概要
这一章,我们对WeakHashMap进行学习。
我们先对WeakHashMap有个整体认识,然后再学习它的源码,最后再通过实例来学会使用WeakHashMap。
第1部分 WeakHashMap介绍
第2部分 WeakHashMap数据结构
第3部分 WeakHashMap源码解析(基于JDK1.6.0_45)
第4部分 WeakHashMap遍历方式
第5部分 WeakHashMap示例
转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/admin/EditPosts.aspx?postid=3311092
基本介绍
WeakHashMap简介
WeakHashMap 继承于AbstractMap,实现了Map接口。
和HashMap一样,WeakHashMap 也是一个散列表,它存储的内容也是键值对(key-value)映射,而且键和值都可以是null。
不过WeakHashMap的键是“弱键”。在 WeakHashMap 中,当某个键不再正常使用时,会被从WeakHashMap中被自动移除。更精确地说,对于一个给定的键,其映射的存在并不阻止垃圾回收器对该键的丢弃,这就使该键成为可终止的,被终止,然后被回收。某个键被终止时,它对应的键值对也就从映射中有效地移除了。
这个“弱键”的原理呢?大致上就是,通过WeakReference和ReferenceQueue实现的。 WeakHashMap的key是“弱键”,即是WeakReference类型的;ReferenceQueue是一个队列,它会保存被GC回收的“弱键”。实现步骤是:
(01) 新建WeakHashMap,将“键值对”添加到WeakHashMap中。
实际上,WeakHashMap是通过数组table保存Entry(键值对);每一个Entry实际上是一个单向链表,即Entry是键值对链表。
(02) 当某“弱键”不再被其它对象引用,并被GC回收时。在GC回收该“弱键”时,这个“弱键”也同时会被添加到ReferenceQueue(queue)队列中。
(03) 当下一次我们需要操作WeakHashMap时,会先同步table和queue。table中保存了全部的键值对,而queue中保存被GC回收的键值对;同步它们,就是删除table中被GC回收的键值对。
这就是“弱键”如何被自动从WeakHashMap中删除的步骤了。
和HashMap一样,WeakHashMap是不同步的。可以使用 Collections.synchronizedMap 方法来构造同步的 WeakHashMap。
WeakHashMap的构造函数
WeakHashMap共有4个构造函数,如下:
// 默认构造函数。WeakHashMap()// 指定“容量大小”的构造函数WeakHashMap(int capacity)// 指定“容量大小”和“加载因子”的构造函数WeakHashMap(int capacity, float loadFactor)// 包含“子Map”的构造函数WeakHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> map)
WeakHashMap的API
void clear()Object clone()boolean containsKey(Object key)boolean containsValue(Object value)Set<Entry<K, V>> entrySet()V get(Object key)boolean isEmpty()Set<K> keySet()V put(K key, V value)void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> map)V remove(Object key)int size()Collection<V> values()
数据结构
WeakHashMap的继承关系如下
java.lang.Object↳ java.util.AbstractMap<K, V>↳ java.util.WeakHashMap<K, V>public class WeakHashMap<K,V>extends AbstractMap<K,V>implements Map<K,V> {}
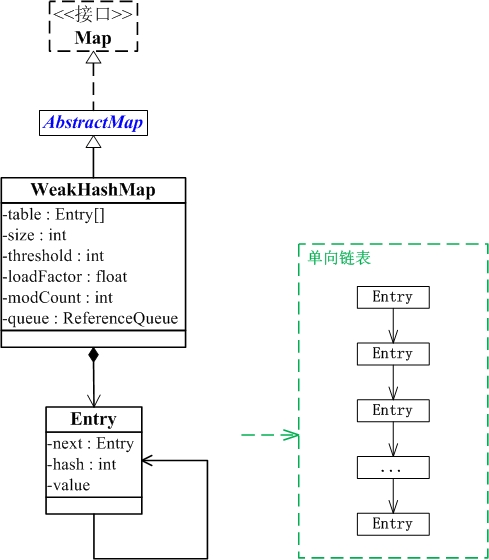
WeakHashMap与Map关系如下图:
从图中可以看出:
(01) WeakHashMap继承于AbstractMap,并且实现了Map接口。
(02) WeakHashMap是哈希表,但是它的键是”弱键”。WeakHashMap中保护几个重要的成员变量:table, size, threshold, loadFactor, modCount, queue。
table是一个Entry[]数组类型,而Entry实际上就是一个单向链表。哈希表的”key-value键值对”都是存储在Entry数组中的。
size是Hashtable的大小,它是Hashtable保存的键值对的数量。
threshold是Hashtable的阈值,用于判断是否需要调整Hashtable的容量。threshold的值=”容量*加载因子”。
loadFactor就是加载因子。
modCount是用来实现fail-fast机制的
queue保存的是“已被GC清除”的“弱引用的键”。
源码解析(基于JDK1.6.0_45)
下面对WeakHashMap的源码进行说明
package java.util;import java.lang.ref.WeakReference;import java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue;public class WeakHashMap<K,V>extends AbstractMap<K,V>implements Map<K,V> {// 默认的初始容量是16,必须是2的幂。private static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;// 最大容量(必须是2的幂且小于2的30次方,传入容量过大将被这个值替换)private static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;// 默认加载因子private static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;// 存储数据的Entry数组,长度是2的幂。// WeakHashMap是采用拉链法实现的,每一个Entry本质上是一个单向链表private Entry[] table;// WeakHashMap的大小,它是WeakHashMap保存的键值对的数量private int size;// WeakHashMap的阈值,用于判断是否需要调整WeakHashMap的容量(threshold = 容量*加载因子)private int threshold;// 加载因子实际大小private final float loadFactor;// queue保存的是“已被GC清除”的“弱引用的键”。