泛型声明:
interface接口
//如: List , ArrayList
说明:
- 其中,T,K,V不代表值,而是表示类型。
- 任意字母都可以。常用T表示,是Type的缩写
泛型实例化:
要在类名后面指定类型参数的值(类型)。如:
- List
strList = new ArrayList 0); - Iterator
iterator = customers.iterator();
练习:
- 创建3个学生对象
- 放入到 HashMap中,要求Key是 String name, Value就是学生对象
- 使用两种方式遍历
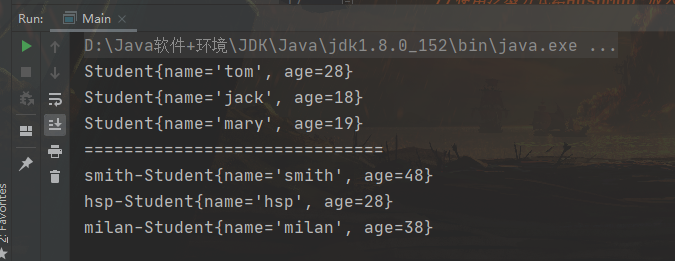
package test;import java.util.*;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {//使用泛型方式给HashSet 放入3个学生对象HashSet<Student> students = new HashSet<Student>();students.add(new Student("jack", 18));students.add(new Student("tom", 28));students.add(new Student("mary", 19));//遍历for (Student student : students) {System.out.println(student);}//使用泛型方式给HashMap 放入3个学生对象//K -> String V->StudentHashMap<String, Student> hm = new HashMap<String, Student>();/*public class HashMap<K,V> {}*/hm.put("milan", new Student("milan", 38));hm.put("smith", new Student("smith", 48));hm.put("hsp", new Student("hsp", 28));//迭代器 EntrySet/*public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> es;return (es = entrySet) == null ? (entrySet = new EntrySet()) : es;}*/Set<Map.Entry<String, Student>> entries = hm.entrySet();/*public final Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() {return new EntryIterator();}*/Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Student>> iterator = entries.iterator();System.out.println("==============================");while (iterator.hasNext()) {Map.Entry<String, Student> next = iterator.next();System.out.println(next.getKey() + "-" + next.getValue());}}}/*** 创建 3个学生对象* 放入到HashSet中学生对象, 使用.* 放入到 HashMap中,要求 Key 是 String name, Value 就是 学生对象* 使用两种方式遍历*/class Student {private String name;private int age;public Student(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Student{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}}