案例一:
翻转Sting中的字符序列
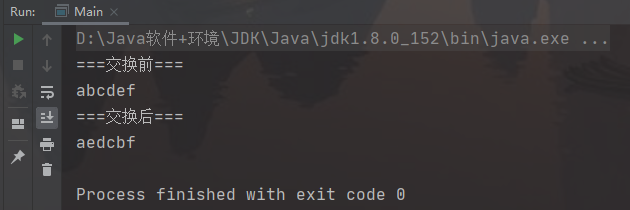
package test;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {//测试String str = "abcdef";System.out.println("===交换前===");System.out.println(str);try {str = reverse(str, 1, 41);} catch (Exception e) {System.out.println(e.getMessage());return;}System.out.println("===交换后===");System.out.println(str);}/*** (1) 将字符串中指定部分进行反转。比如将"abcdef"反转为"aedcbf"* (2) 编写方法 public static String reverse(String str, int start , int end) 搞定* 思路分析* (1) 先把方法定义确定* (2) 把 String 转成 char[] ,因为char[] 的元素是可以交换的*/public static String reverse(String str, int start, int end) {if(!(str != null && start >= 0 && end > start && end < str.length())) {throw new RuntimeException("参数不正确");}char[] chars = str.toCharArray();char temp = ' '; //交换辅助变量for (int i = start, j = end; i < j; i++, j--) {temp = chars[i];chars[i] = chars[j];chars[j] = temp;}//使用chars 重新构建一个String 返回即可return new String(chars);}}
案例二:
输入用户名、密码、邮箱,如果信息录入正确,则提示注册成功,否则生成异常对象要求:
- 用户名长度为2或3或4
- 密码的长度为6,要求全是数字isDigital
- 邮箱中包含@和、并且@在.的前面
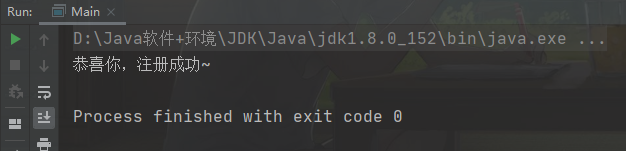
package test;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {String name = "abc";String pwd = "123456";String email = "ti@i@sohu.com";try {userRegister(name, pwd, email);System.out.println("恭喜你,注册成功~");} catch (Exception e) {System.out.println(e.getMessage());}}/*** 输入用户名、密码、邮箱,如果信息录入正确,则提示注册成功,否则生成异常对象* 要求:* (1) 用户名长度为2或3或4* (2) 密码的长度为6,要求全是数字 isDigital* (3) 邮箱中包含@和. 并且@在.的前面* <p>* 思路分析* (1) 先编写方法 userRegister(String name, String pwd, String email) {}* (2) 针对 输入的内容进行校核,如果发现有问题,就抛出异常,给出提示* (3) 单独的写一个方法,判断 密码是否全部是数字字符 boolean*/public static void userRegister(String name, String pwd, String email) {//再加入一些校验if (!(name != null && pwd != null && email != null)) {throw new RuntimeException("参数不能为null");}//过关//第一关int userLength = name.length();if (!(userLength >= 2 && userLength <= 4)) {throw new RuntimeException("用户名长度为2或3或4");}//第二关if (!(pwd.length() == 6 && isDigital(pwd))) {throw new RuntimeException("密码的长度为6,要求全是数字");}//第三关int i = email.indexOf('@');int j = email.indexOf('.');if (!(i > 0 && j > i)) {throw new RuntimeException("邮箱中包含@和. 并且@在.的前面");}}//单独的写一个方法,判断 密码是否全部是数字字符 booleanpublic static boolean isDigital(String str) {char[] chars = str.toCharArray();for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {if (chars[i] < '0' || chars[i] > '9') {return false;}}return true;}}