// 弱引用和ReferenceQueue 是联合使用的:如果弱引用所引用的对象被垃圾回收,Java虚拟机就会把这个弱引用加入到与之关联的引用队列中private final ReferenceQueue<K> queue = new ReferenceQueue<K>();// WeakHashMap被改变的次数private volatile int modCount;// 指定“容量大小”和“加载因子”的构造函数public WeakHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {if (initialCapacity < 0)throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Initial Capacity: "+initialCapacity);// WeakHashMap的最大容量只能是MAXIMUM_CAPACITYif (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Load factor: "+loadFactor);// 找出“大于initialCapacity”的最小的2的幂int capacity = 1;while (capacity < initialCapacity)capacity <<= 1;// 创建Entry数组,用来保存数据table = new Entry[capacity];// 设置“加载因子”this.loadFactor = loadFactor;// 设置“WeakHashMap阈值”,当WeakHashMap中存储数据的数量达到threshold时,就需要将WeakHashMap的容量加倍。threshold = (int)(capacity * loadFactor);}// 指定“容量大小”的构造函数public WeakHashMap(int initialCapacity) {this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);}// 默认构造函数。public WeakHashMap() {this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;threshold = (int)(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);table = new Entry[DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY];}// 包含“子Map”的构造函数public WeakHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {this(Math.max((int) (m.size() / DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR) + 1, 16),DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);// 将m中的全部元素逐个添加到WeakHashMap中putAll(m);}// 键为null的mask值。// 因为WeakReference中允许“null的key”,若直接插入“null的key”,将其当作弱引用时,会被删除。// 因此,这里对于“key为null”的清空,都统一替换为“key为NULL_KEY”,“NULL_KEY”是“静态的final常量”。private static final Object NULL_KEY = new Object();// 对“null的key”进行特殊处理private static Object maskNull(Object key) {return (key == null ? NULL_KEY : key);}// 还原对“null的key”的特殊处理private static <K> K unmaskNull(Object key) {return (K) (key == NULL_KEY ? null : key);}// 判断“x”和“y”是否相等static boolean eq(Object x, Object y) {return x == y || x.equals(y);}// 返回索引值// h & (length-1)保证返回值的小于lengthstatic int indexFor(int h, int length) {return h & (length-1);}// 清空table中无用键值对。原理如下:// (01) 当WeakHashMap中某个“弱引用的key”由于没有再被引用而被GC收回时,// 被回收的“该弱引用key”也被会被添加到"ReferenceQueue(queue)"中。// (02) 当我们执行expungeStaleEntries时,// 就遍历"ReferenceQueue(queue)"中的所有key// 然后就在“WeakReference的table”中删除与“ReferenceQueue(queue)中key”对应的键值对private void expungeStaleEntries() {Entry<K,V> e;while ( (e = (Entry<K,V>) queue.poll()) != null) {int h = e.hash;int i = indexFor(h, table.length);Entry<K,V> prev = table[i];Entry<K,V> p = prev;while (p != null) {Entry<K,V> next = p.next;if (p == e) {if (prev == e)table[i] = next;elseprev.next = next;e.next = null; // Help GCe.value = null; // " "size--;break;}prev = p;p = next;}}}// 获取WeakHashMap的table(存放键值对的数组)private Entry[] getTable() {// 删除table中“已被GC回收的key对应的键值对”expungeStaleEntries();return table;}// 获取WeakHashMap的实际大小public int size() {if (size == 0)return 0;// 删除table中“已被GC回收的key对应的键值对”expungeStaleEntries();return size;}public boolean isEmpty() {return size() == 0;}// 获取key对应的valuepublic V get(Object key) {Object k = maskNull(key);// 获取key的hash值。