02) 通过快速随机访问遍历LinkedList
int size = list.size();
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
list.get(i);
}
(03) 通过另外一种for循环来遍历LinkedList
for (Integer integ:list)
;
(04) 通过pollFirst()来遍历LinkedList
while(list.pollFirst() != null)
;
(05) 通过pollLast()来遍历LinkedList
while(list.pollLast() != null)
;
(06) 通过removeFirst()来遍历LinkedList
try {
while(list.removeFirst() != null)
;
} catch (NoSuchElementException e) {
}
(07) 通过removeLast()来遍历LinkedList
try {
while(list.removeLast() != null)
;
} catch (NoSuchElementException e) {
}
测试这些遍历方式效率的代码如下:
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
/*
* @desc 测试LinkedList的几种遍历方式和效率
*
* @author skywang
*/
public class LinkedListThruTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 通过Iterator遍历LinkedList
iteratorLinkedListThruIterator(getLinkedList()) ;
// 通过快速随机访问遍历LinkedList
iteratorLinkedListThruForeach(getLinkedList()) ;
// 通过for循环的变种来访问遍历LinkedList
iteratorThroughFor2(getLinkedList()) ;
// 通过PollFirst()遍历LinkedList
iteratorThroughPollFirst(getLinkedList()) ;
// 通过PollLast()遍历LinkedList
iteratorThroughPollLast(getLinkedList()) ;
// 通过removeFirst()遍历LinkedList
iteratorThroughRemoveFirst(getLinkedList()) ;
// 通过removeLast()遍历LinkedList
iteratorThroughRemoveLast(getLinkedList()) ;
}
private static LinkedList getLinkedList() {
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
for (int i=0; i<100000; i++)
llist.addLast(i);
return llist;
}
/**
* 通过快迭代器遍历LinkedList
*/
private static void iteratorLinkedListThruIterator(LinkedList<Integer> list) {
if (list == null)
return ;
// 记录开始时间
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(Iterator iter = list.iterator(); iter.hasNext();)
iter.next();
// 记录结束时间
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
long interval = end - start;
System.out.println("iteratorLinkedListThruIterator:" + interval+" ms");
}
/**
* 通过快速随机访问遍历LinkedList
*/
private static void iteratorLinkedListThruForeach(LinkedList<Integer> list) {
if (list == null)
return ;
// 记录开始时间
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
int size = list.size();
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
list.get(i);
}
// 记录结束时间
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
long interval = end - start;
System.out.println("iteratorLinkedListThruForeach:" + interval+" ms");
}
/**
* 通过另外一种for循环来遍历LinkedList
*/
private static void iteratorThroughFor2(LinkedList<Integer> list) {
if (list == null)
return ;
// 记录开始时间
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (Integer integ:list)
;
// 记录结束时间
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
long interval = end - start;
System.out.println("iteratorThroughFor2:" + interval+" ms");
}
/**
* 通过pollFirst()来遍历LinkedList
*/
private static void iteratorThroughPollFirst(LinkedList<Integer> list) {
if (list == null)
return ;
// 记录开始时间
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
while(list.pollFirst() != null)
;
// 记录结束时间
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
long interval = end - start;
System.out.println("iteratorThroughPollFirst:" + interval+" ms");
}
/**
* 通过pollLast()来遍历LinkedList
*/
private static void iteratorThroughPollLast(LinkedList<Integer> list) {
if (list == null)
return ;
// 记录开始时间
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
while(list.pollLast() != null)
;
// 记录结束时间
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
long interval = end - start;
System.out.println("iteratorThroughPollLast:" + interval+" ms");
}
/**
* 通过removeFirst()来遍历LinkedList
*/
private static void iteratorThroughRemoveFirst(LinkedList<Integer> list) {
if (list == null)
return ;
// 记录开始时间
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
while(list.removeFirst() != null)
;
} catch (NoSuchElementException e) {
}
// 记录结束时间
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
long interval = end - start;
System.out.println("iteratorThroughRemoveFirst:" + interval+" ms");
}
/**
* 通过removeLast()来遍历LinkedList
*/
private static void iteratorThroughRemoveLast(LinkedList<Integer> list) {
if (list == null)
return ;
// 记录开始时间
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
while(list.removeLast() != null)
;
} catch (NoSuchElementException e) {
}
// 记录结束时间
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
long interval = end - start;
System.out.println("iteratorThroughRemoveLast:" + interval+" ms");
}
}
执行结果:
iteratorLinkedListThruIterator:8 ms
iteratorLinkedListThruForeach:3724 ms
iteratorThroughFor2:5 ms
iteratorThroughPollFirst:8 ms
iteratorThroughPollLast:6 ms
iteratorThroughRemoveFirst:2 ms
iteratorThroughRemoveLast:2 ms
由此可见,遍历LinkedList时,使用removeFist()或removeLast()效率最高。但用它们遍历时,会删除原始数据;若单纯只读取,而不删除,应该使用第3种遍历方式。
无论如何,千万不要通过随机访问去遍历LinkedList!
