CSS Properties
Now that we’ve gone over adding HTML tags to the page, let’s cover adding styles to those tags. We can do quite a lot with styles! We can change:
- Typography
- Colors
- Appearance (Corners, Borders, Decorations)
- Layout
- Position
- Inline vs Block
- Animations
- and many more
CSS styles are always written in property: value pairs (like background: blue;) and terminated with a semicolon.
Applying CSS to an HTML file
CSS can be applied to HTML tags in three different ways.
- Inline using an HTML tag’s
styleattribute<div style="background: blue; color: white;">Hello </div>
- Via a
<style>tag in the HTML page - Through an external CSS file
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./css-demo-finished.css" />
Targeting specific elements
Inline styles are always applied directly to the element you place them on, but <style> tags and external CSS files need a way to match elements with their respective style sets. This is done with CSS selectors. When selectors are combined with CSS styles, we call this a ruleset.
CSS rulesets take on the following form:
selector1,selector2 {property1: value1;property2: value2;}
Here’s a more detailed view from Chris Eppstein: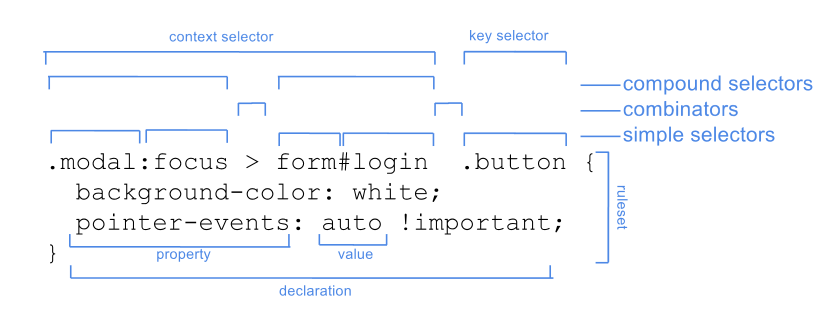
Selectors can be a single tag, class, ID, or attribute. It can also be a combination of those elements.
Below is a series of selectors and property/value combinations that we’ll apply to our CSS demo page.
/* Targeting the entire page */body {font: 1.2em sans-serif;}/* Targeting an HTML tag */h1 {/* Color name */color: black;/* 6-digit hex */background: #ababab;/* Margin: specified separately for each side */margin-bottom: 15px;margin-top: 15px;/* Shorthand: Padding applies to all sides */padding: 10px;/* Border shorthand and 3-digit hex */border: 1px solid #ddd;}/* Overriding inherited styles */span {color: #004578;}/* Sibling selector */a ~ a {/* Changing elements from inline to block */display: block;}/* Targeting a class name */.tiles {display: flex;}/* Descendant selector */.tiles img {width: 100%;}/* Direct descendant selector */.tiles > div {/* rgb color */background: rgb(10, 10, 10);color: white;flex-basis: 100%;/* Padding/margin shorthand. Goes clockwise from top.10px - all10px 20px - top/bottom left/right10px 20px 15px - top left/right bottom*/padding: 10px 20px 15px;margin: 10px 20px 10px 0;border: 1px solid white;}/* Qualified selector */div.important-links {background: #004578;}/* Style inheritance only works for unstyled elements */a {color: white;}/* Hover pseudo-selector */a:hover {color: #ccc;}/* Positional pseudo-selector */.tiles > div:last-child {/* overrides margin-right but leaves other margins alone */margin-right: 0;}/* ID selector */#contact-form {display: flex;flex-direction: column;}/* Attribute selector */input[type='submit'] {margin-top: 10px;}
注:本节 demo 中的 style.css 代码都已屏蔽,可以一步步取消屏蔽观察 CSS 效果。