int h = HashMap.hash(k.hashCode());Entry[] tab = getTable();int index = indexFor(h, tab.length);Entry<K,V> e = tab[index];// 在“该hash值对应的链表”上查找“键值等于key”的元素while (e != null) {if (e.hash == h && eq(k, e.get()))return e.value;e = e.next;}return null;}// WeakHashMap是否包含keypublic boolean containsKey(Object key) {return getEntry(key) != null;}// 返回“键为key”的键值对Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {Object k = maskNull(key);int h = HashMap.hash(k.hashCode());Entry[] tab = getTable();int index = indexFor(h, tab.length);Entry<K,V> e = tab[index];while (e != null && !(e.hash == h && eq(k, e.get())))e = e.next;return e;}// 将“key-value”添加到WeakHashMap中public V put(K key, V value) {K k = (K) maskNull(key);int h = HashMap.hash(k.hashCode());Entry[] tab = getTable();int i = indexFor(h, tab.length);for (Entry<K,V> e = tab[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {// 若“该key”对应的键值对已经存在,则用新的value取代旧的value。然后退出!if (h == e.hash && eq(k, e.get())) {V oldValue = e.value;if (value != oldValue)e.value = value;return oldValue;}}// 若“该key”对应的键值对不存在于WeakHashMap中,则将“key-value”添加到table中modCount++;Entry<K,V> e = tab[i];tab[i] = new Entry<K,V>(k, value, queue, h, e);if (++size >= threshold)resize(tab.length * 2);return null;}// 重新调整WeakHashMap的大小,newCapacity是调整后的单位void resize(int newCapacity) {Entry[] oldTable = getTable();int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;return;}// 新建一个newTable,将“旧的table”的全部元素添加到“新的newTable”中,// 然后,将“新的newTable”赋值给“旧的table”。Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];transfer(oldTable, newTable);table = newTable;if (size >= threshold / 2) {threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor);} else {// 删除table中“已被GC回收的key对应的键值对”expungeStaleEntries();transfer(newTable, oldTable);table = oldTable;}}// 将WeakHashMap中的全部元素都添加到newTable中private void transfer(Entry[] src, Entry[] dest) {for (int j = 0; j < src.length; ++j) {Entry<K,V> e = src[j];src[j] = null;while (e != null) {Entry<K,V> next = e.next;Object key = e.get();if (key == null) {e.next = null; // Help GCe.value = null; // " "size--;} else {int i = indexFor(e.hash, dest.length);e.next = dest[i];dest[i] = e;}e = next;}}}// 将"m"的全部元素都添加到WeakHashMap中public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {int numKeysToBeAdded = m.size();if (numKeysToBeAdded == 0)return;// 计算容量是否足够,// 若“当前实际容量 < 需要的容量”,则将容量x2。if (numKeysToBeAdded > threshold) {int targetCapacity = (int)(numKeysToBeAdded / loadFactor + 1);if (targetCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)targetCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;int newCapacity = table.length;while (newCapacity < targetCapacity)newCapacity <<= 1;if (newCapacity > table.length)resize(newCapacity);}// 将“m”中的元素逐个添加到WeakHashMap中。for (Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e : m.entrySet())put(e.getKey(), e.getValue());}// 删除“键为key”元素public V remove(Object key) {Object k = maskNull(key);// 获取哈希值。