五.api示例
下面通过一个示例来学习如何使用LinkedList的常用API
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
/*
* @desc LinkedList测试程序。
*
* @author skywang
* @email kuiwu-wang@163.com
*/
public class LinkedListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 测试LinkedList的API
testLinkedListAPIs() ;
// 将LinkedList当作 LIFO(后进先出)的堆栈
useLinkedListAsLIFO();
// 将LinkedList当作 FIFO(先进先出)的队列
useLinkedListAsFIFO();
}
/*
* 测试LinkedList中部分API
*/
private static void testLinkedListAPIs() {
String val = null;
//LinkedList llist;
//llist.offer("10");
// 新建一个LinkedList
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
//---- 添加操作 ----
// 依次添加1,2,3
llist.add("1");
llist.add("2");
llist.add("3");
// 将“4”添加到第一个位置
llist.add(1, "4");
System.out.println("\nTest \"addFirst(), removeFirst(), getFirst()\"");
// (01) 将“10”添加到第一个位置。 失败的话,抛出异常!
llist.addFirst("10");
System.out.println("llist:"+llist);
// (02) 将第一个元素删除。 失败的话,抛出异常!
System.out.println("llist.removeFirst():"+llist.removeFirst());
System.out.println("llist:"+llist);
// (03) 获取第一个元素。 失败的话,抛出异常!
System.out.println("llist.getFirst():"+llist.getFirst());
System.out.println("\nTest \"offerFirst(), pollFirst(), peekFirst()\"");
// (01) 将“10”添加到第一个位置。 返回true。
llist.offerFirst("10");
System.out.println("llist:"+llist);
// (02) 将第一个元素删除。 失败的话,返回null。
System.out.println("llist.pollFirst():"+llist.pollFirst());
System.out.println("llist:"+llist);
// (03) 获取第一个元素。 失败的话,返回null。
System.out.println("llist.peekFirst():"+llist.peekFirst());
System.out.println("\nTest \"addLast(), removeLast(), getLast()\"");
// (01) 将“20”添加到最后一个位置。 失败的话,抛出异常!
llist.addLast("20");
System.out.println("llist:"+llist);
// (02) 将最后一个元素删除。 失败的话,抛出异常!
System.out.println("llist.removeLast():"+llist.removeLast());
System.out.println("llist:"+llist);
// (03) 获取最后一个元素。 失败的话,抛出异常!
System.out.println("llist.getLast():"+llist.getLast());
System.out.println("\nTest \"offerLast(), pollLast(), peekLast()\"");
// (01) 将“20”添加到第一个位置。 返回true。
llist.offerLast("20");
System.out.println("llist:"+llist);
// (02) 将第一个元素删除。 失败的话,返回null。
System.out.println("llist.pollLast():"+llist.pollLast());
System.out.println("llist:"+llist);
// (03) 获取第一个元素。 失败的话,返回null。
System.out.println("llist.peekLast():"+llist.peekLast());
// 将第3个元素设置300。不建议在LinkedList中使用此操作,因为效率低!
llist.set(2, "300");
// 获取第3个元素。不建议在LinkedList中使用此操作,因为效率低!
System.out.println("\nget(3):"+llist.get(2));
// ---- toArray(T[] a) ----
// 将LinkedList转行为数组
String[] arr = (String[])llist.toArray(new String[0]);
for (String str:arr)
System.out.println("str:"+str);
// 输出大小
System.out.println("size:"+llist.size());
// 清空LinkedList
llist.clear();
// 判断LinkedList是否为空
System.out.println("isEmpty():"+llist.isEmpty()+"\n");
}
/**
* 将LinkedList当作 LIFO(后进先出)的堆栈
*/
private static void useLinkedListAsLIFO() {
System.out.println("\nuseLinkedListAsLIFO");
// 新建一个LinkedList
LinkedList stack = new LinkedList();
// 将1,2,3,4添加到堆栈中
stack.push("1");
stack.push("2");
stack.push("3");
stack.push("4");
// 打印“栈”
System.out.println("stack:"+stack);
// 删除“栈顶元素”
System.out.println("stack.pop():"+stack.pop());
// 取出“栈顶元素”
System.out.println("stack.peek():"+stack.peek());
// 打印“栈”
System.out.println("stack:"+stack);
}
/**
* 将LinkedList当作 FIFO(先进先出)的队列
*/
private static void useLinkedListAsFIFO() {
System.out.println("\nuseLinkedListAsFIFO");
// 新建一个LinkedList
LinkedList queue = new LinkedList();
// 将10,20,30,40添加到队列。每次都是插入到末尾
queue.add("10");
queue.add("20");
queue.add("30");
queue.add("40");
// 打印“队列”
System.out.println("queue:"+queue);
// 删除(队列的第一个元素)
System.out.println("queue.remove():"+queue.remove());
// 读取(队列的第一个元素)
System.out.println("queue.element():"+queue.element());
// 打印“队列”
System.out.println("queue:"+queue);
}
}
运行结果:
Test "addFirst(), removeFirst(), getFirst()"
llist:[10, 1, 4, 2, 3]
llist.removeFirst():10
llist:[1, 4, 2, 3]
llist.getFirst():1
Test "offerFirst(), pollFirst(), peekFirst()"
llist:[10, 1, 4, 2, 3]
llist.pollFirst():10
llist:[1, 4, 2, 3]
llist.peekFirst():1
Test "addLast(), removeLast(), getLast()"
llist:[1, 4, 2, 3, 20]
llist.removeLast():20
llist:[1, 4, 2, 3]
llist.getLast():3
Test "offerLast(), pollLast(), peekLast()"
llist:[1, 4, 2, 3, 20]
llist.pollLast():20
llist:[1, 4, 2, 3]
llist.peekLast():3
get(3):300
str:1
str:4
str:300
str:3
size:4
isEmpty():true
useLinkedListAsLIFO
stack:[4, 3, 2, 1]
stack.pop():4
stack.peek():3
stack:[3, 2, 1]
useLinkedListAsFIFO
queue:[10, 20, 30, 40]
queue.remove():10
queue.element():20
queue:[20, 30, 40]