案例三:
split()字符分割
注意:
“|”、“.”、“”、“+”、“\”等不是有效的模式匹配规则表达式,是转义字符,使用split()方法时必须得加”\“才行。(*加转义字符)
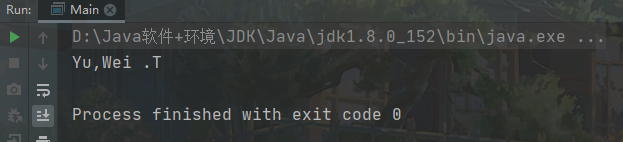
package test;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {String name = "Wei tian Yu";printName(name);}/*** 编写方法: 完成输出格式要求的字符串* 编写java程序,输入形式为: Wei tian Yu的人名,以Yu,Wei .T的形式打印* 出来 。其中.S是中间单词的首字母* 思路分析* (1) 对输入的字符串进行 分割split(" ")* (2) 对得到的String[] 进行格式化String.format()* (3) 对输入的字符串进行校验即可*/public static void printName(String str) {if(str == null) {System.out.println("str 不能为空");return;}String[] names = str.split(" ");if(names.length != 3) {System.out.println("输入的字符串格式不对");return;}String format = String.format("%s,%s .%c", names[2], names[0], names[1].toUpperCase().charAt(0));System.out.println(format);}}
案例四:
字符统计
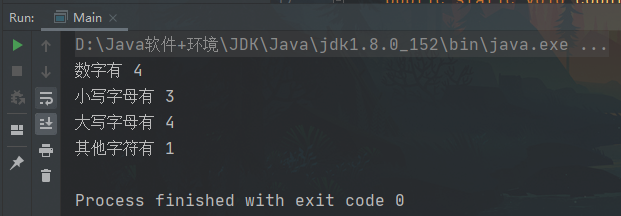
package test;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {String str = "WTY2002 Keep";countStr(str);}/*** 输入字符串,判断里面有多少个大写字母,多少个小写字母,多少个数字* 思路分析* (1) 遍历字符串,如果 char 在 '0'~'9' 就是一个数字* (2) 如果 char 在 'a'~'z' 就是一个小写字母* (3) 如果 char 在 'A'~'Z' 就是一个大写字母* (4) 使用三个变量来记录 统计结果*/public static void countStr(String str) {if (str == null) {System.out.println("输入不能为 null");return;}int strLen = str.length();int numCount = 0;int lowerCount = 0;int upperCount = 0;int otherCount = 0;for (int i = 0; i < strLen; i++) {if(str.charAt(i) >= '0' && str.charAt(i) <= '9') {numCount++;} else if(str.charAt(i) >= 'a' && str.charAt(i) <= 'z') {lowerCount++;} else if(str.charAt(i) >= 'A' && str.charAt(i) <= 'Z') {upperCount++;} else {otherCount++;}}System.out.println("数字有 " + numCount);System.out.println("小写字母有 " + lowerCount);System.out.println("大写字母有 " + upperCount);System.out.println("其他字符有 " + otherCount);}}
案例五:
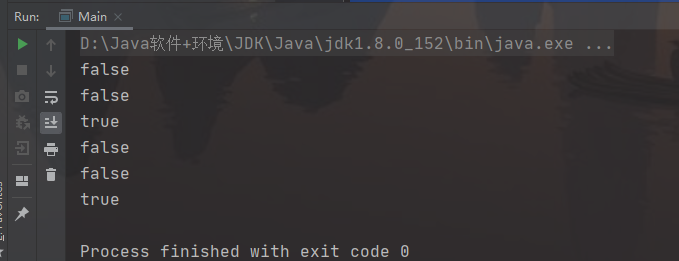
package test;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {String s1 = "WTY2002";Animal a = new Animal(s1);Animal b = new Animal(s1);System.out.println(a == b);System.out.println(a.equals(b));System.out.println(a.name == b.name);String s4 = new String("WTY2002");String s5 = "WTY2002";System.out.println(s1 == s4);System.out.println(s4 == s5);String t1 = "hello" + s1;String t2 = "helloWTY2002";System.out.println(t1.intern() == t2);}}class Animal {String name;public Animal(String name) {this.name = name;}}