int h = HashMap.hash(k.hashCode());Entry[] tab = getTable();int i = indexFor(h, tab.length);Entry<K,V> prev = tab[i];Entry<K,V> e = prev;// 删除链表中“键为key”的元素// 本质是“删除单向链表中的节点”while (e != null) {Entry<K,V> next = e.next;if (h == e.hash && eq(k, e.get())) {modCount++;size--;if (prev == e)tab[i] = next;elseprev.next = next;return e.value;}prev = e;e = next;}return null;}// 删除“键值对”Entry<K,V> removeMapping(Object o) {if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))return null;Entry[] tab = getTable();Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)o;Object k = maskNull(entry.getKey());int h = HashMap.hash(k.hashCode());int i = indexFor(h, tab.length);Entry<K,V> prev = tab[i];Entry<K,V> e = prev;// 删除链表中的“键值对e”// 本质是“删除单向链表中的节点”while (e != null) {Entry<K,V> next = e.next;if (h == e.hash && e.equals(entry)) {modCount++;size--;if (prev == e)tab[i] = next;elseprev.next = next;return e;}prev = e;e = next;}return null;}// 清空WeakHashMap,将所有的元素设为nullpublic void clear() {while (queue.poll() != null);modCount++;Entry[] tab = table;for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; ++i)tab[i] = null;size = 0;while (queue.poll() != null);}// 是否包含“值为value”的元素public boolean containsValue(Object value) {// 若“value为null”,则调用containsNullValue()查找if (value==null)return containsNullValue();// 若“value不为null”,则查找WeakHashMap中是否有值为value的节点。Entry[] tab = getTable();for (int i = tab.length ; i-- > 0 ;)for (Entry e = tab[i] ; e != null ; e = e.next)if (value.equals(e.value))return true;return false;}// 是否包含null值private boolean containsNullValue() {Entry[] tab = getTable();for (int i = tab.length ; i-- > 0 ;)for (Entry e = tab[i] ; e != null ; e = e.next)if (e.value==null)return true;return false;}// Entry是单向链表。// 它是 “WeakHashMap链式存储法”对应的链表。// 它实现了Map.Entry 接口,即实现getKey(), getValue(), setValue(V value), equals(Object o), hashCode()这些函数private static class Entry<K,V> extends WeakReference<K> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {private V value;private final int hash;// 指向下一个节点private Entry<K,V> next;// 构造函数。Entry(K key, V value,ReferenceQueue<K> queue,int hash, Entry<K,V> next) {super(key, queue);this.value = value;this.hash = hash;this.next = next;}public K getKey() {return WeakHashMap.<K>unmaskNull(get());}public V getValue() {return value;}public V setValue(V newValue) {V oldValue = value;value = newValue;return oldValue;}// 判断两个Entry是否相等// 若两个Entry的“key”和“value”都相等,则返回true。// 否则,返回falsepublic boolean equals(Object o) {if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))return false;Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry)o;Object k1 = getKey();Object k2 = e.getKey();if (k1 == k2 || (k1 != null && k1.equals(k2))) {Object v1 = getValue();Object v2 = e.getValue();if (v1 == v2 || (v1 != null && v1.equals(v2)))return true;}return false;}// 实现hashCode()public int hashCode() {Object k = getKey();Object v = getValue();return ((k==null ? 0 : k.hashCode()) ^(v==null ? 0 : v.hashCode()));}public String toString() {return getKey() + "=" + getValue();}}// HashIterator是WeakHashMap迭代器的抽象出来的父类,实现了公共了函数。// 它包含“key迭代器(KeyIterator)”、“Value迭代器(ValueIterator)”和“Entry迭代器(EntryIterator)”3个子类。private abstract class HashIterator<T> implements Iterator<T> {// 当前索引int index;// 当前元素Entry<K,V> entry = null;// 上一次返回元素Entry<K,V> lastReturned = null;// expectedModCount用于实现fast-fail机制。int expectedModCount = modCount;// 下一个键(强引用)Object nextKey = null;// 当前键(强引用)Object currentKey = null;// 构造函数HashIterator() {index = (size() != 0 ? table.length : 0);}// 是否存在下一个元素public boolean hasNext() {Entry[] t = table;// 一个Entry就是一个单向链表// 若该Entry的下一个节点不为空,就将next指向下一个节点;// 否则,将next指向下一个链表(也是下一个Entry)的不为null的节点。