- 对于编译异常,程序中必须处理,比如try-catch 或者throws
- 对于运行时异常,程序中如果没有处理,默认就是throws的方式处理
- 子类重写父类的方法时,对抛出异常的规定:子类重写的方法,所抛出的异常类型要么和父类抛出的异常一致,要么为父类抛出的异常的类型的子类型。
- 在throws过程中,如果有方法 try-catch,就相当于处理异常,就可以不必throws
```java package test;public static void test() /*throws ArithmeticException*/{//发生运行异常,没有catch默认就是throwsint n = 2 / 0;}
import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
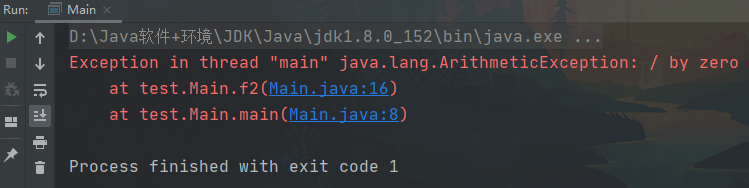
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { f2(); }
public static void f2() /*throws ArithmeticException*/ {//1.对于编译异常,程序中必须处理,比如 try-catch 或者 throws//2.对于运行时异常,程序中如果没有处理,默认就是throws的方式处理int n1 = 10;int n2 = 0;double res = n1 / n2;}public static void f1() throws FileNotFoundException {//这里大家思考问题 调用f3() 报错//1. 因为f3() 方法抛出的是一个编译异常//2. 即这时,就要f1() 必须处理这个编译异常//3. 在f1() 中,要么 try-catch-finally ,或者继续throws 这个编译异常f3(); // 抛出异常}public static void f3() throws FileNotFoundException {FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("d://aa.txt");}public static void f4() {//1. 在f4()中调用方法f5() 是OK//2. 原因是f5() 抛出的是运行异常//3. 而java中,并不要求程序员显示处理,因为有默认处理机制f5();}public static void f5() throws ArithmeticException {}
}
class Father { //父类 public void method() throws RuntimeException { } }
class Son extends Father {//子类
//3. 子类重写父类的方法时,对抛出异常的规定:子类重写的方法,// 所抛出的异常类型要么和父类抛出的异常一致,要么为父类抛出的异常类型的子类型,否则报错!!!//4. 在throws 过程中,如果有方法 try-catch , 就相当于处理异常,就可以不必throws@Overridepublic void method() throws ArithmeticException {}
}
```