while (nextKey == null) {Entry<K,V> e = entry;int i = index;while (e == null && i > 0)e = t[--i];entry = e;index = i;if (e == null) {currentKey = null;return false;}nextKey = e.get(); // hold on to key in strong refif (nextKey == null)entry = entry.next;}return true;}// 获取下一个元素protected Entry<K,V> nextEntry() {if (modCount != expectedModCount)throw new ConcurrentModificationException();if (nextKey == null && !hasNext())throw new NoSuchElementException();lastReturned = entry;entry = entry.next;currentKey = nextKey;nextKey = null;return lastReturned;}// 删除当前元素public void remove() {if (lastReturned == null)throw new IllegalStateException();if (modCount != expectedModCount)throw new ConcurrentModificationException();WeakHashMap.this.remove(currentKey);expectedModCount = modCount;lastReturned = null;currentKey = null;}}// value的迭代器private class ValueIterator extends HashIterator<V> {public V next() {return nextEntry().value;}}// key的迭代器private class KeyIterator extends HashIterator<K> {public K next() {return nextEntry().getKey();}}// Entry的迭代器private class EntryIterator extends HashIterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {public Map.Entry<K,V> next() {return nextEntry();}}// WeakHashMap的Entry对应的集合private transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet = null;// 返回“key的集合”,实际上返回一个“KeySet对象”public Set<K> keySet() {Set<K> ks = keySet;return (ks != null ? ks : (keySet = new KeySet()));}// Key对应的集合// KeySet继承于AbstractSet,说明该集合中没有重复的Key。private class KeySet extends AbstractSet<K> {public Iterator<K> iterator() {return new KeyIterator();}public int size() {return WeakHashMap.this.size();}public boolean contains(Object o) {return containsKey(o);}public boolean remove(Object o) {if (containsKey(o)) {WeakHashMap.this.remove(o);return true;}elsereturn false;}public void clear() {WeakHashMap.this.clear();}}// 返回“value集合”,实际上返回的是一个Values对象public Collection<V> values() {Collection<V> vs = values;return (vs != null ? vs : (values = new Values()));}// “value集合”// Values继承于AbstractCollection,不同于“KeySet继承于AbstractSet”,// Values中的元素能够重复。因为不同的key可以指向相同的value。private class Values extends AbstractCollection<V> {public Iterator<V> iterator() {return new ValueIterator();}public int size() {return WeakHashMap.this.size();}public boolean contains(Object o) {return containsValue(o);}public void clear() {WeakHashMap.this.clear();}}// 返回“WeakHashMap的Entry集合”// 它实际是返回一个EntrySet对象public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> es = entrySet;return es != null ? es : (entrySet = new EntrySet());}// EntrySet对应的集合// EntrySet继承于AbstractSet,说明该集合中没有重复的EntrySet。private class EntrySet extends AbstractSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> {public Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() {return new EntryIterator();}// 是否包含“值(o)”public boolean contains(Object o) {if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))return false;Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry)o;Object k = e.getKey();Entry candidate = getEntry(e.getKey());return candidate != null && candidate.equals(e);}// 删除“值(o)”public boolean remove(Object o) {return removeMapping(o) != null;}// 返回WeakHashMap的大小public int size() {return WeakHashMap.this.size();}// 清空WeakHashMappublic void clear() {WeakHashMap.this.clear();}// 拷贝函数。将WeakHashMap中的全部元素都拷贝到List中private List<Map.Entry<K,V>> deepCopy() {List<Map.Entry<K,V>> list = new ArrayList<Map.Entry<K,V>>(size());for (Map.Entry<K,V> e : this)list.add(new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry<K,V>(e));return list;}// 返回Entry对应的Object[]数组public Object[] toArray() {return deepCopy().toArray();}// 返回Entry对应的T[]数组(T[]我们新建数组时,定义的数组类型)public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {return deepCopy().toArray(a);}}}
说明:WeakHashMap和HashMap都是通过”拉链法”实现的散列表。它们的源码绝大部分内容都一样,这里就只是对它们不同的部分就是说明。
WeakReference是“弱键”实现的哈希表。它这个“弱键”的目的就是:实现对“键值对”的动态回收。当“弱键”不再被使用到时,GC会回收它,WeakReference也会将“弱键”对应的键值对删除。
“弱键”是一个“弱引用(WeakReference)”,在Java中,WeakReference和ReferenceQueue 是联合使用的。在WeakHashMap中亦是如此:如果弱引用所引用的对象被垃圾回收,Java虚拟机就会把这个弱引用加入到与之关联的引用队列中。 接着,WeakHashMap会根据“引用队列”,来删除“WeakHashMap中已被GC回收的‘弱键’对应的键值对”。
另外,理解上面思想的重点是通过 expungeStaleEntries() 函数去理解。
遍历方式
4.1 遍历WeakHashMap的键值对
第一步:根据entrySet()获取WeakHashMap的“键值对”的Set集合。
第二步:通过Iterator迭代器遍历“第一步”得到的集合。
// 假设map是WeakHashMap对象
// map中的key是String类型,value是Integer类型
Integer integ = null;
Iterator iter = map.entrySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)iter.next();
// 获取key
key = (String)entry.getKey();
// 获取value
integ = (Integer)entry.getValue();
}
4.2 遍历WeakHashMap的键
第一步:根据keySet()获取WeakHashMap的“键”的Set集合。
第二步:通过Iterator迭代器遍历“第一步”得到的集合。
// 假设map是WeakHashMap对象
// map中的key是String类型,value是Integer类型
String key = null;
Integer integ = null;
Iterator iter = map.keySet().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
// 获取key
key = (String)iter.next();
// 根据key,获取value
integ = (Integer)map.get(key);
}
4.3 遍历WeakHashMap的值
第一步:根据value()获取WeakHashMap的“值”的集合。
第二步:通过Iterator迭代器遍历“第一步”得到的集合。
// 假设map是WeakHashMap对象
// map中的key是String类型,value是Integer类型
Integer value = null;
Collection c = map.values();
Iterator iter= c.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
value = (Integer)iter.next();
}
WeakHashMap遍历测试程序如下:
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.WeakHashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Collection;
/*
* @desc 遍历WeakHashMap的测试程序。
* (01) 通过entrySet()去遍历key、value,参考实现函数:
* iteratorHashMapByEntryset()
* (02) 通过keySet()去遍历key、value,参考实现函数:
* iteratorHashMapByKeyset()
* (03) 通过values()去遍历value,参考实现函数:
* iteratorHashMapJustValues()
*
* @author skywang
*/
public class WeakHashMapIteratorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int val = 0;
String key = null;
Integer value = null;
Random r = new Random();
WeakHashMap map = new WeakHashMap();
for (int i=0; i<12; i++) {
// 随机获取一个[0,100)之间的数字
val = r.nextInt(100);
key = String.valueOf(val);
value = r.nextInt(5);
// 添加到WeakHashMap中
map.put(key, value);
System.out.println(" key:"+key+" value:"+value);
}
// 通过entrySet()遍历WeakHashMap的key-value
iteratorHashMapByEntryset(map) ;
// 通过keySet()遍历WeakHashMap的key-value
iteratorHashMapByKeyset(map) ;
// 单单遍历WeakHashMap的value
iteratorHashMapJustValues(map);
}
/*
* 通过entry set遍历WeakHashMap
* 效率高!
*/
private static void iteratorHashMapByEntryset(WeakHashMap map) {
if (map == null)
return ;
System.out.println("\niterator WeakHashMap By entryset");
String key = null;
Integer integ = null;
Iterator iter = map.entrySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)iter.next();
key = (String)entry.getKey();
integ = (Integer)entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key+" -- "+integ.intValue());
}
}
/*
* 通过keyset来遍历WeakHashMap
* 效率低!
*/
private static void iteratorHashMapByKeyset(WeakHashMap map) {
if (map == null)
return ;
System.out.println("\niterator WeakHashMap By keyset");
String key = null;
Integer integ = null;
Iterator iter = map.keySet().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
key = (String)iter.next();
integ = (Integer)map.get(key);
System.out.println(key+" -- "+integ.intValue());
}
}
/*
* 遍历WeakHashMap的values
*/
private static void iteratorHashMapJustValues(WeakHashMap map) {
if (map == null)
return ;
Collection c = map.values();
Iterator iter= c.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iter.next());
}
}
}
WeakHashMap使用示例
下面通过实例来学习如何使用WeakHashMap
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.WeakHashMap;
import java.util.Date;
import java.lang.ref.WeakReference;
/**
* @desc WeakHashMap测试程序
*
* @author skywang
* @email kuiwu-wang@163.com
*/
public class WeakHashMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
testWeakHashMapAPIs();
}
private static void testWeakHashMapAPIs() {
// 初始化3个“弱键”
String w1 = new String("one");
String w2 = new String("two");
String w3 = new String("three");
// 新建WeakHashMap
Map wmap = new WeakHashMap();
// 添加键值对
wmap.put(w1, "w1");
wmap.put(w2, "w2");
wmap.put(w3, "w3");
// 打印出wmap
System.out.printf("\nwmap:%s\n",wmap );
// containsKey(Object key) :是否包含键key
System.out.printf("contains key two : %s\n",wmap.containsKey("two"));
System.out.printf("contains key five : %s\n",wmap.containsKey("five"));
// containsValue(Object value) :是否包含值value
System.out.printf("contains value 0 : %s\n",wmap.containsValue(new Integer(0)));
// remove(Object key) : 删除键key对应的键值对
wmap.remove("three");
System.out.printf("wmap: %s\n",wmap );
// ---- 测试 WeakHashMap 的自动回收特性 ----
// 将w1设置null。
// 这意味着“弱键”w1再没有被其它对象引用,调用gc时会回收WeakHashMap中与“w1”对应的键值对
w1 = null;
// 内存回收。这里,会回收WeakHashMap中与“w1”对应的键值对
System.gc();
// 遍历WeakHashMap
Iterator iter = wmap.entrySet().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry en = (Map.Entry)iter.next();
System.out.printf("next : %s - %s\n",en.getKey(),en.getValue());
}
// 打印WeakHashMap的实际大小
System.out.printf(" after gc WeakHashMap size:%s\n", wmap.size());
}
}
运行结果:
wmap:{three=w3, one=w1, two=w2}
contains key two : true
contains key five : false
contains value 0 : false
wmap: {one=w1, two=w2}
next : two - w2
after gc WeakHashMap size:1
WeakHashMap和HashMap的区别
前面对HashMap的源码和WeakHashMap的源码分别进行了分析。在WeakHashMap源码分析博文中有对与HashMap区别的比较,但是不够具体系统。加上本人看了一些相关的博文,发现了一些好的例子来说明这两者的区别,因此,就有了这篇博文。
WeakHashMap和HashMap一样,WeakHashMap也是一个散列表,它存储的内容也是键值对(key-value)映射,而且键和值都可以为null。不过WeakHashMap的键是“弱键”(注:源码中Entry中的定义是这样的:private static class Entry